Chapter 7 – Sections & Objectives
7.1 Tune EIGRP
Configure EIGRP to improve network performance.
7.2 Troubleshoot EIGRP
Troubleshoot common EIGRP configuration issues in a small to medium-sized business network.
7.1 Tune EIGRP
Automatic Summarization
- EIGRP Automatic Summarization
- Summarization limits the number of routing advertisements and the size of the routing table
- EIGRP performs automatic summarization at classful boundaries.
- Configuring EIGRP Automatic Summarization
- R1(config)# router eigrp as-number
- R1(config-router)# auto-summary
- Verifying Auto-Summary
- show ip protocols
- show ip eigrp topology all-links
- show ip route
- Null0 summary route exists when:
- Automatic summarization is enabled.
- There is at least one subnet that was learned via EIGRP.
- There are two or more network EIGRP router configuration mode commands.
- Automatic summarization could cause routing loops
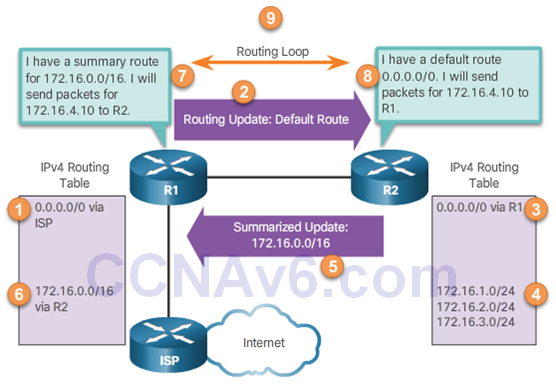
Default Route Propagation
- Propagating a Default Static Route
- The default static route (0.0.0.0 / 0) is usually configured on the router that has a connection to a network outside the EIGRP routing domain; for example, to an ISP.
- One way to propagate the default static route
- The redistribute static command
- Verifying the Propagated Default Route
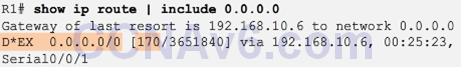
- D – This route was learned from an EIGRP routing update.
- * – The route is a candidate for a default route.
- EX – The route is an external EIGRP route, in this case a static route outside of the EIGRP routing domain.
- 170 – This is the administrative distance of an external EIGRP route.
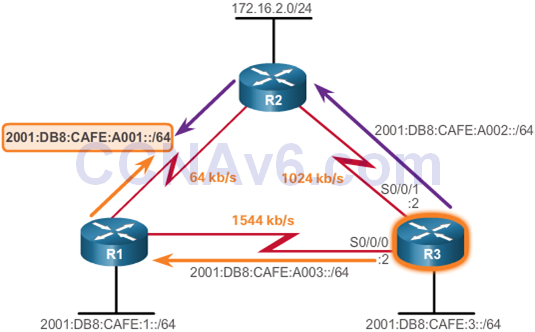
- EIGRP for IPv6: Default Route
- To configure a IPv6 static default route: ipv6 route ::/0 exit-interface
- To propapate a IPv6 static default route: redistribute static
- To verify the propagation of IPv6 static default route: show ipv6 route
Fine-tuning EIGRP Interfaces
- EIGRP Bandwidth Utilization
- By default, EIGRP uses only up to 50 percent of an interface’s bandwidth for EIGRP information. This prevents the EIGRP process from over-utilizing a link and not allowing enough bandwidth for the routing of normal traffic.
- Commands to configure the bandwidth percentage used by EIGRP on an interface:
- IPv4: ip bandwidth-percent eigrp as-number percent
- IPv6: ipv6 bandwidth-percent eigrp as-number percent
- Hello and Hold Timers – Do not have to match with other EIGRP routers
- Hello packets are used to establish and monitor the connection status of neighbors
- Commands to configure the hello intervals per interface:
- ip hello-interval eigrp as-number seconds
- ipv6 hello-interval eigrp as-number seconds
- Hold time tells the router the maximum time that the router should wait to receive the next Hello before declaring that neighbor as unreachable.
- Commands to configure the hold time intervals per interface:
- ip hold-time eigrp as-number seconds
- ipv6 hold-time eigrp as-number seconds
- What are the default hello intervals and hold times for EIGRP?
