Static vs. Dynamic Routes
What Is a Dynamic Routing Protocol?
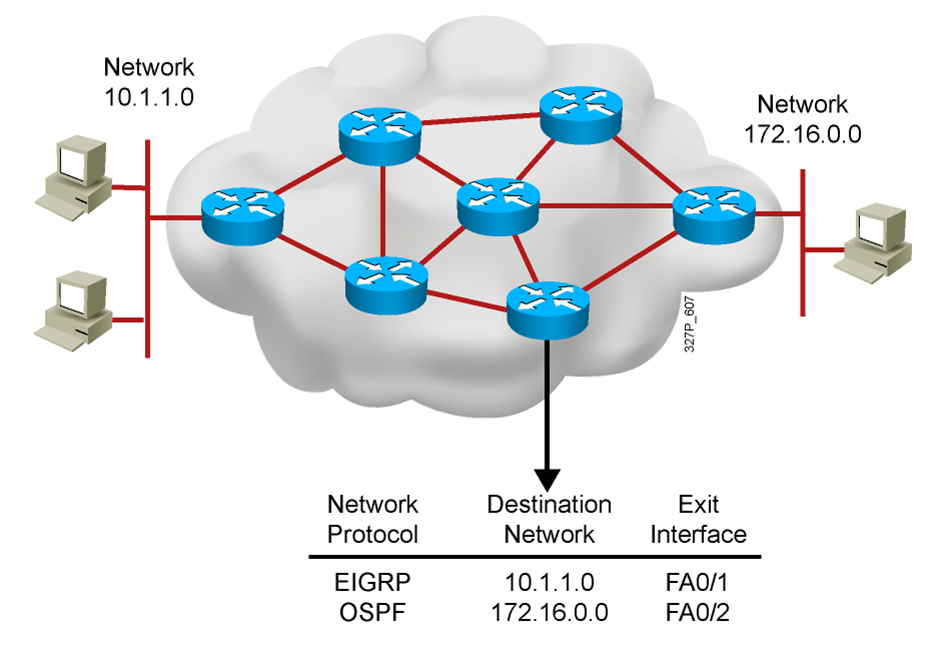
- Routing protocols are used between routers to determine paths to remote networks and maintain those networks in the routing tables.
- After the path is determined, a router can route a routed protocol to the learned networks.
Autonomous Systems: Interior and Exterior Routing Protocols
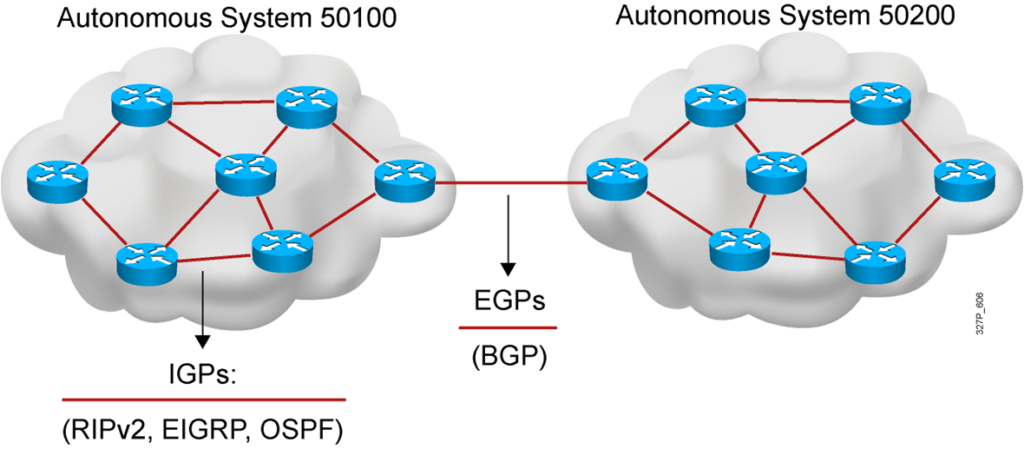
- An autonomous system is a collection of networks within a common administrative domain.
- Interior gateway protocols operate within an autonomous system.
- Exterior gateway protocols connect different autonomous systems.
