1. What are two issues that may cause the failure of a BGP neighbor relationship from forming? (Choose two.)
- neighbor statement being wrong
- neighbor not having a route to the local router
- path to the neighbor being through a static route
- the keepalive timer not matching between BGP peers
- BGP packets being sourced from a loopback interface
2. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast summary command on a router to check the adjacency state with a neighbor router. The value under the State/PfxRcd field shows 0. Which statement describes the status of adjacency between the two routers?
- The adjacency is successfully formed.
- The adjacency is formed, but no message is transmitted.
- Because the neighbor command is wrong, the adjacency is not formed.
- Because there is no Layer 3 connectivity between the two routers, the adjacency is not formed.
3. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast 10.1.1.0 command on router R1 to verify that the network 10.1.1.0 is in the BGP table. The administrator notices that there are two routes to reach the network. Which BGP path attribute is used to determine the best-path?
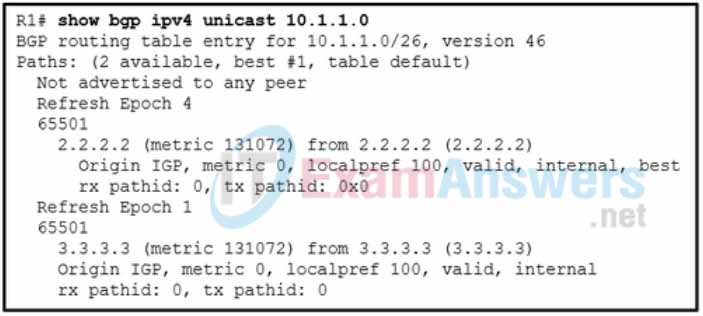
- AIGP
- weight
- BGP RID
- origin code
4. Which statement describes the BGP evaluation criteria of path attributes during the calculation of the best path for a route?
- Prefer the lowest weight attribute.
- Prefer an internal path over an external path.
- Prefer the lowest multi-exit discriminator attribute.
- Prefer the path with the highest neighbor IP address.
5. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator is troubleshooting a BGP adjacency issue between routers R2 and R5. R2 uses loopback0 interface 2.2.2.2 and R5 uses loopback0 interface 5.5.5.5 in the neighbor ip_address remote-as as_number statement in their respective configurations. However, an adjacency does not form. Which two conclusions can be drawn from the troubleshooting process performed on R5? (Choose two.)
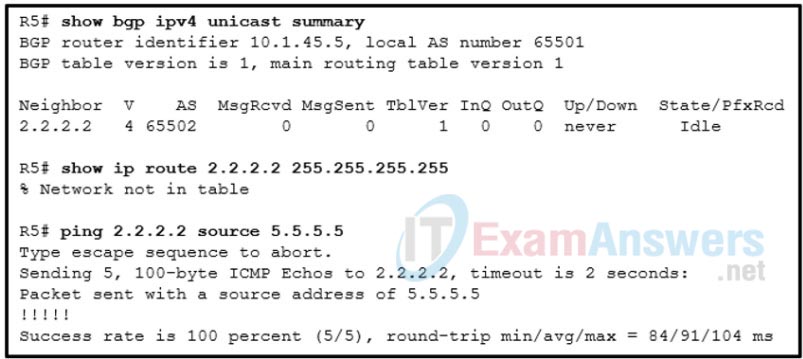
- R2 does not have a route to R5.
- R5 uses the default route to reach R2.
- There is no Layer 3 connectivity between R2 and R5.
- The interface with the IP address 10.1.45.5 on R5 is down.
- The AS number in the neighbor ip_address remote-as as_number statement is incorrectly configured on R2.
6. A network administrator is troubleshooting a BGP network and issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast command on a BGP router. What is a purpose of using this command?
- to verify the status of BGP peering
- to verify IPv4 unicast BGP neighbors
- to verify the IPv4 routes in the BGP table
- to display detailed information about all the BGP neighbors
7. A network technician is verifying the BGP configuration and neighbor relationships on a Cisco router. The technician suspects that one BGP neighbor lost the peering relationship. Which command should the technician use to verify the network link status?
- show ipv4 route bgp
- show ip interface brief
- show bgp ipv4 unicast neighbor
- show bgp ipv4 unicast summary
8. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast command to check the routes in the BGP table. What does the indication of 0.0.0.0 under Next Hop mean?

- The route is learned through IGP.
- The route is learned through a static route.
- The route is the best route for the network prefix.
- The route is originated from a connected network to the router.
9. A network administrator receives a call, from a colleague at the overseas branch office, that a BGP route advertised by the company carries an autonomous number of 64520 in the AS_Path attribute. Which statement describes the situation?
- The ASN is in the experimental ASN range and should not be used at all.
- The ASN is in the private ASN range and should not be used on the internet.
- The ASN is in the reserved ASN range and is allowed to be used on the internet.
- The ASN is in the private ASN range and NAT should be used to translate this ASN to a public ASN to be used on the internet.
10. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv6 unicast | begin Network command on router R1 to verify routes in the IPv6 BGP table. Which statement describes the status of the route 2001:DB8:2::/64?

