CCNA Security 2.0 Study Material – Chapter 6: Securing the Local Area Network
6.0 Introduction
6.0.1 Welcome
6.0.1.1 Chapter 6: Securing the Local Area Network
Chapter 6: Network Layer

Network applications and services on one end device can communicate with applications and services running on another end device. How is this data communicated across the network in an efficient way?
The protocols of the OSI model network layer specify addressing and processes that enable transport layer data to be packaged and transported. The network layer encapsulation enables data to be passed to a destination within a network (or on another network) with minimum overhead.
This chapter focuses on the role of the network layer. It examines how it divides networks into groups of hosts to manage the flow of data packets within a network. It also covers how communication between networks is facilitated. This communication between networks is called routing.
6.1 Endpoint Security
6.1.1 Introducing Endpoint Security
6.1.1.1 Securing LAN Elements
The Network Layer
The network layer, or OSI Layer 3, provides services to allow end devices to exchange data across the network. To accomplish this end-to-end transport, the network layer uses four basic processes:
- Addressing end devices – End devices must be configured with a unique IP address for identification on the network.
- Encapsulation – The network layer encapsulates the protocol data unit (PDU) from the transport layer into a packet. The encapsulation process adds IP header information, such as the IP address of the source (sending) and destination (receiving) hosts.
- Routing – The network layer provides services to direct packets to a destination host on another network. To travel to other networks, the packet must be processed by a router. The role of the router is to select the best path and direct packets toward the destination host in a process known as routing. A packet may cross many intermediary devices before reaching the destination host. Each router a packet crosses to reach the destination host is called a hop.
- De-encapsulation – When the packet arrives at the network layer of the destination host, the host checks the IP header of the packet. If the destination IP address within the header matches its own IP address, the IP header is removed from the packet. After the packet is de-encapsulated by the network layer, the resulting Layer 4 PDU is passed up to the appropriate service at the transport layer.
Unlike the transport layer (OSI Layer 4), which manages the data transport between the processes running on each host, network layer protocols specify the packet structure and processing used to carry the data from one host to another host. Operating without regard to the data carried in each packet allows the network layer to carry packets for multiple types of communications between multiple hosts.
Click Play in the figure to view an animation that demonstrates the exchange of data.
The Exchange of Data
6.1.1.2 Traditional Endpoint Security
Network Layer Protocols
There are several network layer protocols in existence. However, as shown in the figure, there are only two network layer protocols that are commonly implemented:
- Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4)
- Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6)
Note: Legacy network layer protocols are not shown in the figure and are not discussed in this course.
6.1.1.3 The Borderless Network

6.1.1.4 Securing Endpoints in the Borderless Network
Post malware attack questions:
- Where did it come from?
- What was the threat method and point of entry?
- What systems were affected?
- What did the threat do?
- Can I stop the threat and root cause?
- How do we recover from it?
- How do we prevent it from happening again?
Host-Based Protection:
- Antivirus/Antimalware
- SPAM Filtering
- URL Filtering
- Blacklisting
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
6.1.1.5 Modern Endpoint Security Solutions
6.1.1.6 Hardware and Software Encryption of Local Data

6.1.1.7 Activity – Identify Endpoint Security Terminology (DND)
6.1.2 Antimalware Protection
6.1.2.1 Advanced Malware Protection
Encapsulating IP
IP encapsulates the transport layer segment or other data by adding an IP header. This header is used to deliver the packet to the destination host. The IP header remains the same from the time the packet leaves the source host until it arrives at the destination host.
Figure 1 shows the process to create the transport layer PDU. Figure 2 illustrates how the transport layer PDU is then encapsulated by the network layer PDU to create an IP packet.
The process of encapsulating data layer by layer enables the services at the different layers to develop and scale without affecting the other layers. This means the transport layer segments can be readily packaged by IPv4 or IPv6 or by any new protocol that might be developed in the future.
Routers can implement these different network layer protocols to operate concurrently over a network. The routing performed by these intermediate devices only considers the contents of the network layer packet header. In all cases, the data portion of the packet, that is, the encapsulated transport layer PDU, remains unchanged during the network layer processes.
Transport Layer PDU = Segment
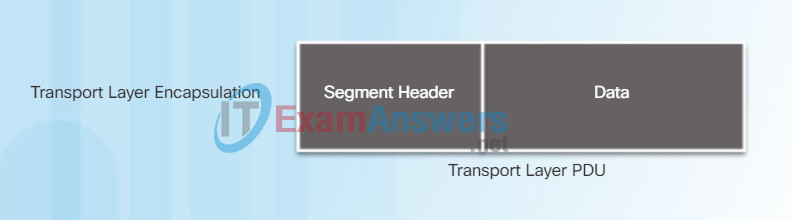
The transport layer adds a header so segments can be reassembled at the destination.
Network Layer PDU = IP Packet
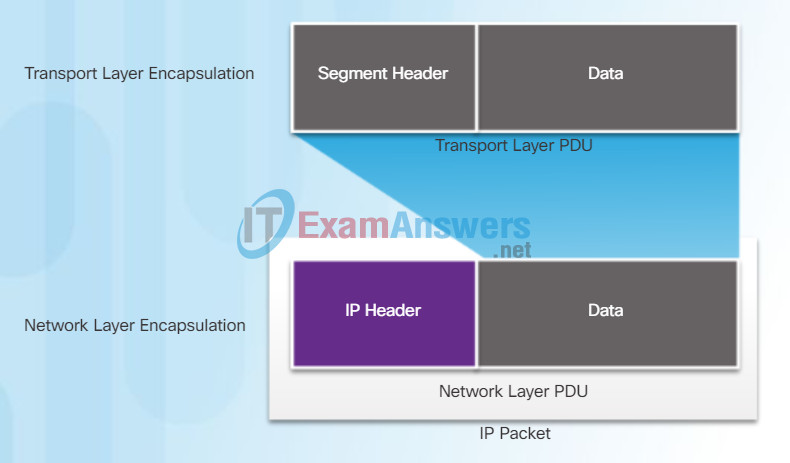
The network layer adds a header so packets can be routed through complex networks and reach their destination. In TCP/IP based networks, the network layer PDU is the IP Packet.
6.1.2.2 AMP and Managed Threat Defense
Characteristics of IP
IP was designed as a protocol with low overhead. It provides only the functions that are necessary to deliver a packet from a source to a destination over an interconnected system of networks. The protocol was not designed to track and manage the flow of packets. These functions, if required, are performed by other protocols at other layers, primarily TCP at Layer 4.
The basic characteristics of IP are described in the figure.

Characteristics of the IP Protocol
- Connectionless: No connection with the destination is established before sending data packets.
- Best Effort: IP is inherently unreliable because packet delivery is not guaranteed.
- Media Independent: Operation is independent of the medium (i.e., copper, fiber optic, or wireless) carrying the data.
6.1.2.3 AMP for Endpoints
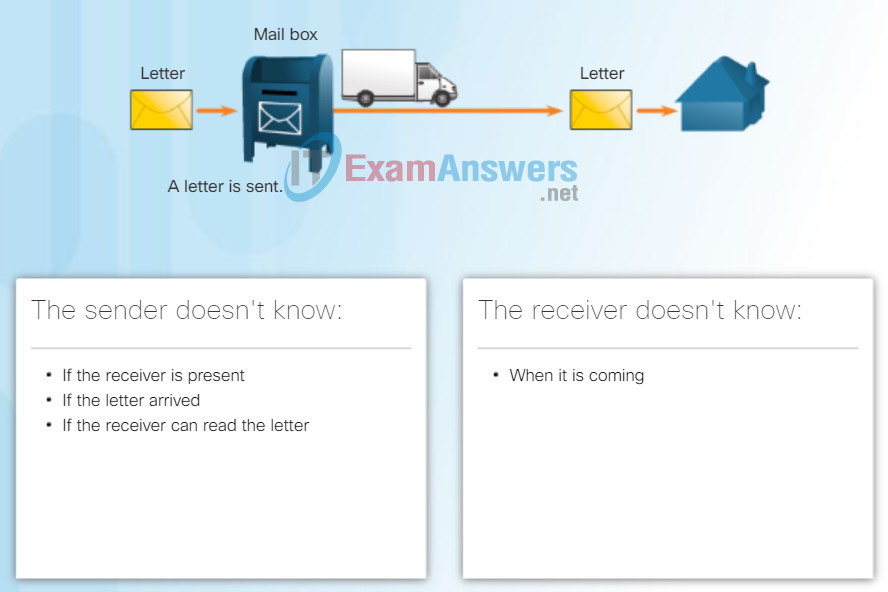
IP – Connectionless
IP is connectionless, meaning that no dedicated end-to-end connection is created before data is sent. As shown in Figure 1, connectionless communication is conceptually similar to sending a letter to someone without notifying the recipient in advance.