Classes of Routing Protocols
Selecting the Best Route Using Metrics
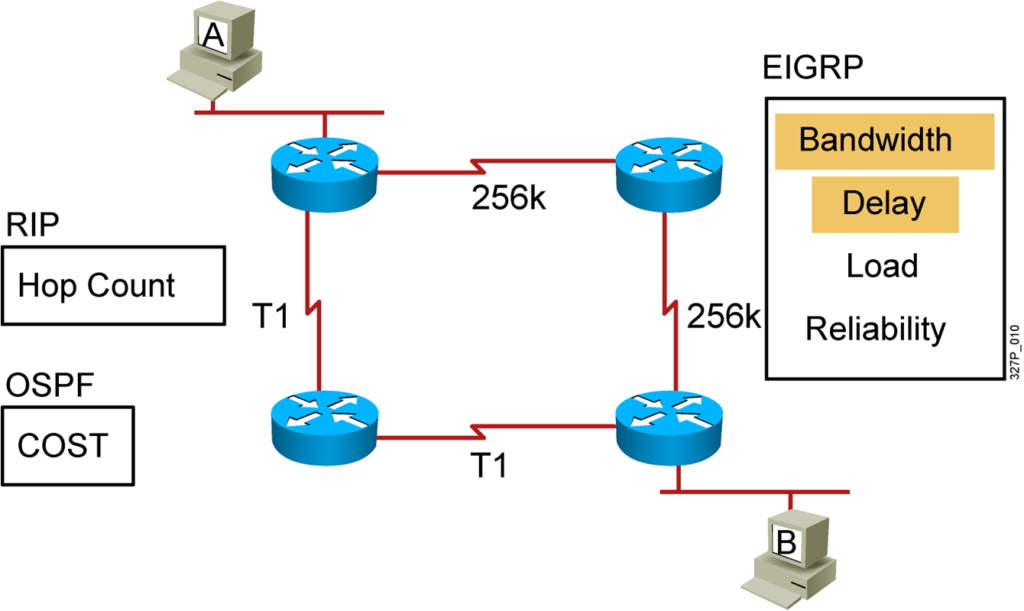
Administrative Distance: Ranking Routing Sources
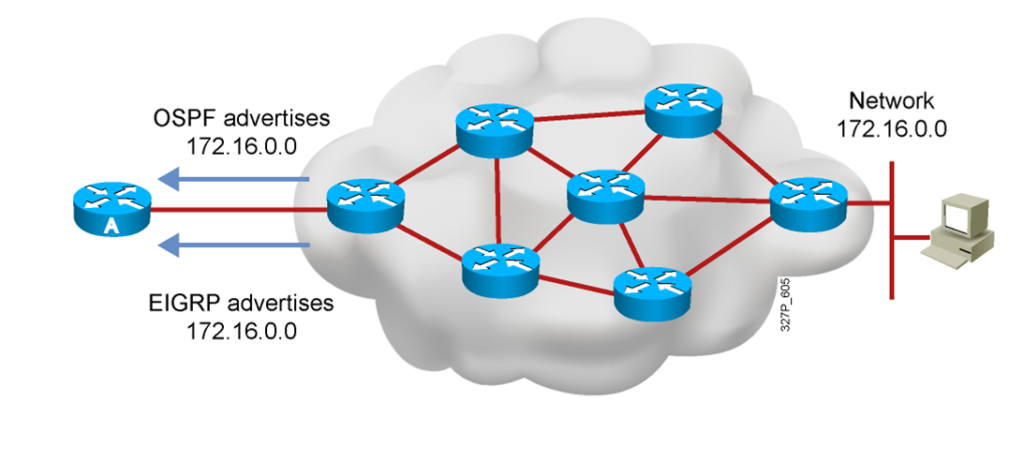
Routers choose the routing source with the best administrative distance:
- OSPF has an administrative distance of 110.
- EIGRP has an administrative distance of 90.
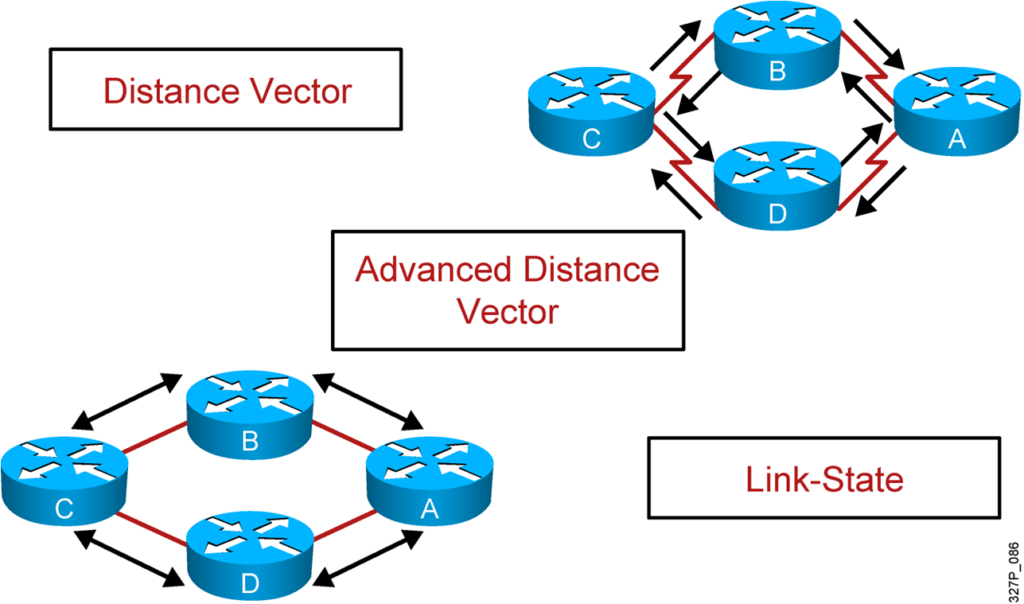
Distance Vector Routing Protocols
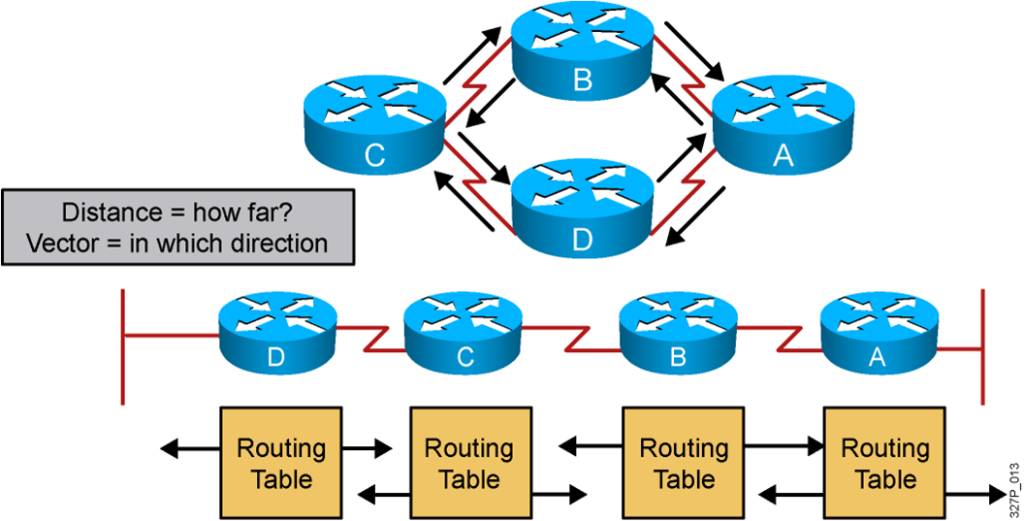
Routers pass periodic copies of their routing table to neighboring routers and accumulate distance vectors.