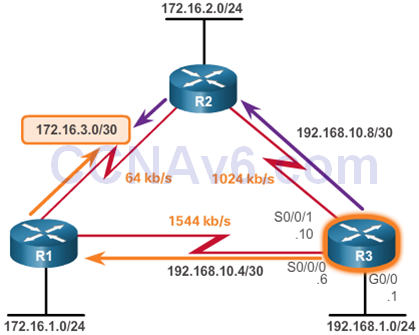
- Load Balancing
- Equal-cost load balancing
- The ability of a router to distribute outbound traffic using all interfaces that have the same metric from the destination address
- IPv4 and IPv6: The maximum-paths value determines the maximum number of routes
- Unequal-cost load balancing
- The ability to balance traffic across multiple routes that have different metrics
- IPv4 and IPv6: The variance command is used to install multiple loop-free routes with unequal cost in a local routing table
7.2 Troubleshoot EIGRP
Components of Troubleshooting EIGRP
- Basic EIGRP Troubleshooting Commands
- Verify the neighbor adjacency
- show ip eigrp neighbors
- show ipv6 eigrp neighbors
- Verify the learned route to remote networks
- show ip route eigrp
- show ipv6 route eigrp
- Verify the various EIGRP settings
- show ip protocols
- show ipv6 protocols
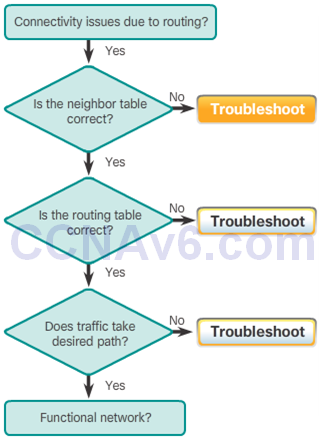
Troubleshoot EIGRP Neighbor Issues
- Layer 3 Connectivity
- Verify the connection
- show ip interface brief or show ipv6 interface brief
- ping ip address
- EIGRP Parameters
- Verify that the routers are in the same EIGRP domain with the same AS number
- show ip protocols or show ipv6 protocols
- Configure AS number
- IPv4: router eigrp as-number
- IPv6: ipv6 router eigrp as-number
- EIGRP Interfaces
- Verify that the router interfaces
- are participating in the EIGRP network
- show ip eigrp interfaces or show ipv6 eigrp interfaces
- show ip protocols or show ipv6 protocols
- show running-config | section eigrp
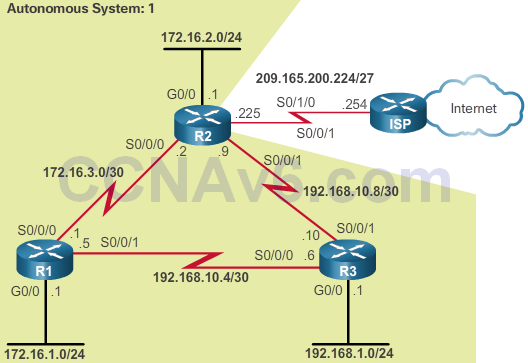
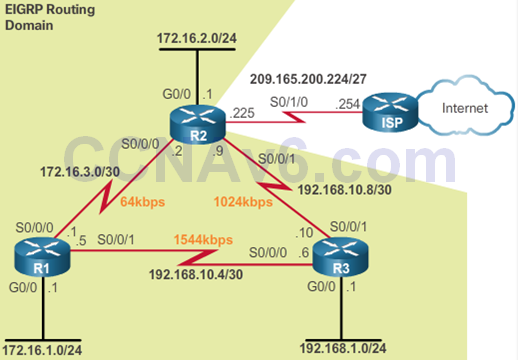
Troubleshoot EIGRP Routing Table Issues
- Passive Interface
- Prevent routers from becoming neighbors
- show ip eigrp neighbors or show ipv6 eigrp neighbors
- The show ip protocols or show ipv6 protocols command is used to verify whether the interface has been configured as passive
- Passive interface is configured if neighbor adjacency is not desirable
- Where would you configure passive interfaces in the graphics?
- Missing Network Statement
- Verify the advertised networks
- show ip protocols or show ipv6 protocols
- show ip route or show ipv6 route
- Configure network statements
- IPv4: network ip-address [mask]
- IPv6: ipv6 eigrp autonomous-system command in interface configuration mode
- Autosummarization
- IPv4: Could cause inconsistent routing
- Disable autosummarization: no auto-summary
- IPv6: All summarization can only be accomplished using EIGRP manual summary routes.
7.3 Chapter Summary
EIGRP is one of the routing protocols commonly used in large enterprise networks. Modifying EIGRP features and troubleshooting problems is one of the most essential skills for a network engineer involved in the implementation and maintenance of large routed enterprise networks that use EIGRP.
Summarization decreases the number of entries in routing updates and lowers the number of entries in local routing tables. It also reduces bandwidth utilization for routing updates and results in faster routing table lookups. EIGRP for IPv4 automatic summarization is disabled by default beginning with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(1)M and 12.2(33). Prior to this, automatic summarization was enabled by default. To enable automatic summarization for EIGRP use the auto-summary command in router configuration mode. Use the show ip protocols command to verify the status of automatic summarization. Examine the routing table to verify that automatic summarization is working.
EIGRP automatically includes summary routes to Null0 to prevent routing loops that are included in the summary but do not actually exist in the routing table. The Null0 interface is a virtual IOS interface that is a route to nowhere, commonly known as “the bit bucket”. Packets that match a route with a Null0 exit interface are discarded.
One method of propagating a default route within the EIGRP routing domain is to use the redistribute static command. This command tells EIGRP to include this static route in its EIGRP updates to other routers. The show ip protocols command verifies that static routes within the EIGRP routing domain are being redistributed.
Use the ip bandwidth-percent eigrp as-number percent interface configuration mode command to configure the percentage of bandwidth that can be used by EIGRP on an interface.
To configure the percentage of bandwidth that can be used by EIGRP for IPv6 on an interface, use the ipv6 bandwidth-percent eigrp command in interface configuration mode. To restore the default value, use the no form of this command.
Hello intervals and hold times are configurable on a per-interface basis in EIGRP and do not have to match with other EIGRP routers to establish or maintain adjacencies.
For IP in EIGRP, Cisco IOS software applies load balancing using up to four equal-cost paths by default. With the maximum-paths router configuration mode command, up to 32 equal-cost routes can be kept in the routing table.
The show ip route command verifies that the router learned EIGRP routes. The show ip protocols command is used to verify that EIGRP displays the currently configured values.
Download Slide PowerPoint (pptx):