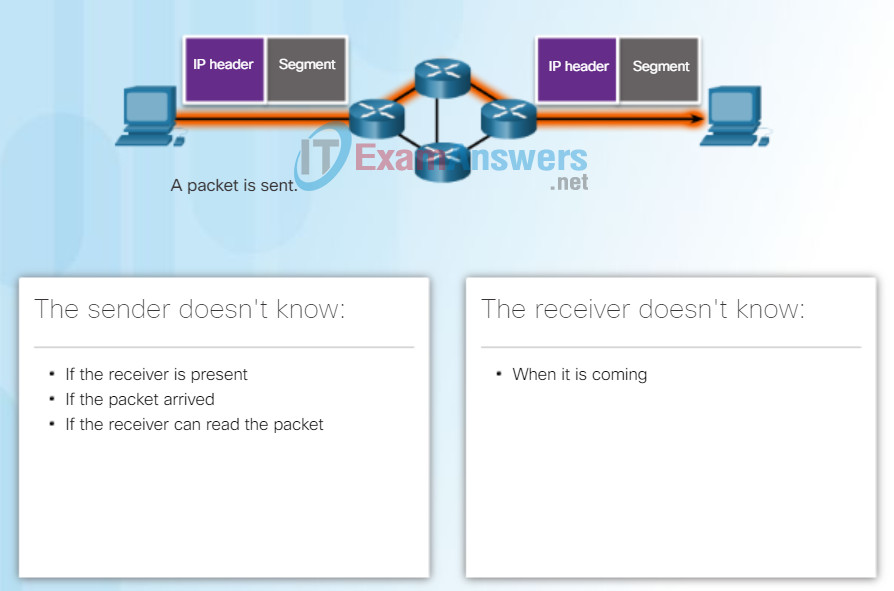
Connectionless data communications work on the same principle. As shown in Figure 2, IP requires no initial exchange of control information to establish an end-to-end connection before packets are forwarded. IP also does not require additional fields in the header to maintain an established connection. This process greatly reduces the overhead of IP. However, with no pre-established end-to-end connection, senders are unaware whether destination devices are present and functional when sending packets, nor are they aware if the destination receives the packet, or if they are able to access and read the packet.
6.1.3 Email and Web Security
6.1.3.1 Securing Email and Web
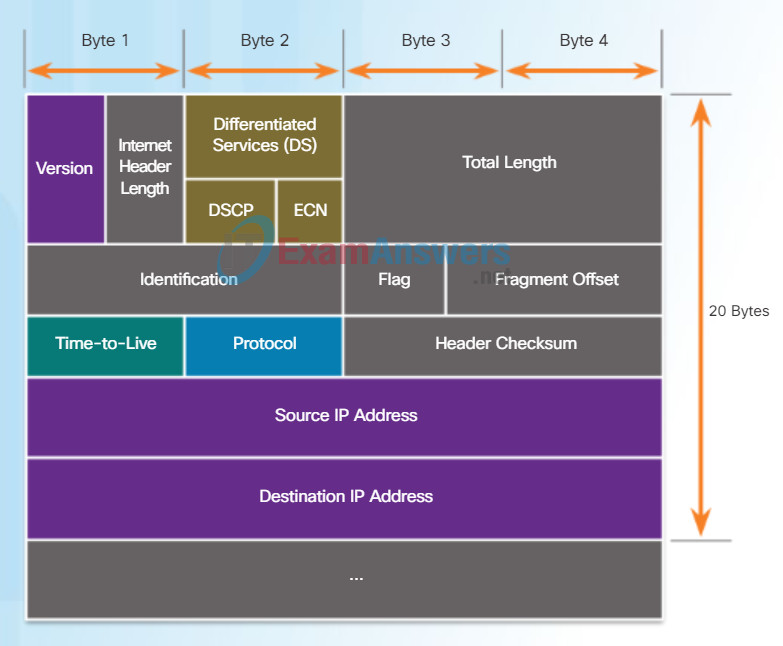
IPv4 Packet Header
An IPv4 packet header consists of fields containing important information about the packet. These fields contain binary numbers which are examined by the Layer 3 process. The binary values of each field identify various settings of the IP packet. Protocol header diagrams, which are read left to right, and top down, provide a visual to refer to when discussing protocol fields. The IP protocol header diagram in the figure identifies the fields of an IPv4 packet.
Significant fields in the IPv4 header include:
- Version – Contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0100 that identifies this as an IP version 4 packet.
- Differentiated Services or DiffServ (DS) – Formerly called the Type of Service (ToS) field, the DS field is an 8-bit field used to determine the priority of each packet. The six most significant bits of the DiffServ field is the Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) and the last two bits are the Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) bits.
- Time-to-Live (TTL) – Contains an 8-bit binary value that is used to limit the lifetime of a packet. The packet sender sets the initial TTL value, and it is decreased by one each time the packet is processed by a router. If the TTL field decrements to zero, the router discards the packet and sends an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Time Exceeded message to the source IP address.
- Protocol – Field is used to identify the next level protocol. This 8-bit binary value indicates the data payload type that the packet is carrying, which enables the network layer to pass the data to the appropriate upper-layer protocol. Common values include ICMP (1), TCP (6), and UDP (17).
- Source IPv4 Address – Contains a 32-bit binary value that represents the source IPv4 address of the packet. The source IPv4 address is always a unicast address.
- Destination IPv4 Address – Contains a 32-bit binary value that represents the destination IPv4 address of the packet. The destination IPv4 address is a unicast, multicast, or broadcast address.
The two most commonly referenced fields are the source and destination IP addresses. These fields identify where the packet is coming from and where it is going. Typically these addresses do not change while travelling from the source to the destination.
The Internet Header Length (IHL), Total Length, and Header Checksum fields are used to identify and validate the packet.
Other fields are used to reorder a fragmented packet. Specifically, the IPv4 packet uses Identification, Flags, and Fragment Offset fields to keep track of the fragments. A router may have to fragment a packet when forwarding it from one medium to another with a smaller MTU.
The Options and Padding fields are rarely used and are beyond the scope of this chapter.
6.1.3.2 Cisco Email Security Appliance
Video Demonstration – Sample IPv4 Headers in Wireshark
6.1.4 Controlling Network Access
6.1.4.1 Cisco Network Admission Control
Limitations of IPv4
Through the years, IPv4 has been updated to address new challenges. However, even with changes, IPv4 still has three major issues:
- IP address depletion – IPv4 has a limited number of unique public IPv4 addresses available. Although there are approximately 4 billion IPv4 addresses, the increasing number of new IP-enabled devices, always-on connections, and the potential growth of less-developed regions have increased the need for more addresses.
- Internet routing table expansion – A routing table is used by routers to make best path determinations. As the number of servers connected to the Internet increases, so too does the number of network routes. These IPv4 routes consume a great deal of memory and processor resources on Internet routers.
- Lack of end-to-end connectivity – Network Address Translation (NAT) is a technology commonly implemented within IPv4 networks. NAT provides a way for multiple devices to share a single public IPv4 address. However, because the public IPv4 address is shared, the IPv4 address of an internal network host is hidden. This can be problematic for technologies that require end-to-end connectivity.

6.1.4.2 Cisco NAC Functions
Introducing IPv6
In the early 1990s, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) grew concerned about the issues with IPv4 and began to look for a replacement. This activity led to the development of IP version 6 (IPv6). IPv6 overcomes the limitations of IPv4 and is a powerful enhancement with features that better suit current and foreseeable network demands.
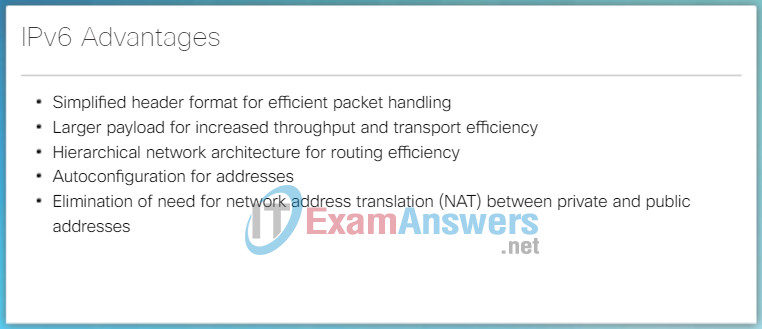
Improvements that IPv6 provides include:
- Increased address space – IPv6 addresses are based on 128-bit hierarchical addressing as opposed to IPv4 with 32 bits.
- Improved packet handling – The IPv6 header has been simplified with fewer fields.
- Eliminates the need for NAT – With such a large number of public IPv6 addresses, NAT between a private IPv4 address and a public IPv4 is not needed. This avoids some of the NAT-induced application problems experienced by applications requiring end-to-end connectivity.
The 32-bit IPv4 address space provides approximately 4,294,967,296 unique addresses. IPv6 address space provides 340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456, or 340 undecillion addresses, which is roughly equivalent to every grain of sand on Earth.
The figure provides a visual to compare the IPv4 and IPv6 address space.
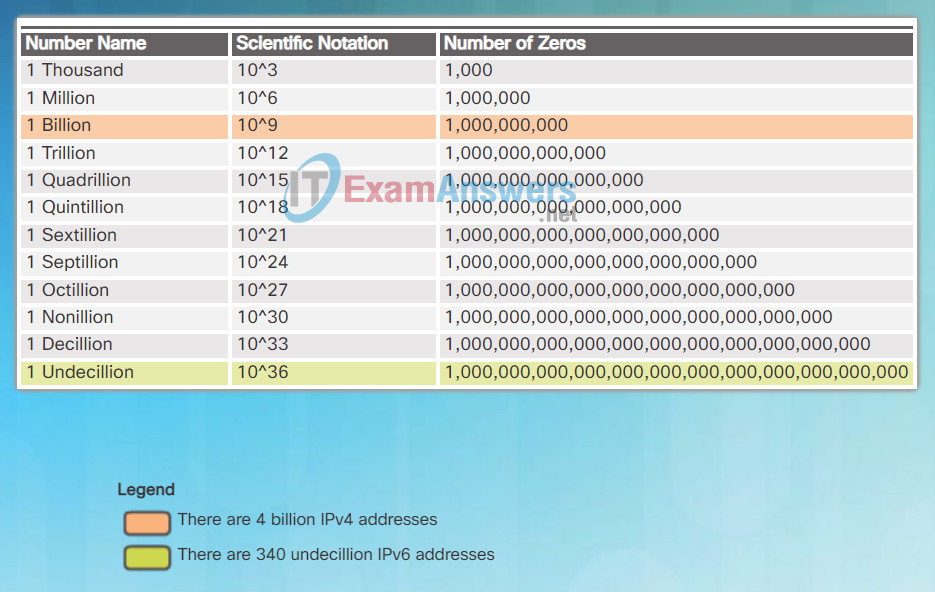
How Many Addresses Are Available with IPv6?