Sources of Information and Discovering Routes
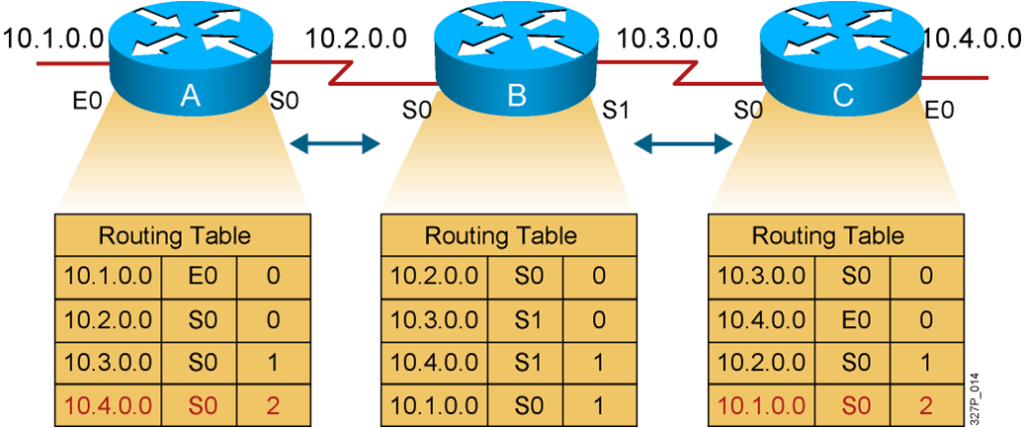
Routers discover the best path to destinations from each neighbor.
Maintaining Routing Information
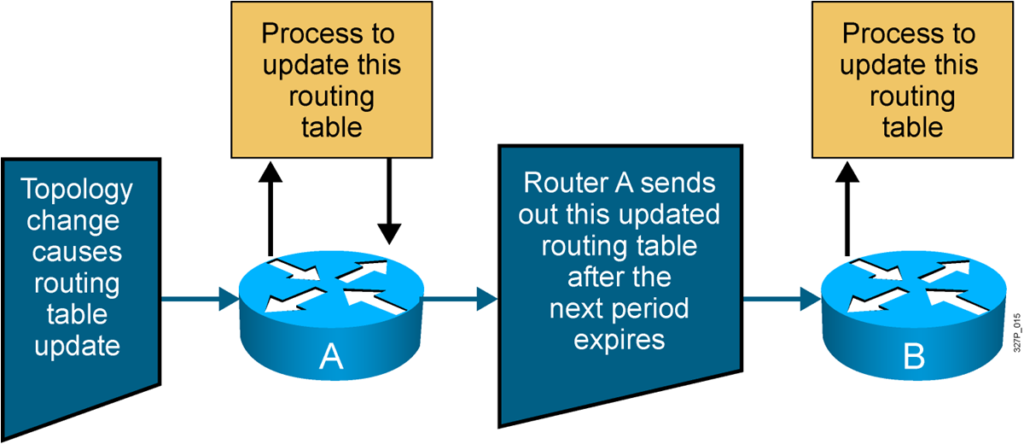
Updates proceed step by step from router to router.
