Checkpoint Exam: Incident Response – Cyber Threat Management (CyberTM) Module 6 Group Exam Answers
1. Which type of data would be considered an example of volatile data?
- temp files
- web browser cache
- memory registers
- log files
Explanation: Volatile data is data stored in memory such as registers, cache, and RAM, or it is data that exists in transit. Volatile memory is lost when the computer loses power.
2. Keeping data backups offsite is an example of which type of disaster recovery control?
- preventive
- corrective
- detective
- management
Explanation: A disaster recovery plan enables an organization to prepare for potential disasters and minimize the resulting downtime.
3. Which NIST-defined incident response stakeholder is responsible for coordinating incident response with other stakeholders and minimizing the damage of an incident?
- management
- IT support
- the legal department
- human resources
Explanation: The management team creates the policies, designs the budget, and is in charge of staffing all departments. Management is also responsible for coordinating the incident response with other stakeholders and minimizing the damage of an incident.
4. What type of exercise interrupts services to verify that all aspects of a business continuity plan are able to respond to a certain type of incident?
- Tabletop exercise
- Functional test
- Operational exercise
Explanation: Operational exercises: At the most extreme are full operational exercises, or simulations. These are designed to interrupt services to verify that all aspects of a plan are in place and sufficient to respond to the type of incident that is being simulated.
5. Match the intrusion event defined in the Diamond Model of intrusion to the description.
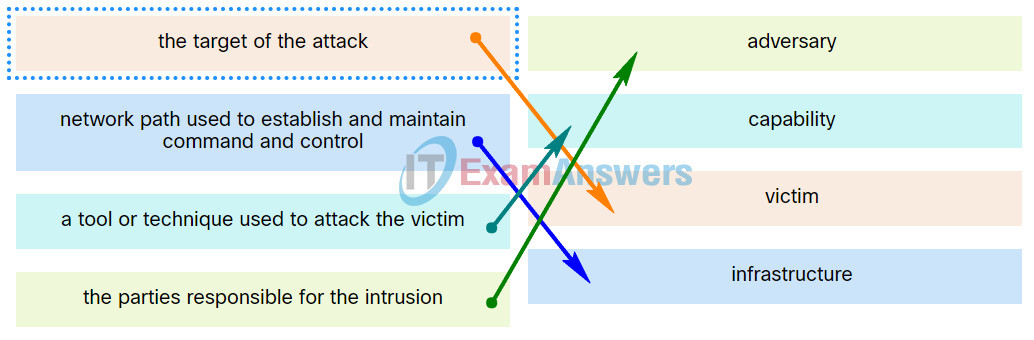
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| network path used to establish and maintain command and controlk |
infrastructure |
| a tool or technique used to attack the victim |
capability |
| the parties responsible for the intrusion |
adversary |
| the target of the attack |
victim |
6. What is a chain of custody?
- the disciplinary measures an organization may perform if an incident is caused by an employee
- the documentation surrounding the preservation of evidence related to an incident
- a plan ensuring that each party involved in an incident response understands how to collect evidence
- a list of all of the stakeholders that were exploited by an attacker
Explanation: A chain of custody refers to the documentation of evidence collected about an incident that is used by authorities during an investigation.
7. According to the Cyber Kill Chain model, after a weapon is delivered to a targeted system, what is the next step that a threat actor would take?
- installation
- action on objectives
- exploitation
- weaponization
Explanation: The Cyber Kill Chain specifies seven steps (or phases) and sequences that a threat actor must complete to accomplish an attack:
– Reconnaissance – The threat actor performs research, gathers intelligence, and selects targets.
– Weaponization – The threat actor uses the information from the reconnaissance phase to develop a weapon against specific targeted systems.
– Delivery – The weapon is transmitted to the target using a delivery vector.
– Exploitation – The threat actor uses the weapon delivered to break the vulnerability and gain control of the target.
– Installation – The threat actor establishes a back door into the system to allow for continued access to the target.
– Command and Control (CnC) – The threat actor establishes command and control (CnC) with the target system.
– Action on Objectives – The threat actor is able to take action on the target system, thus achieving the original objective.
8. In which step of the NIST incident response process does the CSIRT perform an analysis to determine which networks, systems, or applications are affected; who or what originated the incident; and how the incident is occurring?