6.1.4.3 Cisco NAC Components
Encapsulating IPv6
One of the major design improvements of IPv6 over IPv4 is the simplified IPv6 header.
For instance, the IPv4 header shown in Figure 1 consists of 20 octets (up to 60 bytes if the Options field is used) and 12 basic header fields, not including the Options field and Padding field. As highlighted in the figure, for IPv6, some fields have remained the same, some fields have changed names and positions, and some IPv4 fields are no longer required.
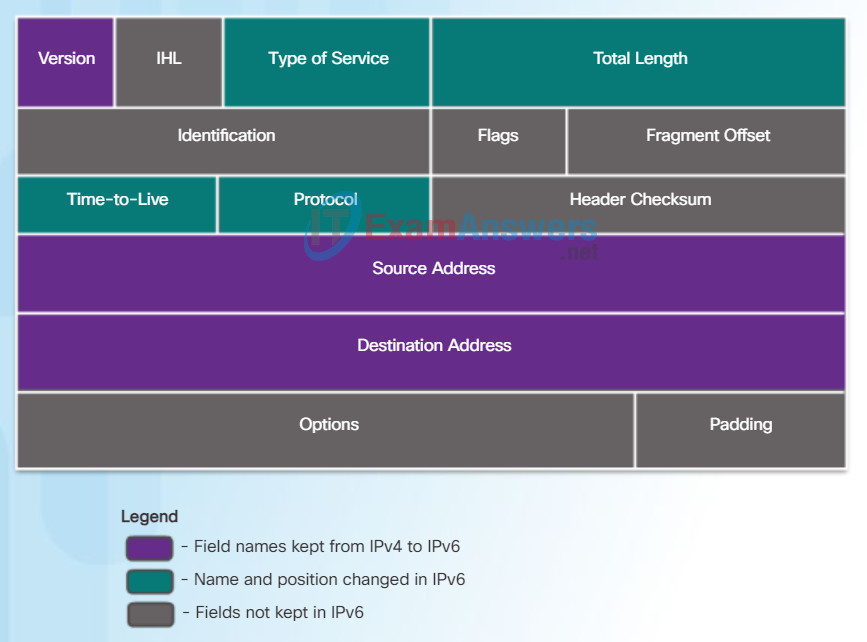
IPv4 Header
In contrast, the simplified IPv6 header shown in Figure 2 consists of 40 octets (largely due to the length of the source and destination IPv6 addresses) and 8 header fields (3 IPv4 basic header fields and 5 additional header fields). As highlighted in this figure, some fields have kept the same names as IPv4, some fields have changed names or positions, and a new field has been added.
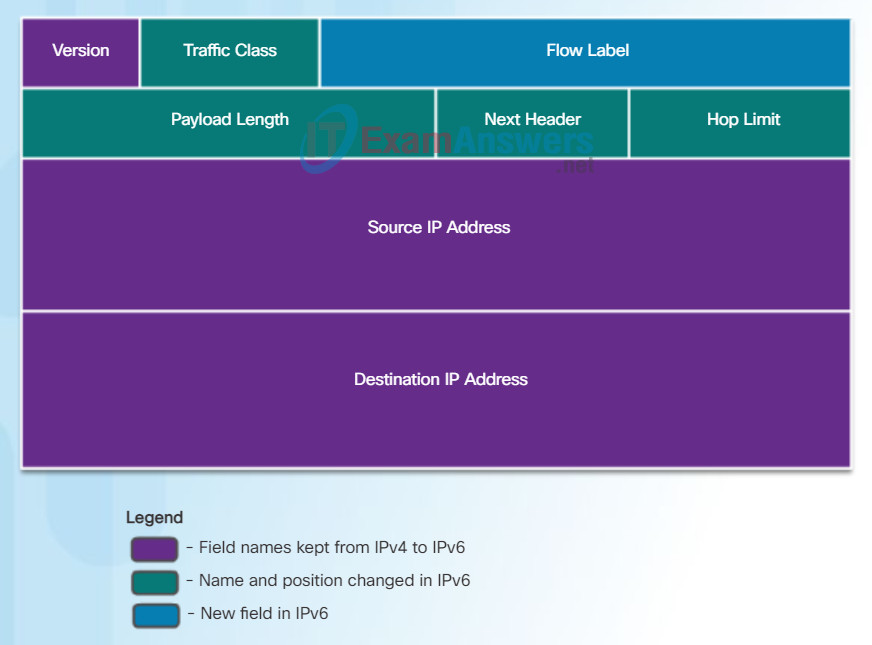
IPv6 Header
The IPv6 simplified header offers several advantages over IPv4 as listed in Figure 3.
6.1.4.4 Network Access for Guests
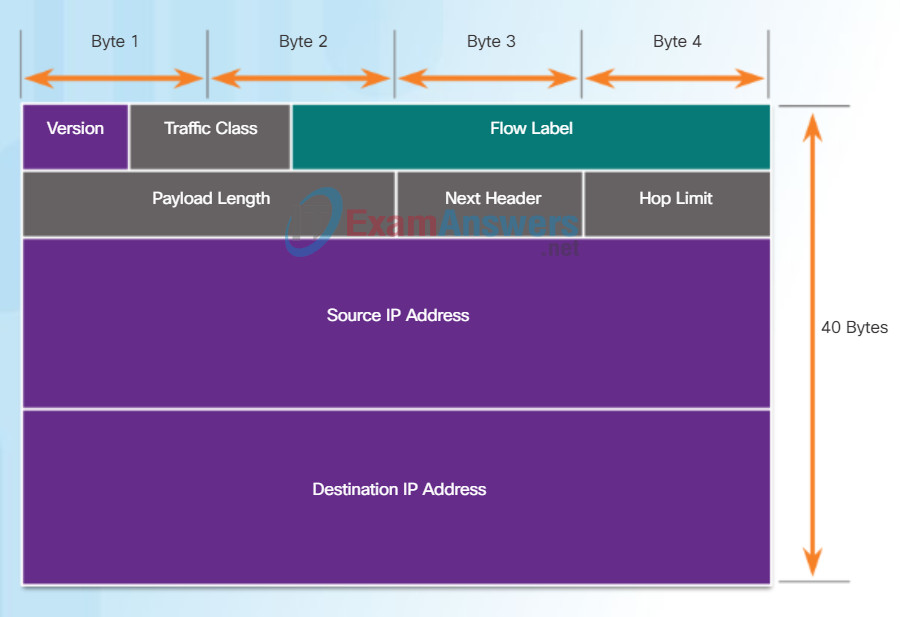
IPv6 Packet Header
The fields in the IPv6 packet header include:
- Version – This field contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0110 that identifies this as an IP version 6 packet.
- Traffic Class – This 8-bit field is equivalent to the IPv4 Differentiated Services (DS) field.
- Flow Label – This 20-bit field suggests that all packets with the same flow label receive the same type of handling by routers.
- Payload Length – This 16-bit field indicates the length of the data portion or payload of the IPv6 packet.
- Next Header – This 8-bit field is equivalent to the IPv4 Protocol field. It indicates the data payload type that the packet is carrying, enabling the network layer to pass the data to the appropriate upper-layer protocol.
- Hop Limit – This 8-bit field replaces the IPv4 TTL field. This value is decremented by a value of 1 by each router that forwards the packet. When the counter reaches 0, the packet is discarded, and an ICMPv6 Time Exceeded message is forwarded to the sending host, indicating that the packet did not reach its destination because the hop limit was exceeded.
- Source IPv6 Address – This 128-bit field identifies the IPv6 address of the sending host.
- Destination IPv6 Address – This 128-bit field identifies the IPv6 address of the receiving host.
An IPv6 packet may also contain extension headers (EH), which provide optional network layer information. Extension headers are optional and are placed between the IPv6 header and the payload. EHs are used for fragmentation, security, to support mobility and more.
Unlike IPv4, routers do not fragment routed IPv6 packets.
Fields in the IPv6 Packet Header
6.1.4.5 Cisco NAC Profiler
6.2 Layer 2 Security Considerations
6.2.1 Layer 2 Security Threats
6.2.1.1 Describe Layer 2 Vulnerabilities
Host Forwarding Decision
Another role of the network layer is to direct packets between hosts. A host can send a packet to:
- Itself – A host can ping itself by sending a packet to a special IPv4 address of 127.0.0.1, which is referred to as the loopback interface. Pinging the loopback interface tests the TCP/IP protocol stack on the host.
- Local host – This is a host on the same local network as the sending host. The hosts share the same network address.
- Remote host – This is a host on a remote network. The hosts do not share the same network address.
Whether a packet is destined for a local host or a remote host is determined by the IPv4 address and subnet mask combination of the source (or sending) device compared to the IPv4 address and subnet mask of the destination device.
In a home or business network, you may have several wired and wireless devices interconnected together using an intermediate device, such as a LAN switch and/or a wireless access point (WAP). This intermediate device provides interconnections between local hosts on the local network. Local hosts can reach each other and share information without the need for any additional devices. If a host is sending a packet to a device that is configured with the same IP network as the host device, the packet is simply forwarded out of the host interface, through the intermediate device, and to the destination device directly.
Of course, in most situations we want our devices to be able to connect beyond the local network segment, such as out to other homes, businesses, and the Internet. Devices that are beyond the local network segment are known as remote hosts. When a source device sends a packet to a remote destination device, then the help of routers and routing is needed. Routing is the process of identifying the best path to a destination. The router connected to the local network segment is referred to as the default gateway.