Inconsistent Routing Entries:Counting to Infinity and Routing Loops
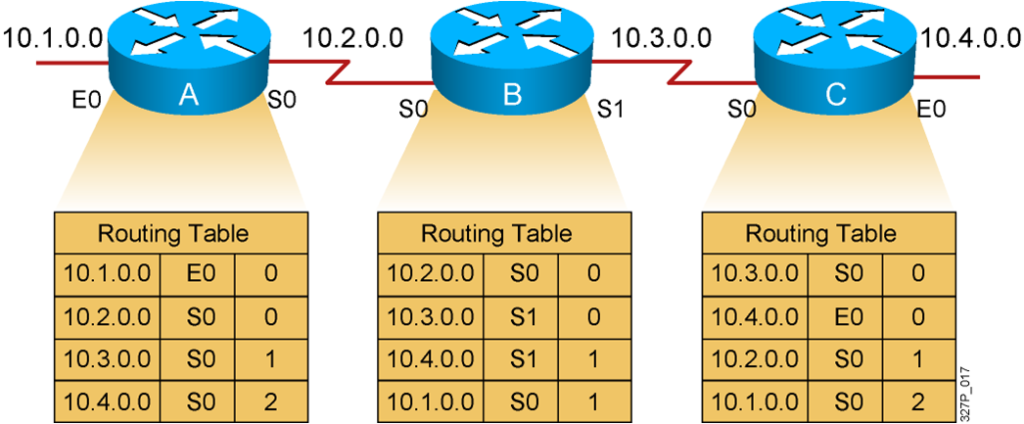
Each node maintains the distance from itself to each possible destination network.
Counting to Infinity
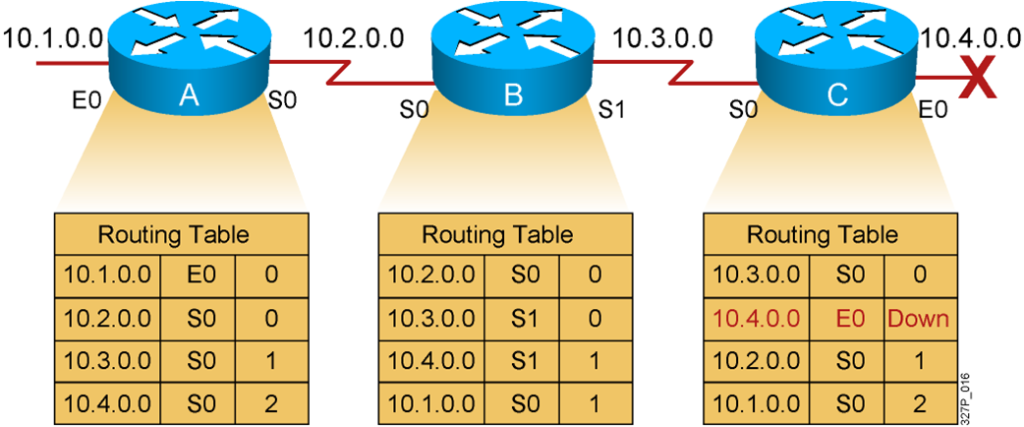
Slow convergence produces inconsistent routing.
Counting to Infinity (Cont.)
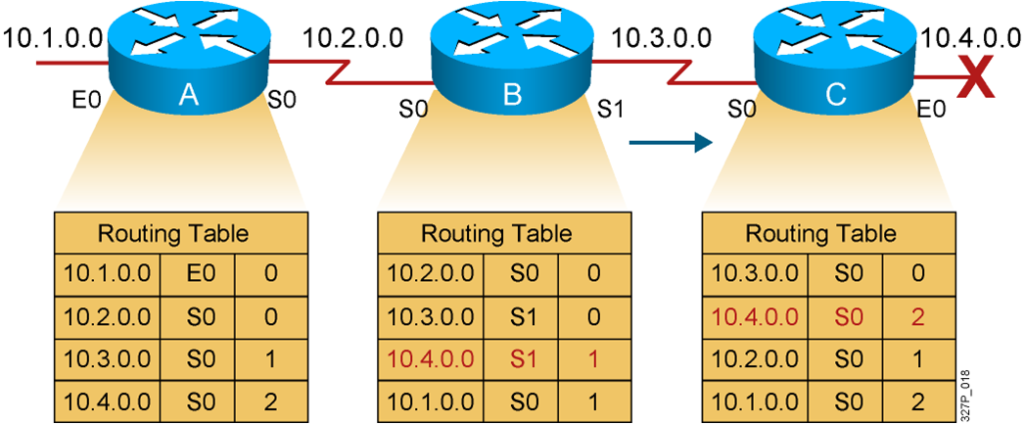
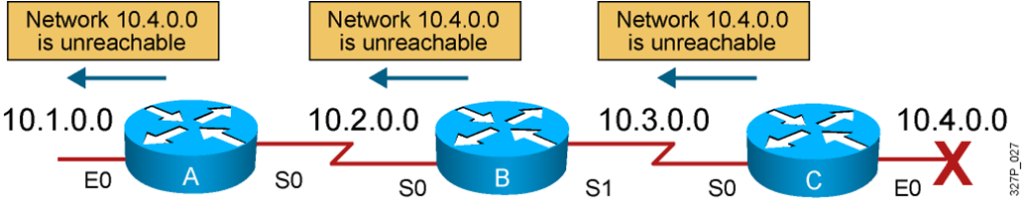
Router C concludes that the best path to network 10.4.0.0 is through router B.
