Module Group Exam 2 – Network Defense (NetDef) Module 4 – 8 Group Exam – Checkpoint Exam: Firewalls, Cryptography, and Cloud Security
How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
1. Refer to the exhibit. An administrator has configured a standard ACL on R1 and applied it to interface serial 0/0/0 in the outbound direction. What happens to traffic leaving interface serial 0/0/0 that does not match the configured ACL statements?

- The resulting action is determined by the destination IP address and port number.
- The resulting action is determined by the destination IP address.
- The traffic is dropped.
- The source IP address is checked and, if a match is not found, traffic is routed out interface serial 0/0/1.
Explanation: Any traffic that does not match one of the statements in an ACL has the implicit deny applied to it, which means the traffic is dropped.
2. When an inbound Internet-traffic ACL is being implemented, what should be included to prevent the spoofing of internal networks?
- ACEs to prevent broadcast address traffic
- ACEs to prevent traffic from private address spaces
- ACEs to prevent ICMP traffic
- ACEs to prevent SNMP traffic
- ACEs to prevent HTTP traffic
Explanation: Common ACEs to assist with antispoofing include blocking packets that have a source address in the 127.0.0.0/8 range, any private address, or any multicast addresses. Furthermore, the administrator should not allow any outbound packets with a source address other than a valid address that is used in the internal networks of the organization.
3. Refer to the exhibit. What is the result of adding the established argument to the end of the ACE?

- 192.168.254.0 /23 traffic is allowed to reach any network.
- Any IP traffic is allowed to reach the 192.168.254.0 255.255.254.0 network as long as it is in response to an originated request.
- Any traffic is allowed to reach the 192.168.254.0 255.255.254.0 network.
- Any TCP traffic is allowed to reach the 192.168.254.0 255.255.254.0 network if it is in response to an originated request.
Explanation: The established argument allows TCP return traffic from established connections to be sent on an outgoing interface to a network.
4. What single access list statement matches all of the following networks?
- 192.168.16.0
- 192.168.17.0
- 192.168.18.0
- 192.168.19.0
- access-list 10 permit 192.168.16.0 0.0.0.255
- access-list 10 permit 192.168.16.0 0.0.3.255
- access-list 10 permit 192.168.16.0 0.0.15.255
- access-list 10 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.15.255
Explanation: The ACL statement access-list 10 permit 192.168.16.0 0.0.3.255 will match all four network prefixes. All four prefixes have the same 22 high order bits. These 22 high order bits are matched by the network prefix and wildcard mask of 192.168.16.0 0.0.3.255.
5. Refer to the exhibit. The IPv6 access list LIMITED_ACCESS is applied on the S0/0/0 interface of R1 in the inbound direction. Which IPv6 packets from the ISP will be dropped by the ACL on R1?
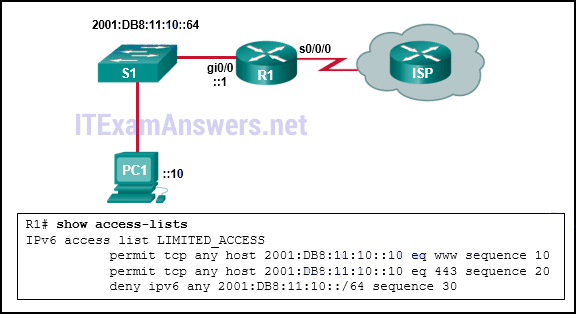
- neighbor advertisements that are received from the ISP router
- HTTPS packets to PC1
- ICMPv6 packets that are destined to PC1
- packets that are destined to PC1 on port 80
Explanation: The access list LIMITED_ACCESS will block ICMPv6 packets from the ISP. Both port 80, HTTP traffic, and port 443, HTTPS traffic, are explicitly permitted by the ACL. The neighbor advertisements from the ISP router are implicitly permitted by the implicit permit icmp any any nd-na statement at the end of all IPv6 ACLs.
6. What are two characteristics of a stateful firewall? (Choose two.)
- uses static packet filtering techniques
- uses connection information maintained in a state table
- prevents Layer 7 attacks
- analyzes traffic at Layers 3, 4 and 5 of the OSI model
- uses complex ACLs which can be difficult to configure
Explanation: Stateful firewalls are the most versatile and the most common firewall technologies in use. Stateful firewalls provide stateful packet filtering by using connection information maintained in a state table. Stateful filtering is a firewall architecture that is classified at the network layer. It also analyzes traffic at OSI Layers 4 and 5. Stateful firewalls cannot prevent application layer attacks because they do not examine the actual contents of an HTTP connection.