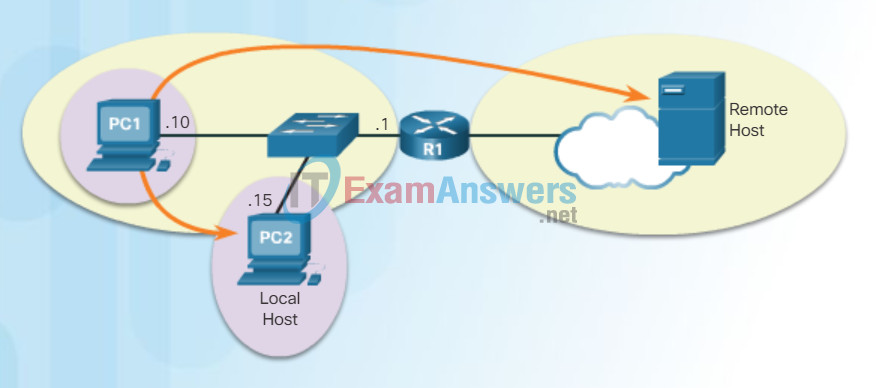
Three Types of Destinations
6.2.1.2 Switch Attack Categories
Default Gateway
The default gateway is the network device that can route traffic to other networks. It is the router that can route traffic out of the local network.
If you use the analogy that a network is like a room, then the default gateway is like a doorway. If you want to get to another room or network you need to find the doorway.
Alternatively, a PC or computer that does not know the IP address of the default gateway is like a person, in a room, that does not know where the doorway is. They can talk to other people in the room or network, but if they do not know the default gateway address, or there is no default gateway, then there is no way out.
The figure lists functions provided by the default gateway.
A Default Gateway …
- Routes traffic to other networks.
- Has a local IP address in the same address range as other hosts on the network.
- Can take data in and forward data out.
6.2.1.3 Activity – Identify Switch Attack Types
Using the Default Gateway
A host’s routing table will typically include a default gateway. The host receives the IPv4 address of the default gateway either dynamically from Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or configured manually. In the figure, PC1 and PC2 are configured with the default gateway’s IPv4 address of 192.168.10.1. Having a default gateway configured creates a default route in the routing table of the PC. A default route is the route or pathway your computer will take when it tries to contact a remote network.
The default route is derived from the default gateway configuration and is placed in the host computer’s routing table. Both PC1 and PC2 will have a default route to send all traffic destined to remote networks to R1.
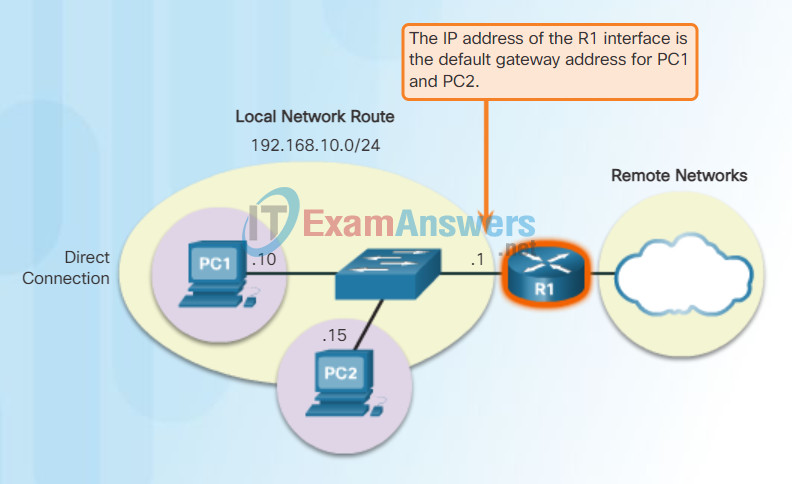
Host Default Gateway
6.2.2 CAM Table Attacks
6.2.2.1 Basic Switch Operation
Router Packet Forwarding Decision
When a host sends a packet to another host, it will use its routing table to determine where to send the packet. If the destination host is on a remote network, the packet is forwarded to the default gateway.
What happens when a packet arrives at the default gateway, which is usually a router? The router looks at its routing table to determine where to forward packets.
The routing table of a router can store information about:
- Directly-connected routes – These routes come from the active router interfaces. Routers add a directly connected route when an interface is configured with an IP address and is activated. Each of the router’s interfaces is connected to a different network segment.
- Remote routes – These routes come from remote networks connected to other routers. Routes to these networks can be manually configured on the local router by the network administrator or dynamically configured by enabling the local router to exchange routing information with other routers using a dynamic routing protocol.
- Default route – Like a host, routers also use a default route as a last resort if there is no other route to the desired network in the routing table.
The figure identifies the directly connected networks and remote networks of router R1.
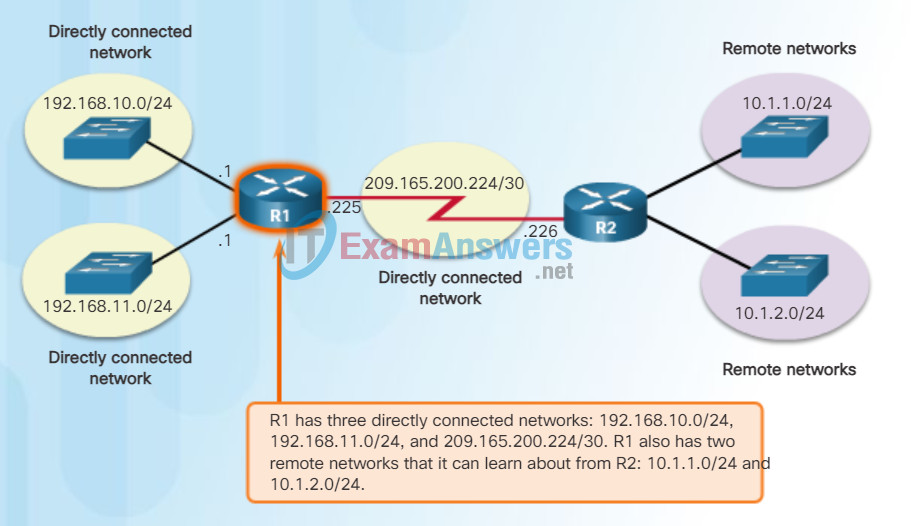
Directly Connected and Remote Network Routes
6.2.2.2 CAM Table Operation Example
IPv4 Router Routing Table
On a Cisco IOS router, the show ip route command can be used to display the router’s IPv4 routing table, as shown in the figure.
In addition to providing routing information for directly-connected networks and remote networks, the routing table also has information on how the route was learned, the trustworthiness and rating of the route, when the route was last updated, and which interface to use to reach the requested destination.
When a packet arrives at the router interface, the router examines the packet header to determine the destination network. If the destination network matches a route in the routing table, the router forwards the packet using the information specified in the routing table. If there are two or more possible routes to the same destination, the metric is used to decide which route appears in the routing table.
The figure shows the routing table of R1 depicted in the network diagram.
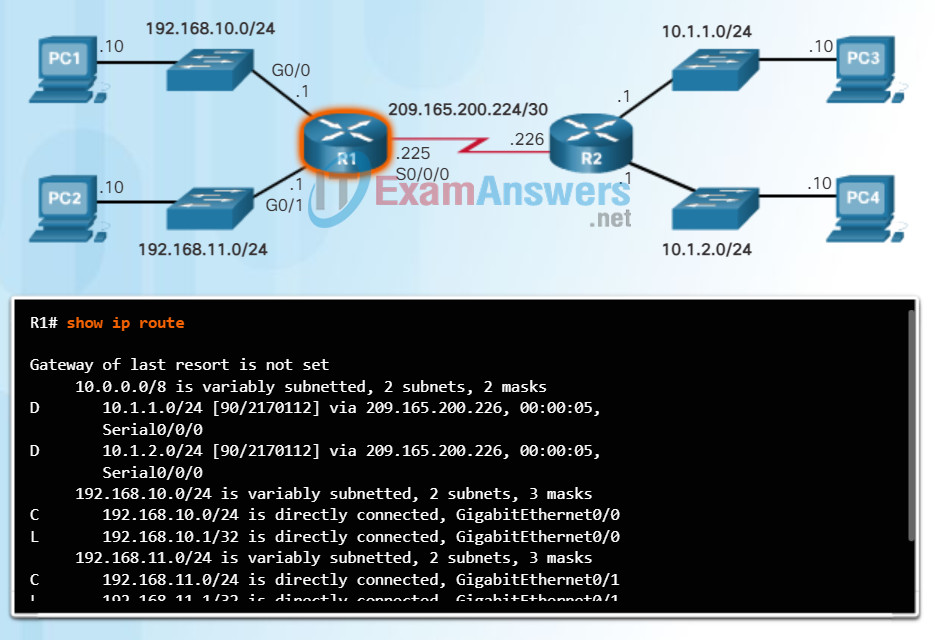
R1 IPv4 Router Routing Table
6.2.2.3 CAM Table Attac
Video Demonstration – Introducing the IPv4 Routing Table
Unlike a host computer’s routing table, there are no column headings identifying the information contained in a router’s routing table. It is important to learn the meaning of the different items included in each entry of the routing table.
6.2.2.4 CAM Table Attack Tools
Directly Connected Routing Table Entries
When a router interface is configured with an IPv4 address, a subnet mask, and is activated, the following two routing table entries are automatically created:
- C – Identifies a directly-connected network. Directly-connected networks are automatically created when an interface is configured with an IP address and activated.
- L – Identifies that this is a local interface. This is the IPv4 address of the interface on the router.