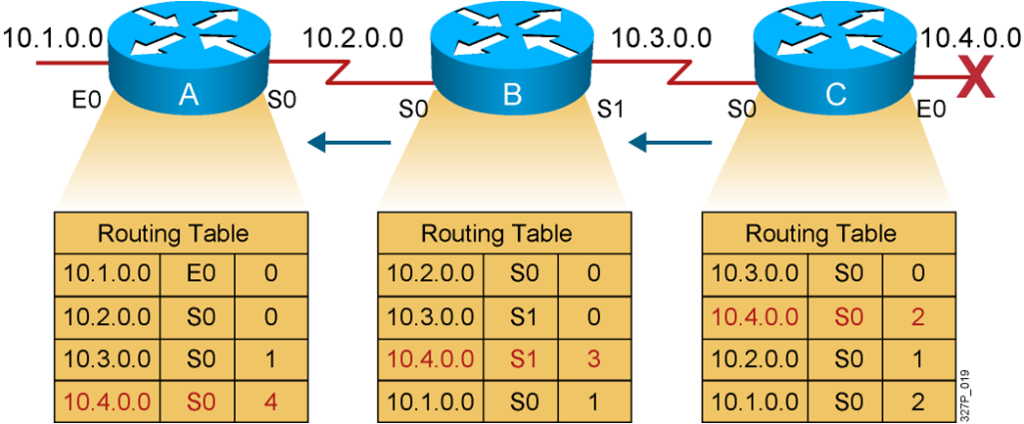
Router A updates its table to reflect the new but erroneous hop count.
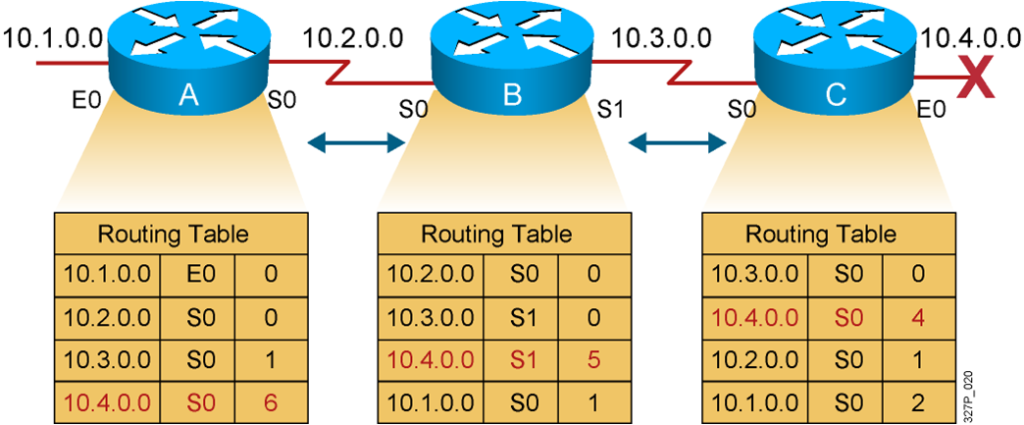
The hop count for network 10.4.0.0 counts to infinity.
Solution to Counting to Infinity:Defining a Maximum
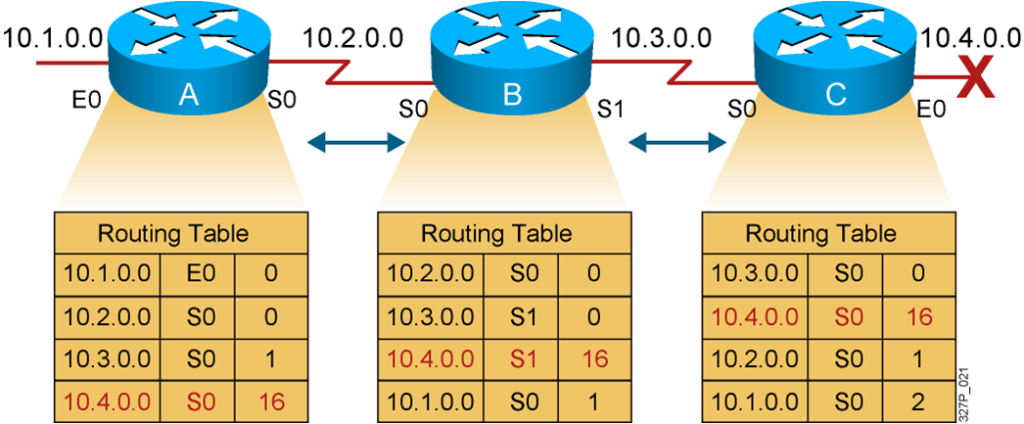
A limit is set on the number of hops to prevent infinite loops.
