10.1.1.4 Packet Tracer – Map a Network Using CDP (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
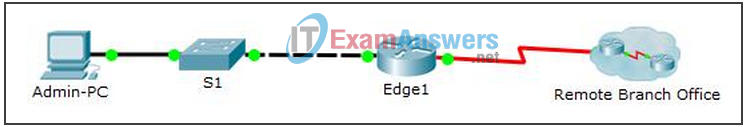
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Local Interface and Connected Neighbor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Edge1 | G0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | G0/1 – S1 |
| S0/0/0 | 209.165.200.5 | 255.255.255.252 | S0/0/0 – ISP | |
| Branch-Edge | S0/0/1 | 209.165.200.10 | 255.255.255.252 | S0/0/1 – ISP |
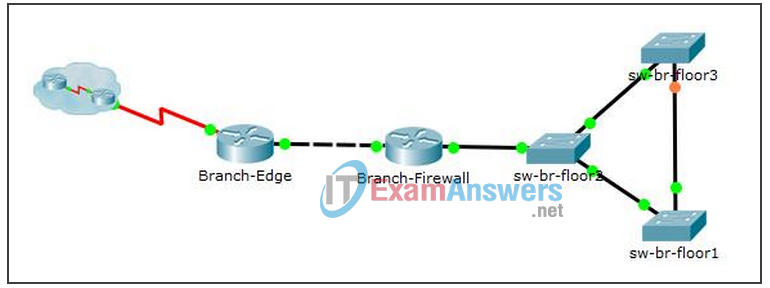
| Branch-Edge | G0/0 | 192.168.3.249 | 255.255.255.248 | G0/0 – Branch-Firewall |
| Branch-Firewall | G0/0 | 192.168.3.253 | 255.255.255.248 | G0/0 – Branch-Edge |
| Branch-Firewall | G0/1 | 192.168.4.129 | 255.255.255.128 | G0/1 – sw-br-floor2 |
| sw-br-floor1 | G0/1 | G0/1 – sw-br-floor3 | ||
| sw-br-floor1 | G0/2 | G0/2 – sw-br-floor2 | ||
| sw-br-floor2 | G0/1 | G0/1 – Branch-Firewall | ||
| sw-br-floor2 | G0/2 | G0/2 – sw-br-floor1 | ||
| sw-br-floor2 | F0/24 | F0/24 – sw-br-floor3 | ||
| sw-br-floor2 | SVI | 192.168.4.132 | 255.255.255.128 | |
| sw-br-floor3 | F0/24 | F0/24 – sw-br-floor2 | ||
| sw-br-floor3 | G0/1 | G0/1 – sw-br-floor1 | ||
| sw-br-floor3 | SVI | 192.168.4.133 | 255.255.255.128 |
Objectives
Map a network using CDP and SSH remote access.
Background / Scenario
A senior network administrator requires you to map the Remote Branch Office network and discover the name of a recently installed switch that still needs an IP address to be configured. Your task is to create a map of the branch office network. You must record all of the network device names, IP addresses and subnet masks, and physical interfaces interconnecting the network devices, as well as the name of the switch that does not have an IP address.
To map the network, you will use SSH for remote access and the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to discover information about neighboring network devices, like routers and switches. Because CDP is a Layer 2 protocol, it can be used to discover information about devices that do not have IP addresses. You will record the gathered information to complete the Addressing Table and provide a topology diagram of the Remote Branch Office network.
You will need the IP address for the remote branch office, which is 209.165.200.10. The local and remote administrative usernames and passwords are:
Local Network
Username: admin01
Password: S3cre7P@55
Branch Office Network
Username: branchadmin
Password: S3cre7P@55
Part 1: Use SSH to Remotely Access Network Devices
In Part 1, you will use the Admin-PC to remotely access the Edge1 gateway router. Next, from the Edge1 router you will SSH into the Remote Branch Office.
a. On the Admin-PC, open a command prompt.
b. SSH into the gateway router at 192.168.1.1 using the username admin01 and the password S3cre7P@55.