The figure describes the routing table entries on R1 for the directly-connected network 192.168.10.0. These entries were automatically added to the routing table when the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface was configured and activated. Click each plus sign to view more information about directly-connected routing table entries.
Note: Local interface entries did not appear in routing tables prior to IOS Release 15.
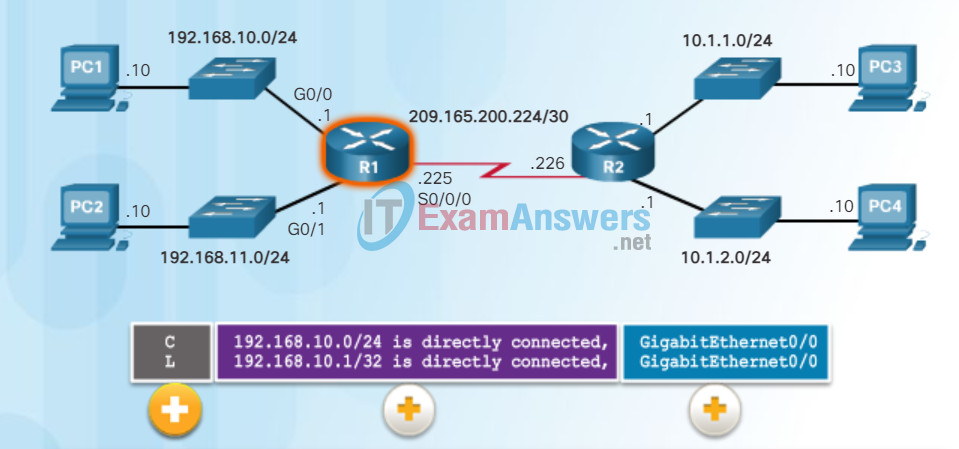
Understanding Local Route Entries
- Route Source: Identifies how the network was learned by the router.
- Destination Network: Identifies the destination network and how it was learned.
- Outgoing Interface: Identifies the exit interface to use to forward a packet toward the final destination.
6.2.3 Mitigating CAM Table Attacks
6.2.3.1 Countermeasure for CAM Table Attacks
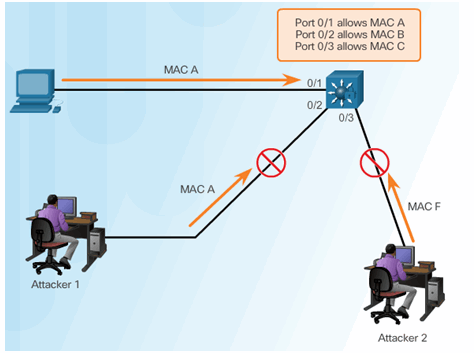
6.2.3.2 Port Security
Enabling Port Security
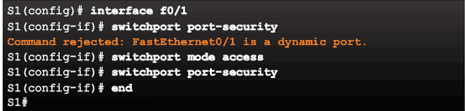
Verifying Port Security

Port Security Options
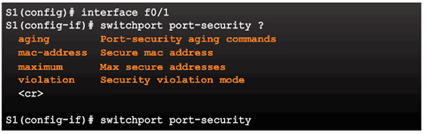
6.2.3.3 Enabling Port Security Options
Setting the Maximum Number of Mac Addresses

Manually Configuring Mac Addresses

Learning Connected Mac Addresses Dynamically

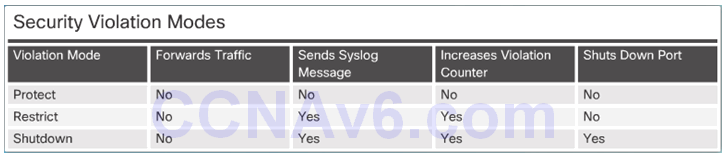
6.2.3.4 Port Security Violations
Security Violation Modes:
- Protect
- Restrict
- Shutdown
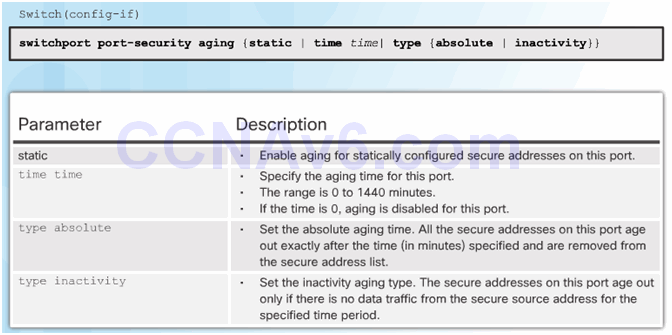
6.2.3.5 Port Security Aging
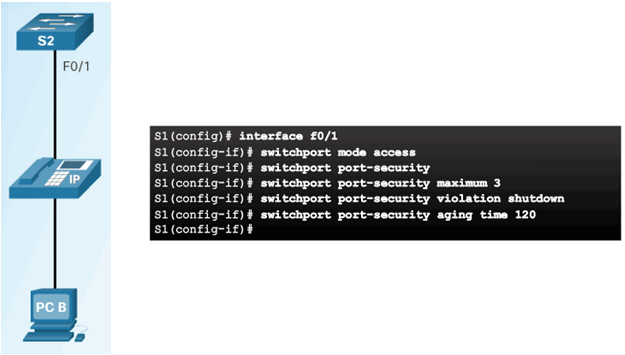
6.2.3.6 Port Security with IP Phones
6.2.3.7 SNMP MAC Address Notification
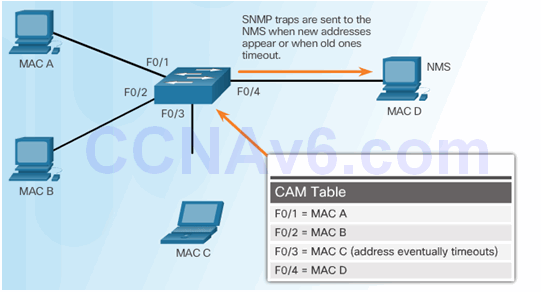
6.2.4 Mitigating VLAN Attacks
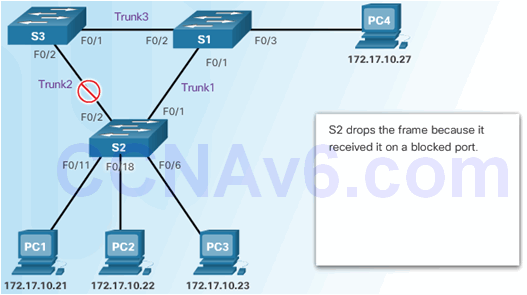
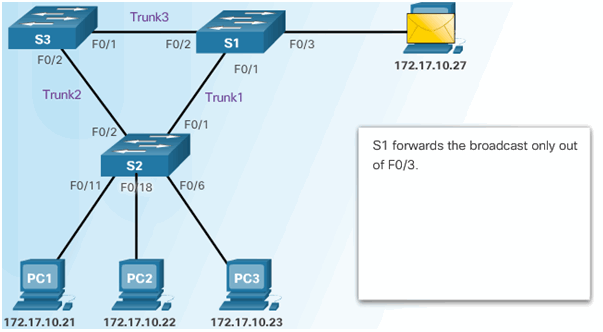
6.2.4.1 VLAN Hopping Attacks
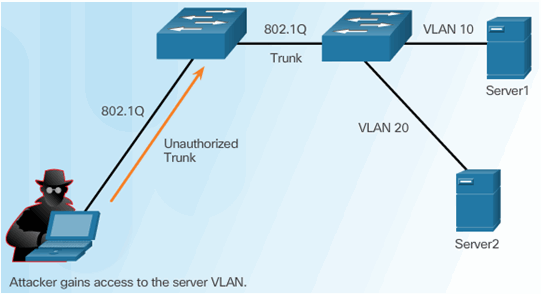
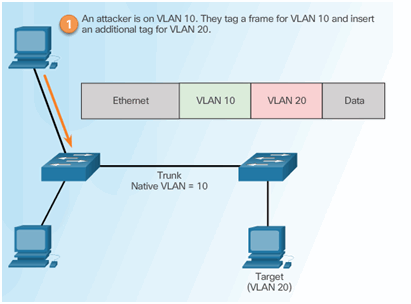
6.2.4.2 VLAN Double-Tagging Attack
Step 1 – Double Tagging Attack
Step 2 – Double Tagging Attack
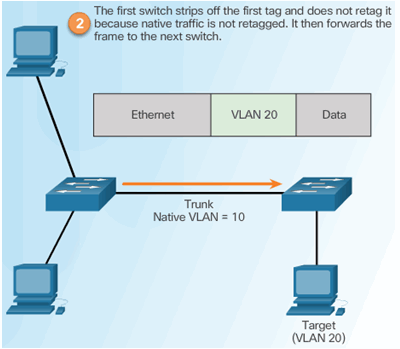
Step 3 – Double Tagging Attack
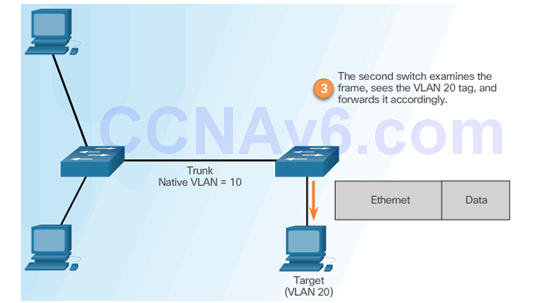
6.2.4.3 Mitigating VLAN Hopping Attacks
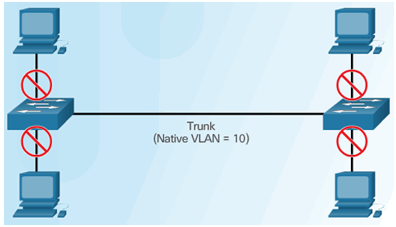
6.2.4.4 PVLAN Edge Feature