Routing Loops
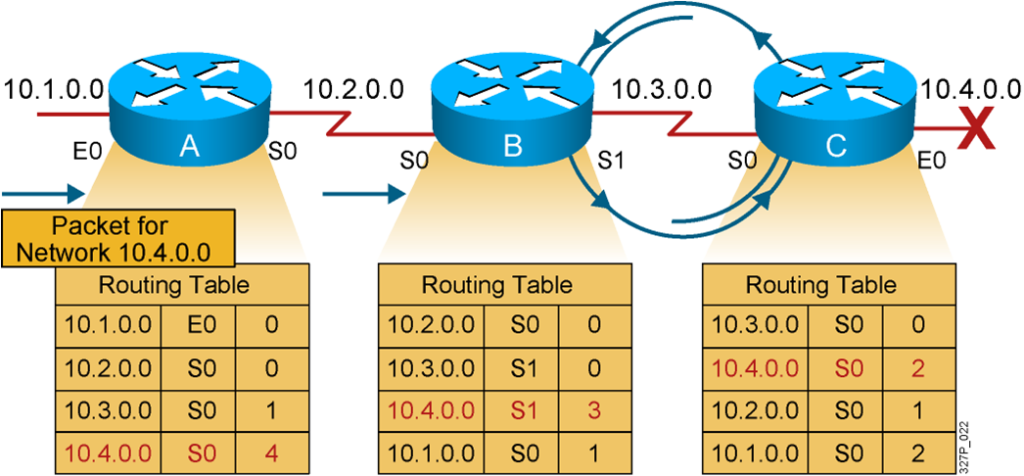
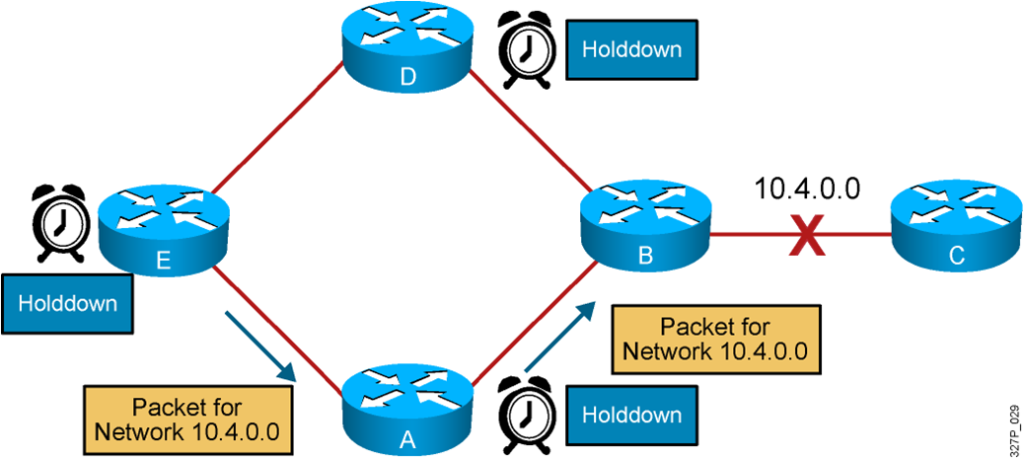
Packets for network 10.4.0.0 bounce (loop) between routers B and C.
Solution to Routing Loops: Split Horizon
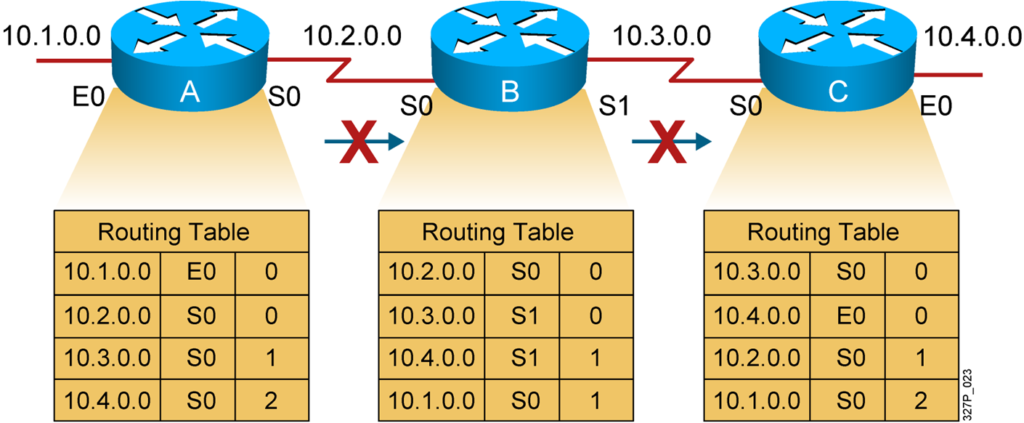
It is never useful to send information about a route back in the direction from which the original information came.
Solution to Routing Loops:Route Poisoning and Poison Reverse
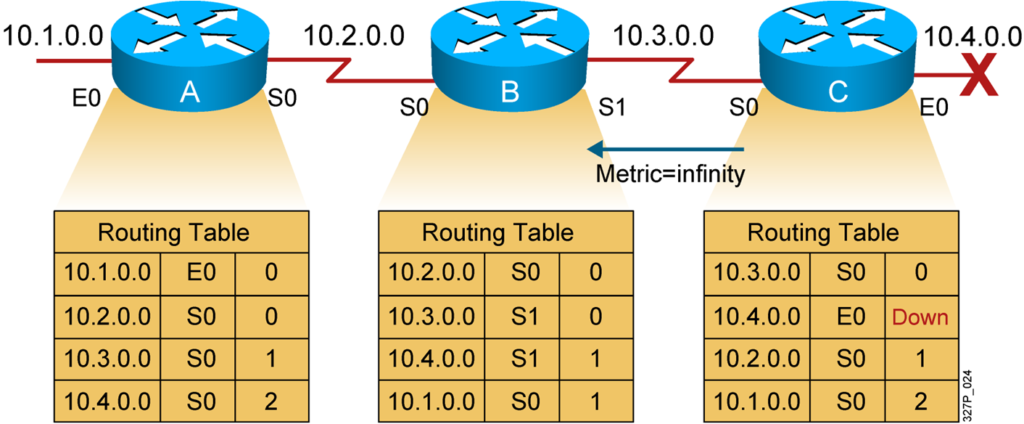
Routers advertise the distance of routes that have gone down to infinity.