- detection
- attacker identification
- scoping
- incident notification
Explanation: In the detection and analysis phase of the NIST incident response process life cycle, the CSIRT should immediately perform an initial analysis to determine the scope of the incident, such as which networks, systems, or applications are affected; who or what originated the incident; and how the incident is occurring.
9. Which task describes threat attribution?
- obtaining the most volatile evidence
- reporting the incident to the proper authorities
- evaluating the server alert data
- determining who is responsible for the attack
Explanation: Threat attribution refers to determining the individual, organization, or nation responsible for a successful intrusion or attack incident. The security investigation team correlates all the evidence in order to identify commonalities between tactics, techniques, and procedures (TPPs) for known and unknown threat actors.
10. Place the seven steps defined in the Cyber Kill Chain in the correct order.
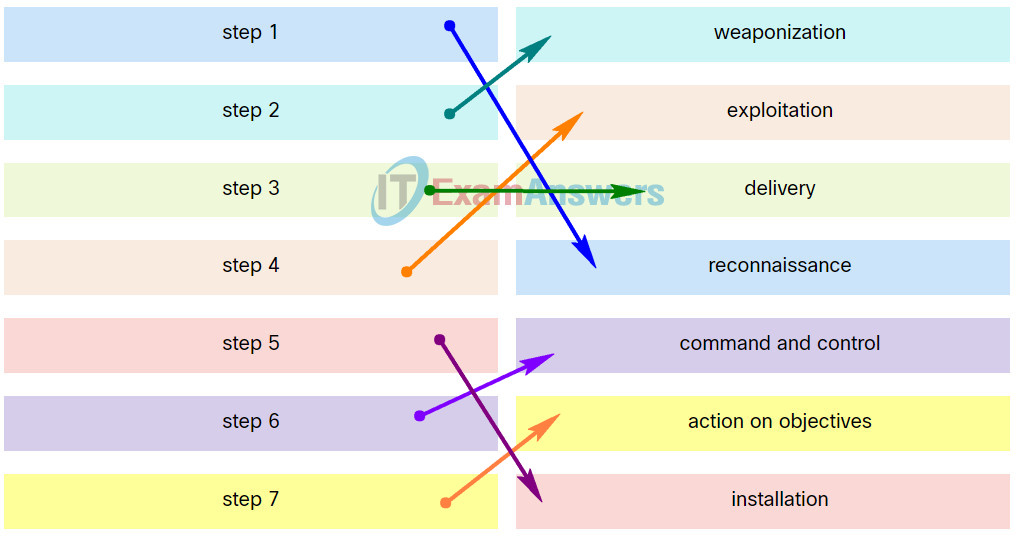
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| step 1 |
reconnaissance |
| step 2 |
weaponization |
| step 3 |
delivery |
| step 4 |
exploitation |
| step 5 |
installation |
| step 6 |
command and control |
| step 7 |
action on objectives |
11. Match the NIST incident response stakeholder with the role.
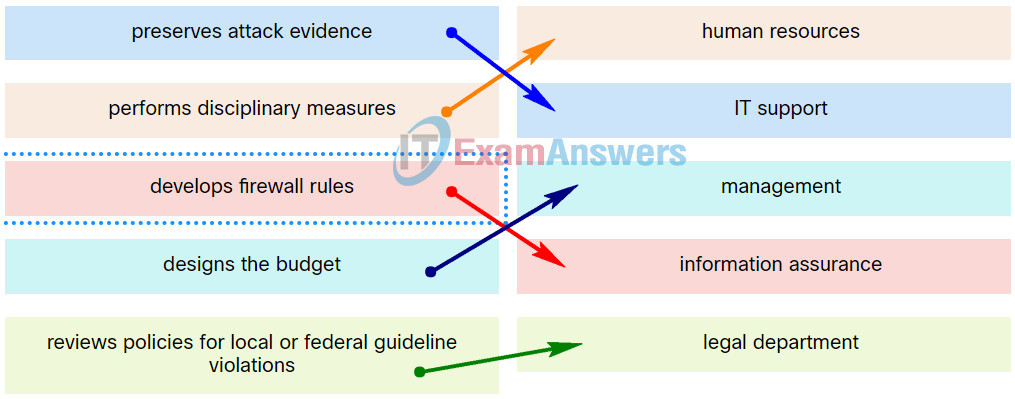
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| preserves attack evidence |
IT support |
| designs the budget |
management |
| reviews policies for local or federal guideline violations |
legal department |
| performs disciplinary measures |
human resources |
| develops firewall rules |
information assurance |
12. Which type of controls restore the system after a disaster or an event?
- Preventive controls
- Detective controls
- Corrective controls
Explanation: Corrective measures include controls that restore the system after a disaster or an event.