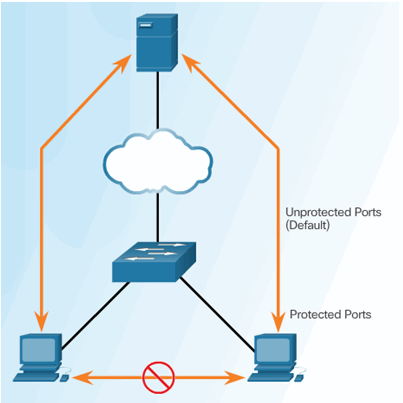
6.2.4.5 PVLAN Edge

6.2.4.6 Private VLANs
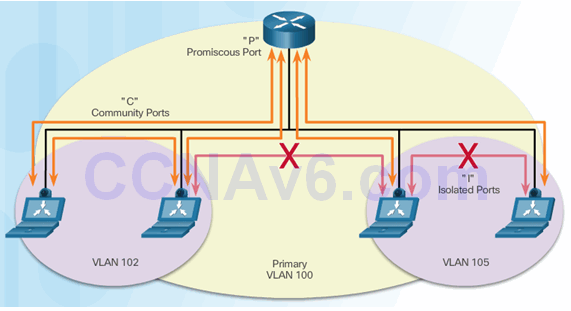
6.2.4.7 Video Demonstration – Private VLAN Tutorial and Demonstration
6.2.5 Mitigating DHCP Attacks
6.2.5.1 DHCP Spoofing Attack
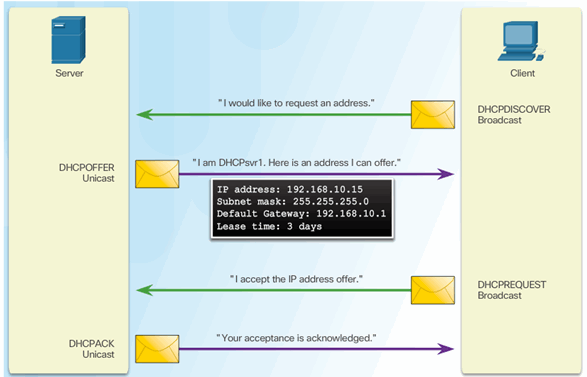
6.2.5.2 DHCP Starvation Attack
Attacker Initiates a Starvation Attack
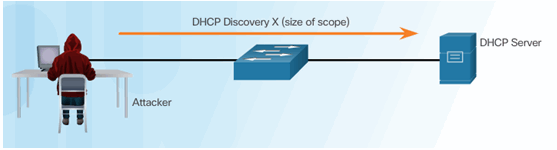
DHCP Server Offers Parameters
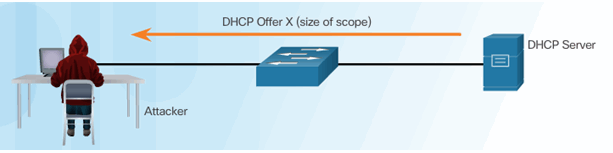
Client Requests all Offers
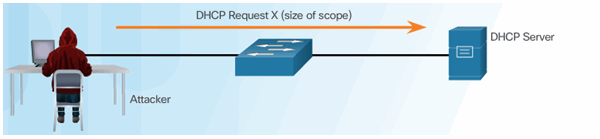
DHCP Server Acknowledges All Requests
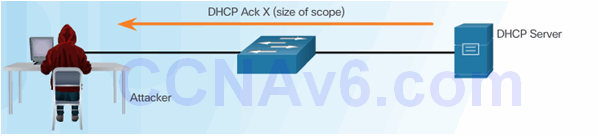
6.2.5.3 Mitigating DHCP Attacks
The switch will deny packets containing specific information:
- Unauthorized DHCP server messages from an untrusted port
- Unauthorized DHCP client messages not adhering to the snooping binding table or rate limits
- DHCP relay-agent packets that include option-82 information on an untrusted port
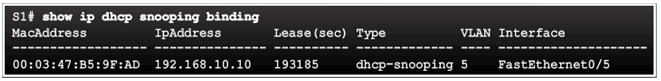
6.2.5.4 Configuring DHCP Snooping
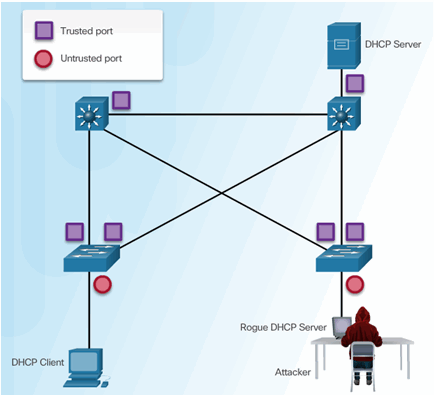
6.2.5.5 Configuring DHCP Snooping Example
DHCP Snooping Reference Topology
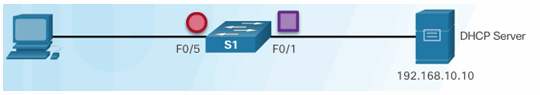
Configuring a Maximum Number of MAC Addresses
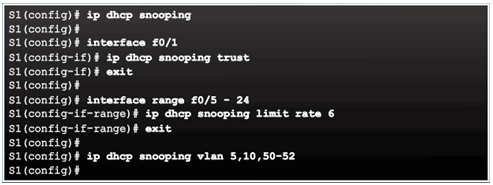
Verifying DHCP Snooping
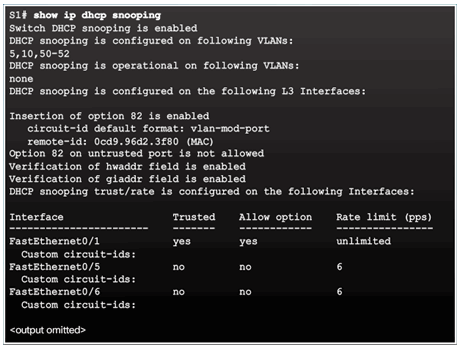
Configuring a Maximum Number of MAC Addresses
6.2.6 Mitigating ARP Attacks
6.2.6.1 ARP Spoofing and ARP Poisoning Attack
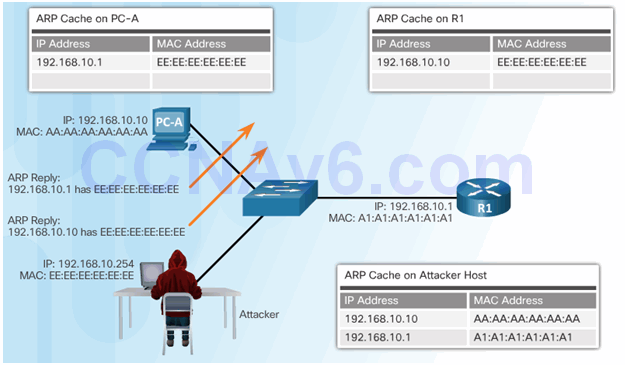
6.2.6.2 Mitigating ARP Attacks
Dynamic ARP Inspection:
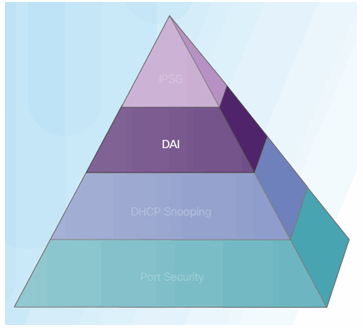
6.2.6.3 Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection
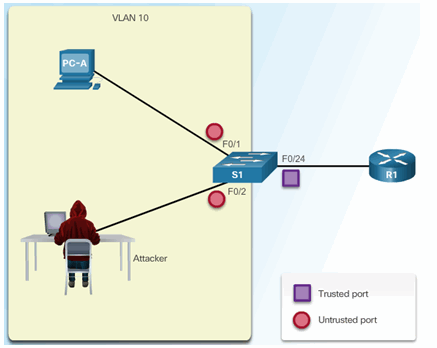
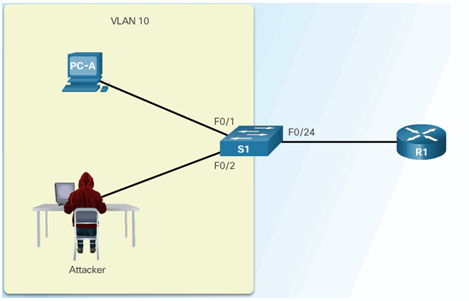
6.2.6.4 Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection Example
ARP Reference Topology
Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection

Checking Source, Destination, and IP
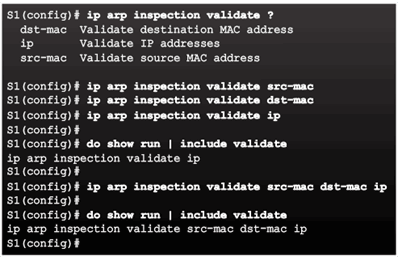
6.2.7 Mitigating Address Spoofing Attacks
6.2.7.1 Address Spoofing Attack
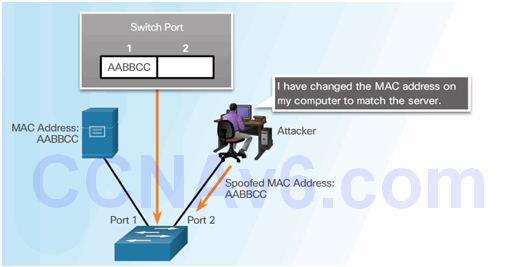
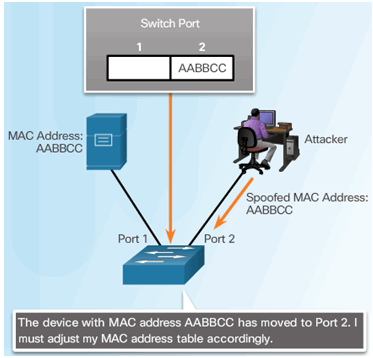
6.2.7.2 Mitigating Address Spoofing Attacks