Solution to Routing Loops:Route Poisoning and Poison Reverse (Cont.)
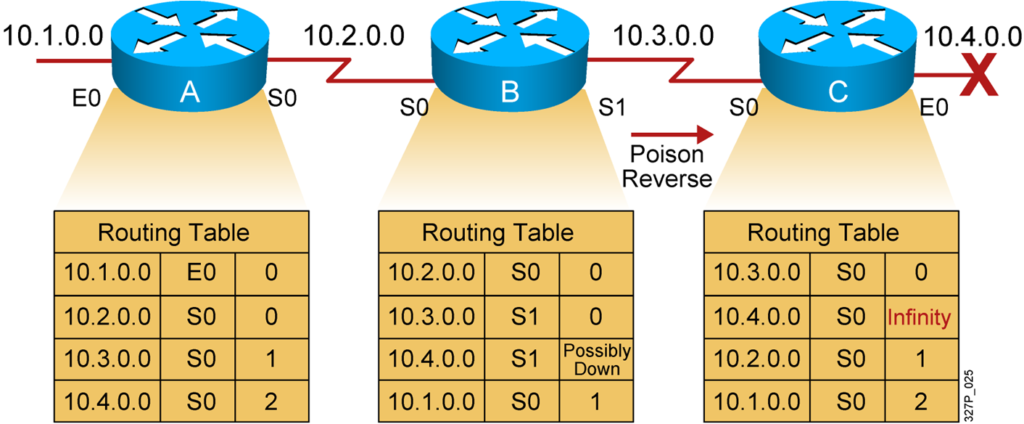
Poison reverse overrides split horizon.
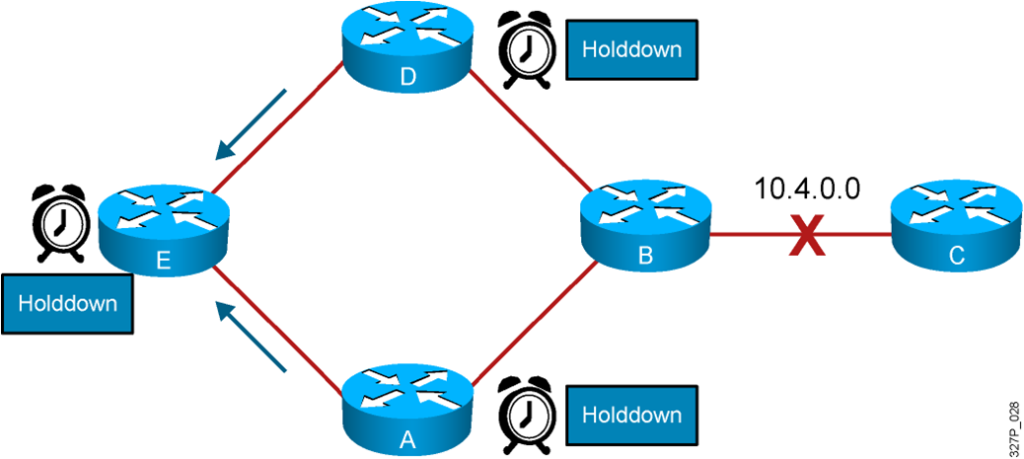
Solution to Routing Loops: Hold-Down Timers
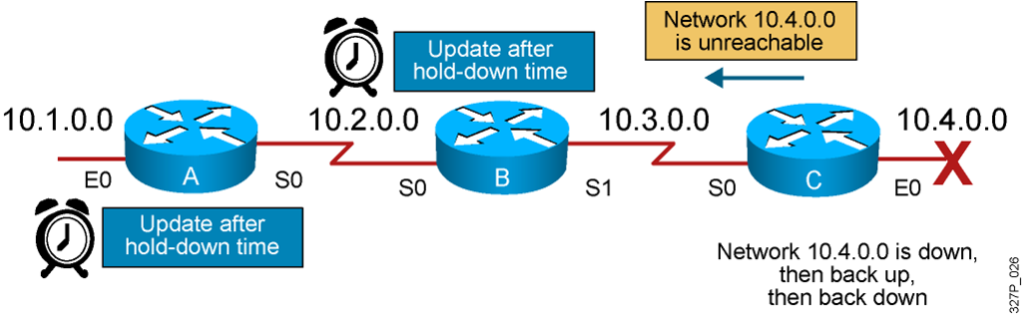
The router keeps an entry for the “possibly down” state in the network, allowing time for other routers to recompute for this topology change.