13. A company is applying the NIST.SP800-61 r2 incident handling process to security events. What are two examples of incidents that are in the category of precursor? (Choose two.)
- a host that has been verified as infected with malware
- multiple failed logins from an unknown source
- an IDS alert message being sent
- log entries that show a response to a port scan
- a newly-discovered vulnerability in Apache web servers
Explanation: As an incident category, the precursor is a sign that an incident might occur in the future. Examples of precursors are log entries that show a response to a port scan or a newly-discovered vulnerability in web servers using Apache.
14. What will a threat actor do to create a back door on a compromised target according to the Cyber Kill Chain model?
- Add services and autorun keys.
- Open a two-way communications channel to the CnC infrastructure.
- Obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload.
- Collect and exfiltrate data.
Explanation: Once a target system is compromised, the threat actor will establish a back door into the system to allow for continued access to the target. Adding services and autorun keys is a way to create a point of persistent access.
15. What is the objective the threat actor in establishing a two-way communication channel between the target system and a CnC infrastructure?
- to allow the threat actor to issue commands to the software that is installed on the target
- to steal network bandwidth from the network where the target is located
- to send user data stored on the target to the threat actor
- to launch a buffer overflow attack
Explanation: In the command and control phase of the Cyber Kill Chain, the threat actor establishes command and control (CnC) with the target system. With the two-way communication channel, the threat actor is able to issue commands to the malware software installed on the target.
16. Which type of evidence supports an assertion based on previously obtained evidence?
- best evidence
- direct evidence
- indirect evidence
- corroborating evidence
Explanation: Corroborating evidence is evidence that supports a proposition already supported by initial evidence, therefore confirming the original proposition. Circumstantial evidence is evidence other than first-hand accounts of events provided by witnesses.
17. What is specified in the plan element of the NIST incident response plan?
- metrics for measuring the incident response capability and effectiveness
- incident handling based on the mission of the organization
- organizational structure and the definition of roles, responsibilities, and levels of authority
- priority and severity ratings of incidents
Explanation: NIST recommends creating policies, plans, and procedures for establishing and maintaining a CSIRC. One component of the plan element is to develop metrics for measuring the incident response capability and its effectiveness.
18. A cybersecurity analyst has been called to a crime scene that contains several technology items including a computer. Which technique will be used so that the information found on the computer can be used in court?
- log collection
- Tor
- rootki
- unaltered disk image
Explanation: A normal file copy does not recover all data on a storage device so an unaltered disk image is commonly made. An unaltered disk image preserves the original evidence, thus preventing inadvertent alteration during the discovery phase. It also allows recreation of the original evidence.
19. According to NIST, which step in the digital forensics process involves identifying potential sources of forensic data, its acquisition, handling, and storage?
- reporting
- examination
- collection
- analysis
Explanation: NIST describes the digital forensics process as involving the following four steps:
* Collection – the identification of potential sources of forensic data and acquisition, handling, and storage of that data.
* Examination – assessing and extracting relevant information from the collected data. This may involve decompression or decryption of the data.
* Analysis – drawing conclusions from the data. Salient features, such as people, places, times, events, and so on should be documented.
* Reporting – preparing and presenting information that resulted from the analysis. Reporting should be impartial and alternative explanations should be offered if appropriate.
20. Which activity is typically performed by a threat actor in the installation phase of the Cyber Kill Chain?
- Obtain an automated tool to deliver the malware payload.
- Harvest email addresses of user accounts.
- Install a web shell on the target web server for persistent access.
- Open a two-way communication channel to the CnC infrastructure.
Explanation: In the installation phase of the Cyber Kill Chain, the threat actor establishes a back door into the system to allow for continued access to the target.