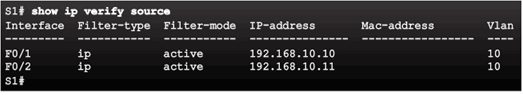
For each untrusted port, there are two possible levels of IP traffic security filtering:
- Source IP address filter
- Source IP and MAC address filter
6.2.7.3 Configuring IP Source Guard
IP Source Guard Reference Topology
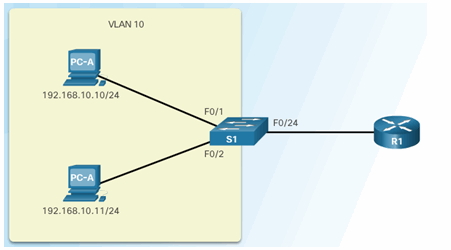
Configuring IP Source Guard

Checking IP Source Guard
6.2.8 Spanning Tree Protocol
6.2.8.1 Introduction to the Spanning Tree Protocol
6.2.8.2 Various Implementations of STP
6.2.8.3 STP Port Roles
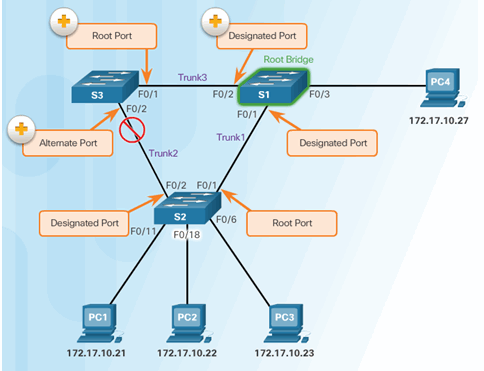
6.2.8.4 STP Root Bridge
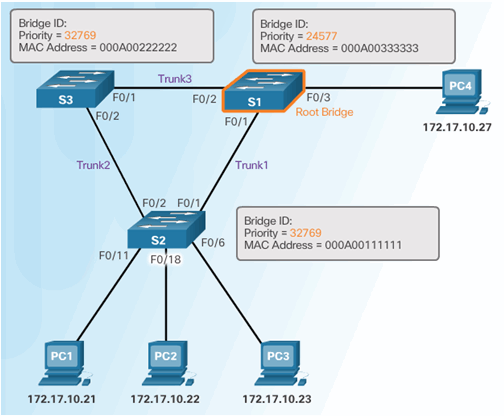
6.2.8.5 STP Path Cost
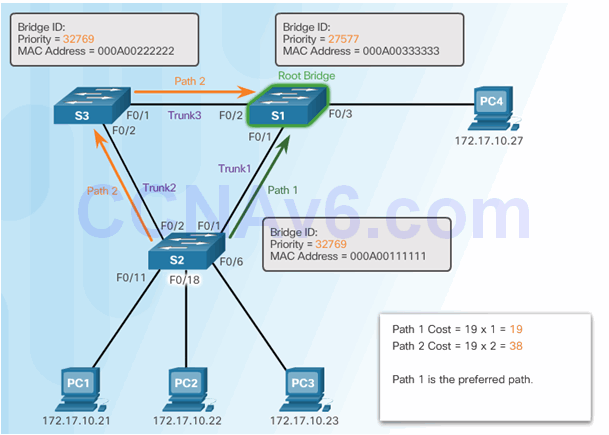
6.2.8.6 802.1D BPDU Frame Format
6.2.8.7 BPDU Propagation and Process
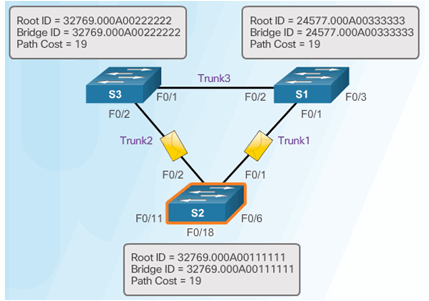
6.2.8.8 Extended System ID
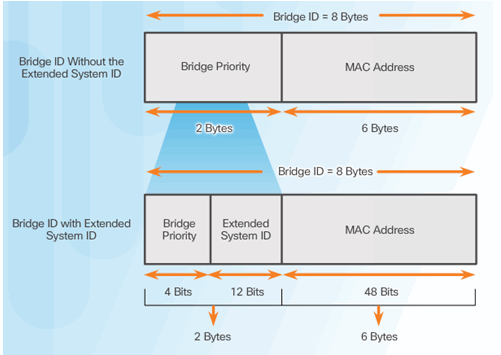
6.2.8.9 Select the Root Bridge
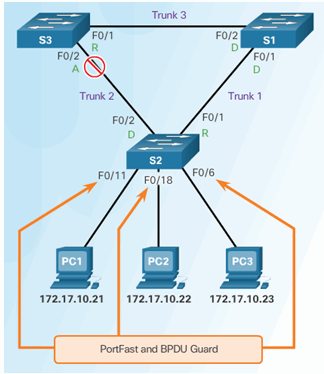
6.2.8.10 Activity – Identify the 802.1D RSTP Port Roles
6.2.8.11 Activity – Troubleshoot STP Configuration Issues
6.2.8.12 Video Demonstration – Observing Spanning Tree Protocol Operation
6.2.9 Mitigating STP Attacks
6.2.9.1 STP Manipulation Attacks
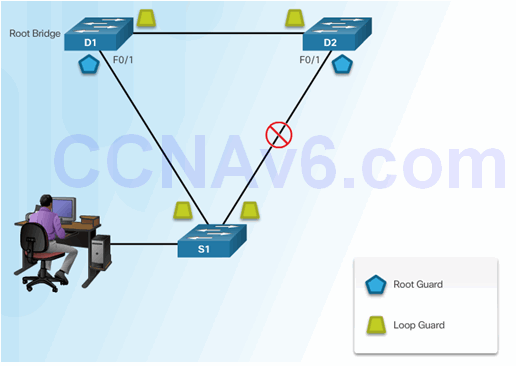
Spoofing the Root Bridge
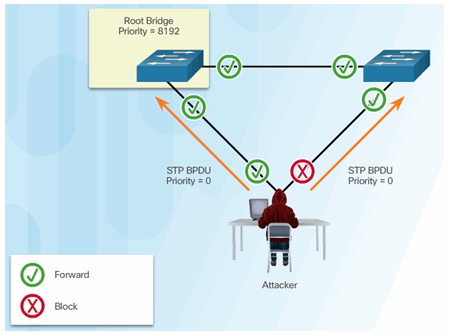
Successful STP Manipulation Attack
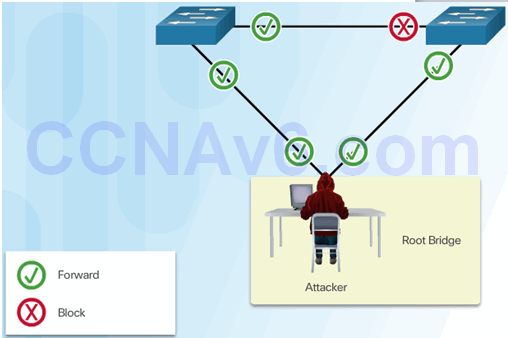
6.2.9.2 Mitigating STP Attacks
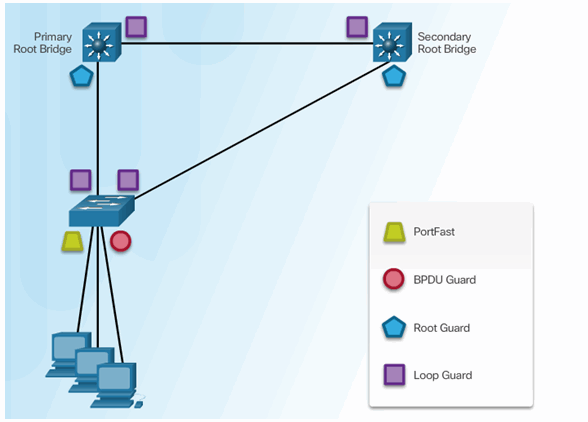
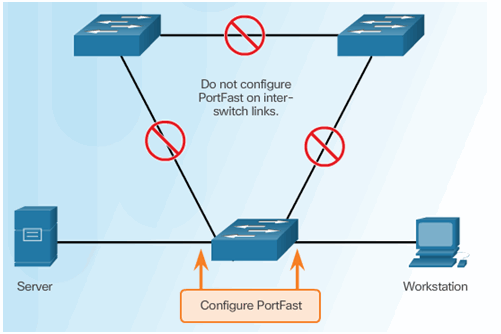
6.2.9.3 Configuring PortFast
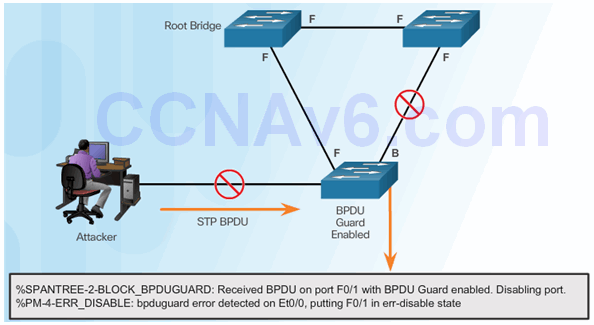
6.2.9.4 Configuring BPDU Guard
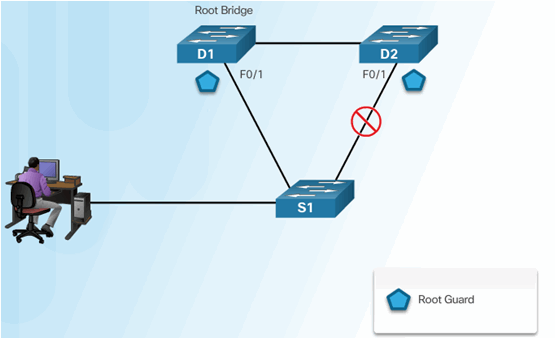
6.2.9.5 Configuring Root Guard
6.2.9.6 Configuring Loop Guard
6.3 Summary
6.3.1 Conclusion
6.3.1.1 Lab – Securing Layer 2 Switche
6.3.1.1 Lab – Securing Layer 2 Switches
A Router is a Computer
There are many types of infrastructure routers available. In fact, Cisco routers are designed to address the needs of many different types of businesses and networks:
- Branch – Teleworkers, small businesses, and medium-size branch sites. Includes Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISR) G2 (2nd generation).