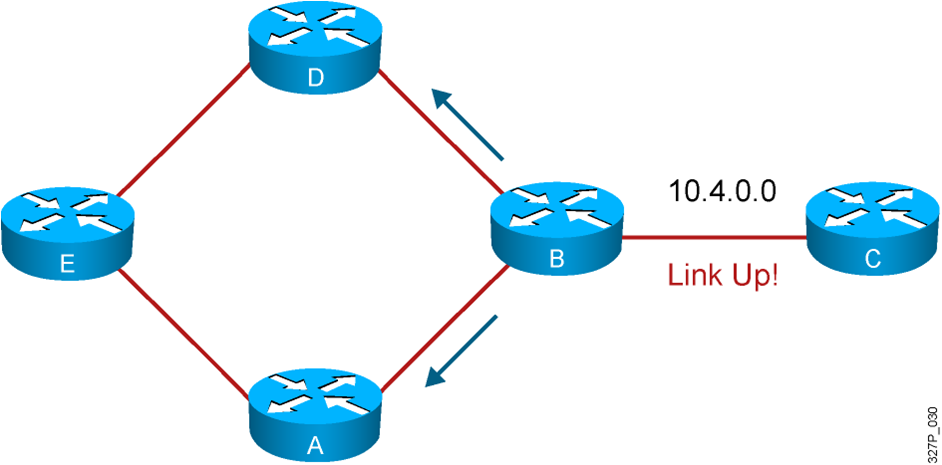
Triggered Updates
The router sends updates when a change in its routing table occurs.
Eliminating Routing Loops
Eliminating Routing Loops (Cont.)
Link-State Routing Protocols
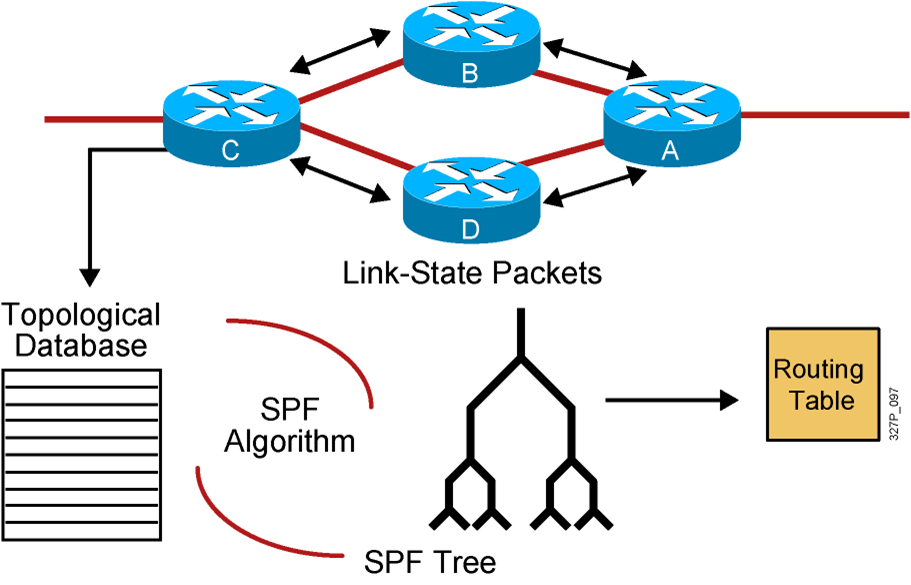
After an initial flood of LSAs, link-state routers pass small, event-triggered link-state updates to all other routers.
OSPF Hierarchical Routing
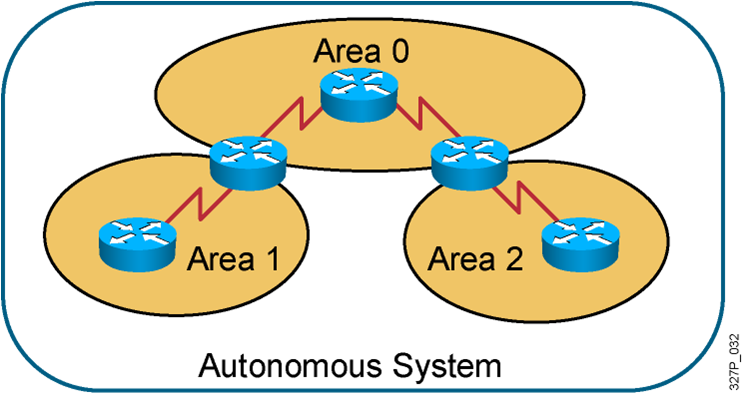
- Consists of areas and autonomous systems
- Minimizes routing update traffic
Link-State Routing Protocol Algorithms
Benefits and Drawbacks of Link-State Routing
- Benefits of link-state routing:
–Fast convergence:
- Changes are reported immediately by the affected source
–Robustness against routing loops:
- Routers know the topology
- Link-state packets are sequenced and acknowledged
–Hierarchical network design enables optimization of resources.
- Drawbacks of link-state routing:
–Significant demands for resources:
- Memory (three tables: adjacency, topology, forwarding)
- CPU (Dijkstra’s algorithm can be intensive, especially when there are many instabilities)
–Requires very strict network design
–Configuration can be complex when tuning various parameters and when design is complex
Summary
- Dynamic routing requires administrators to configure either a distance vector or link-state routing protocol.
- Distance vector routing protocols incorporate solutions such as split horizon, route poisoning, and hold-down timers to prevent routing loops.
- Link-state routing protocols scale to large network infrastructures better than distance vector routing protocols, but they require more planning to implement.