- It is redistributed into BGP.
- It will not be installed in the routing table.
- It is the best route for the prefix 2001:DB8:2::/64.
- It can be reached via the local address ::FFFF:2.2.2.2.
11. A network administrator is troubleshooting a BGP network where some BGP routes are missing from BGP tables. The administrator has verified that BGP peers were formed as expected. What are two possible reasons that routes would not appear in the BGP table or the routing table? (Choose two.)
- BGP split-horizon rule
- mismatched authentication being used
- missing or bad network mask command
- no Layer 3 connectivity to neighbor routers
- only EBGP being used to establish adjacency
12. Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator issues the show bgp ipv4 unicast | begin Network command on router R5 to verify routes in the BGP table. The administrator realizes that the route 10.1.1.0/24 and the component subnets learned from router R1 with IP address of 1.1.1.1 will not be installed in the routing table. What is a possible solution to the issue?
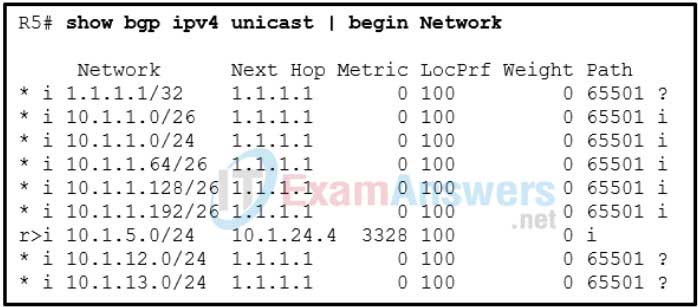
- Set the weight to 100 on R5 for these routes.
- Set the local preference to 200 on R5 for these routes.
- Create a static route to reach the 10.1.1.0/24 network on R5.
- Establish fully meshed IBGP peers among these networks.
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. Which commands enable you to identify the IPv4 unicast BGP neighbor adjacencies that have been formed? (Choose two.)
- show ip route bgp
- show bgp ipv4 unicast
- show bgp ipv4 unicast summary
- show bgp ipv4 unicast neighbors
2. In the output of show bgp ipv4 unicast summary, how can you determine whether a neighbor relationship is successfully established?
- The neighbor is listed in the output.
- The Version column has a 4 in it.
- The State/PfxRcd column has a number in it.
- The State/PfxRcd column has the word Active in it.
3. Which of the following are reasons a BGP neighbor relationship might not form? (Choose two.)
- The BGP timers are mismatched.
- The BGP packets are sourced from the wrong IP address.
- The neighbor is reachable using a default route.
- The network command is misconfigured.
4. Which TCP port number is used to form BGP sessions?
- 110
- 123
- 179
- 443
5. What is the BGP state of a neighbor if a TCP session cannot be formed?
- Open
- Idle
- Active
- Established
6. What could prevent a route from being advertised to another BGP router? (Choose three.)
- Mismatched timers
- Split-horizon rule
- Missing network mask command
- Route filtering
7. Which command enables you to verify the IPv4 BGP routes that have been learned from all BGP neighbors?
- show ip route bgp
- show bgp ipv4 unicast
- show bgp ipv4 unicast summary
- show bgp ipv4 unicast neighbors
8. What occurs when the next hop of a BGP-learned route is not reachable?
- The route is discarded.
- The route is placed in the BGP table and advertised to other neighbors.
- The route is placed in the BGP table and not marked as valid.
- The route is placed in the BGP table and in the routing table.
9. Which of the following describes the BGP split-horizon rule?
- A BGP router that receives a BGP route from an iBGP peering shall not advertise that route to another router that is an iBGP peer.
- A BGP router that receives a BGP route from an eBGP peering shall not advertise that route to another router that is an iBGP peer.
- A BGP router that receives a BGP route from an eBGP peering shall not advertise that route to another router that is an eBGP peer.
- A BGP router that receives a BGP route from an iBGP peering shall discard the route.
10. Which of the following administrative distances are correct? (Choose two.)
- 20 for eBGP
- 20 for iBGP
- 200 for eBGP
- 200 for iBGP
11. Which of the following correctly identifies the order of BGP attributes for the best-path decision process?
- Weight, local preference, route origin, AS_Path, origin code, MED
- AS_Path, origin code, MED, weight, local preference, route origin
- Local preference, weight, route origin, AS_Path, origin code, MED
- Weight, local preference, route origin, AS_Path, MED, origin code
12. What do you need to do when using MP-BGP? (Choose two.)
- Activate the IPv6 neighbors in address family configuration mode.
- Activate the IPv6 neighbors in router configuration mode.
- Define the IPv6 neighbors in router configuration mode.
- Define the IPv6 neighbors in address family configuration mode.
13. Which command enables you to verify the IPv6 unicast BGP routes that have been learned?
- show bgp ipv6 unicast
- show bgp ipv6 unicast summary
- show bgp ipv6 unicast neighbor
- show ipv6 route bgp

Superb! Neatly explained.