PC> ssh –l admin01 192.168.1.1 Open Password: Edge1#
Note: Notice that you are placed directly into privileged EXEC mode. This is because the admin01 user account is set to privilege level 15.
c. Use the show ip interface brief and show interfaces commands to document the Edge1 router’s physical interfaces, IP addresses, and subnet masks in the Addressing Table.
Edge1# show ip interface brief Edge1# show interfaces
d. Using the Edge1 router’s CLI, you will SSH into the Remote Branch Office at 209.165.200.10 with the username branchadmin and the same password:
Edge1# ssh –l branchadmin 209.165.200.10 Open Password: Branch-Edge#
After connecting to the Remote Branch Office at 209.165.200.10 what piece of previously missing information can now be added to the Addressing Table above?
The Branch-Edge router hostname
Part 2: Use CDP to Discover Neighboring Devices
You are now remotely connected to the Branch-Edge router. Using CDP, begin looking for connected network devices.
a. Issue the show ip interface brief and show interfaces commands to document the Branch-Edge router’s network interfaces, IP addresses, and subnet masks. Add the missing information to the Addressing Table to map the network:
Branch-Edge# show ip interface brief Branch-Edge# show interfaces
b. Security best practice recommends only running CDP when needed, so CDP may need to be turned on. Use a show cdp command to test its status.
Branch-Edge# show cdp % CDP is not enabled
c. You need to turn on CDP, but it is a good idea to only broadcast CDP information to internal network devices and not to external networks. To do this, disable CDP on the s0/0/1 interface and then turn on the CDP protocol.
Branch-Edge# configure terminal Branch-Edge(config)# interface s0/0/1 Branch-Edge(config-if)# no cdp enable Branch-Edge(config-if)# exit Branch-Edge(config)# cdp run
d. Issue a show cdp neighbors command to find any neighboring network devices.
Note: CDP will only show connected Cisco devices that are also running CDP.
Branch-Edge# show cdp neighbors
Is there a neighboring network device? What type of device is it? What is its name? On what interface is it connected? Is the device’s IP address listed? Record the information in the Addressing Table.
It is a router. Its name is Branch-Firewall and it is connected on interface G0/0. The IP address of the device is not listed.
e. To find the IP address of the neighboring device use the show cdp neighbors detail command and record the ip address:
Branch-Edge# show cdp neighbors detail
Aside from the neighboring device’s IP address, what other piece of potentially sensitive information is listed?
The neighboring device’s IOS software version.
f. Now that you know the IP address of the neighbor device, you need to connect to it with SSH in order to discover other devices that may be its neighbors.
Note: To connect with SSH use the same Remote Branch Office username and password.
Branch-Edge# ssh –l branchadmin <the ip address of the neighbor device>
After successfully connecting with SSH, what does the command prompt show?
Branch-Firewall#
g. You are remotely connected to the next neighbor. Use the show cdp neighbors command, and the show cdp neighbors detail command, to discover other connected neighbor devices.
What types of network devices neighbor this device? Record any newly discovered devices in the Addressing Table. Include their hostname, interfaces, and IP addresses.
A router (Branch-Edge) and a switch (sw-br-floor2). The sw-br-floor2 switch is a newly discovered device located at 192.168.4.132 on the G0/1 interface.
h. Continue discovering new network devices using SSH and the show CDP commands. Eventually, you will reach the end of the network and there will be no more devices to discover.
What is the name of the switch that does not have an IP address on the network?
sw-br-floor1
i. Draw a topology of the Remote Branch Office network using the information you have gathered using CDP.
Suggested Scoring Rubric
| Activity Section | Possible Points | Earned Points |
|---|---|---|
| Part 1 Question | 2 | |
| Question d | 2 | |
| Part 2 Questions | 8 | |
| Question d | 2 | |
| Question e | 1 | |
| Question f | 1 | |
| Question g | 2 | |
| Question h | 2 | |
| Packet Tracer | 10 | |
| Addressing Scheme Documentation | 60 | |
| Topology Documentation | 20 | |
| Total Point | 100 |