- WAN – Large businesses, organizations, and enterprises. Includes the Cisco Catalyst Series Switches and the Cisco Aggregation Services Routers (ASR).
- Service Provider – Large service providers. Includes Cisco ASR, Cisco CRS-3 Carrier Routing System, and 7600 Series routers.
The focus of CCNA certification is on the branch family of routers. The figure displays the Cisco 1900, 2900, and 3900 G2 Integrated Services Routers.
Regardless of their function, size or complexity, all router models are essentially computers. Just like computers, tablets, and smart devices, routers also require:
- Central processing units (CPU).
- Operating systems (OS).
- Memory consisting of random-access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), nonvolatile random-access memory (NVRAM), and flash.’

Cisco Integrated Service Routers
6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer – Layer 2 Security
6.3.1.2 Packet Tracer – Layer 2 Security
Router CPU and OS
Like all computers, tablets, gaming consoles, and smart devices, Cisco devices require a CPU to execute OS instructions, such as system initialization, routing functions, and switching functions.
The highlighted component in the figure is the CPU of a Cisco 1941 router with the heatsink attached. The heatsink helps dissipate the heat generated by the CPU.
The CPU requires an OS to provide routing and switching functions. The Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) is the system software used for most Cisco devices regardless of the size and type of the device. It is used for routers, LAN switches, small wireless access points, large routers with dozens of interfaces, and many other devices.
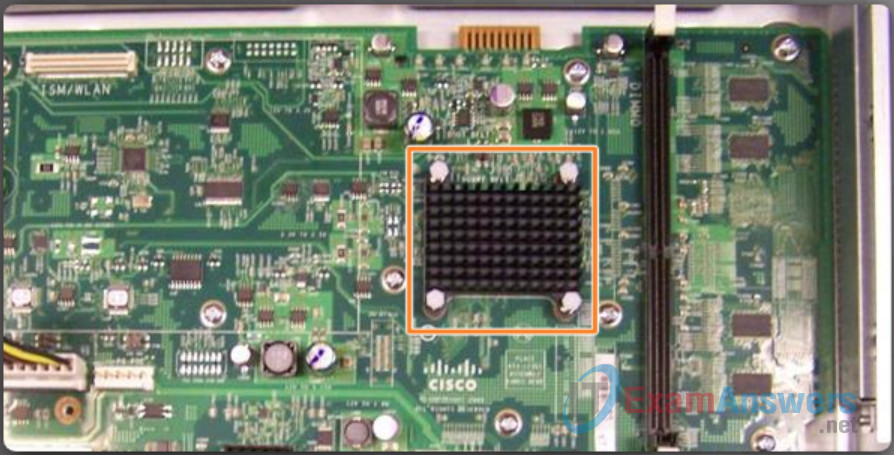

Router CPU
6.3.1.3 Packet Tracer – Layer 2 VLAN Security
6.3.1.3 Packet Tracer – Layer 2 VLAN Security
Router Memory
A router has access to volatile or non-volatile memory storage. Volatile memory requires continual power to maintain its information. When the router is powered down or restarted, the content is erased and lost. Non-volatile memory retains its information even when a device is rebooted.
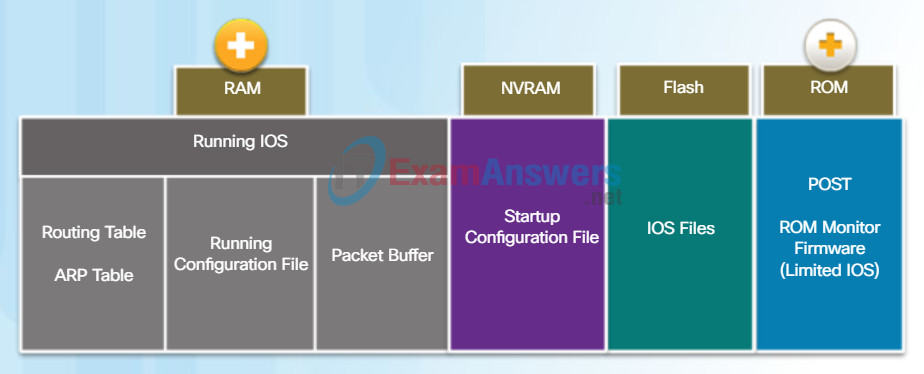
Specifically, a Cisco router uses four types of memory:
- RAM – This is volatile memory used in Cisco routers to store applications, processes, and data needed to be executed by the CPU. Cisco routers use a fast type of RAM called synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM). Click RAM in the figure to view more information.
- ROM – This non-volatile memory is used to store crucial operational instructions and a limited IOS. Specifically, ROM is firmware embedded on an integrated circuit inside the router which can only be altered by Cisco. Click ROM in the figure to view more information.
- NVRAM – This is non-volatile memory is used as the permanent storage for the startup configuration file (startup-config).
- Flash – This non-volatile computer memory used as permanent storage for the IOS and other system related files such as log files, voice configuration files, HTML files, backup configurations, and more. When a router is rebooted, the IOS is copied from flash into RAM.
All router platforms have default settings and components. For instance, the Cisco 1941 comes with 512 MB of SDRAM but is upgradable up to 2.0 GB. The Cisco 1941 routers also come with 256 MB of flash but are upgradable using two external Compact Flash slots. Each slot can support high-speed storage cards upgradable to 4GB. Click here to learn more about the Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Router.
Router Memory
RAM
RAM uses the following applications and processes:
- The IOS image and running configuration file
- The routing table used to determine the best path to use to forward packets
- The ARP cache used to map IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses
- The Packet buffer used to temporarily store packets before forwarding to the destination
ROM
ROM stores the following:
- Bootup information that provides the startup instructions
- Power-on self-test (POST) that tests all the hardware components
- Limited IOS to provide a backup version of the IOS. It is used for loading a full feature IOS when it has been deleted or corrupted.
6.3.1.4 Chapter 6: Securing the Local Area Network
Inside a Router
Although there are several different types and models of routers, every router has the same general hardware components.
The figure shows the inside of a Cisco 1841 first generation ISR. Click the components to see a brief description of each. The figure also includes images of other components found in a router, such as the power supply, cooling fan, heat shields, and an advanced integration module (AIM), which are beyond the scope of this chapter.
Note: A networking professional should be familiar with and understand the function of the main internal components of a router, rather than the exact location of those components inside a specific router. Depending on the model, those components are located in different places inside the router.
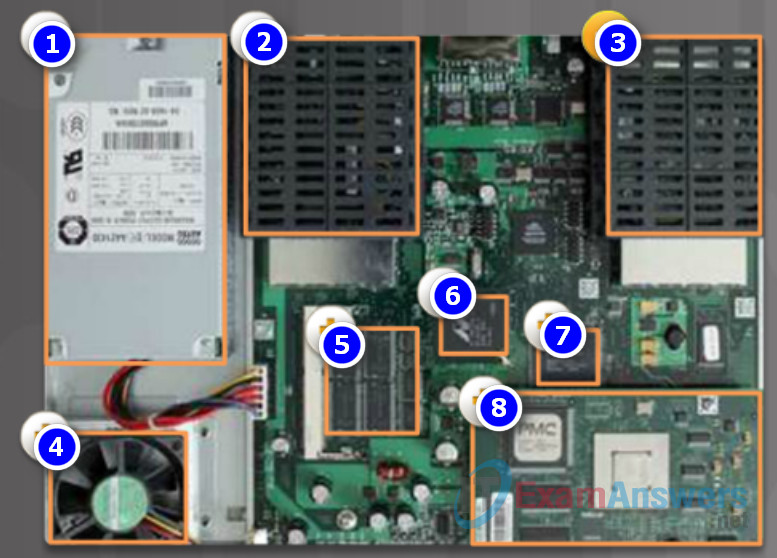
- Power Supply
- Shield for WAN interface card WIC or high-speed WIC (HWIC)
- Shield for WAN interface card WIC or high-speed WIC (HWIC)
- Fan
- Synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM) used for holding the running configuration and routing tables, and for supporting packet buffering.
- Nonvolatile RAM (NVRAM) and boot flash memory used for storing the ROMMON boot code as well as NVRAM data.
- CPU
- Advanced Integration Module (AIM) option that offloads processor-intensive functions such as encryption from the main CPU.