7. How does a firewall handle traffic when it is originating from the public network and traveling to the DMZ network?
- Traffic that is originating from the public network is inspected and selectively permitted when traveling to the DMZ network.
- Traffic that is originating from the public network is usually forwarded without inspection when traveling to the DMZ network.
- Traffic that is originating from the public network is usually blocked when traveling to the DMZ network.
- Traffic that is originating from the public network is usually permitted with little or no restriction when traveling to the DMZ network.
Explanation: Traffic originating from the public network and traveling toward the DMZ is selectively permitted and inspected. This type of traffic is typically email, DNS, HTTP, or HTTPS traffic. Return traffic from the DMZ to the public network is dynamically permitted.
8. Which type of firewall is commonly part of a router firewall and allows or blocks traffic based on Layer 3 and Layer 4 information?
- stateless firewall
- proxy firewall
- stateful firewall
- application gateway firewall
Explanation: A stateless firewall uses a simple policy table look-up that filters traffic based on specific criteria. These firewalls are usually part of a router firewall. They permit or deny traffic based on Layer 3 and Layer 4 information.
9. What is one limitation of a stateful firewall?
- not as effective with UDP- or ICMP-based traffic
- poor log information
- cannot filter unnecessary traffic
- weak user authentication
Explanation: Limitations of stateful firewalls include the following:
Stateful firewalls cannot prevent application layer attacks.
Protocols such as UDP and ICMP are not stateful and do not generate information needed for a state table.
An entire range of ports must sometimes be opened in order to support specific applications that open multiple ports.
Stateful firewalls lack user authentication.
10. How does a firewall handle traffic when it is originating from the private network and traveling to the DMZ network?
- The traffic is selectively denied based on service requirements.
- The traffic is selectively permitted and inspected.
- The traffic is usually blocked.
- The traffic is usually permitted with little or no restrictions.
Explanation: Traffic originating from the private network is inspected as it travels toward the public or DMZ network. This traffic is permitted with little or no restriction. Inspected traffic returning from the DMZ or public network to the private network is permitted.
11. When a Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall is being configured, which three actions can be applied to a traffic class? (Choose three.)
- reroute
- queue
- drop
- pass
- shape
- inspect
Explanation: The inspect CCP action is similar to the classic firewall ip inspect command in that it inspects traffic going through the firewall and allowing return traffic that is part of the same flow to pass through the firewall. The drop action is similar to the deny parameter in an ACL. This action drops whatever traffic fits the defined policy. The pass action is similar to a permit ACL statement–traffic is allowed to pass through because it met the criteria of the defined policy statement.
12. Which two statements describe the two configuration models for Cisco IOS firewalls? (Choose two.)
- Both IOS Classic Firewall and ZPF models require ACLs to define traffic filtering policies.
- ZPF must be enabled in the router configuration before enabling an IOS Classic Firewall.
- The IOS Classic Firewall and ZPF cannot be combined on a single interface.
- IOS Classic Firewalls and ZPF models can be enabled on a router concurrently.
- IOS Classic Firewalls must be enabled in the router configuration before enabling ZPF.
Explanation: There are two configuration models for Cisco IOS Firewalls, IOS Classic Firewalls and zone-based policy firewalls (ZPF). Both configuration models can be enabled concurrently on a router but they cannot be combined on a single interface. One benefit of using ZPF is that ZPF is not dependent on ACLs.
13. What are two benefits of using a ZPF rather than a Classic Firewall? (Choose two.)
- With ZPF, the router will allow packets unless they are explicitly blocked.
- ZPF policies are easy to read and troubleshoot.
- Multiple inspection actions are used with ZPF.
- The ZPF is not dependent on ACLs.
- ZPF allows interfaces to be placed into zones for IP inspection.
Explanation: There are several benefits of a ZPF:
– It is not dependent on ACLs.
– The router security posture is to block unless explicitly allowed.
– Policies are easy to read and troubleshoot with C3PL.
– One policy affects any given traffic, instead of needing multiple ACLs and inspection actions.
In addition, an interface cannot be simultaneously configured as a security zone member and for IP inspection.
14. When using Cisco IOS zone-based policy firewall, where is the inspection policy applied?
- to a zone pair
- to a global service policy
- to a zone
- to an interface
Explanation: After configuring the firewall policy, apply the policy to traffic that would flow between a pair of zones. Use the zone-pair security command in global configuration mode.
15. Which zone-based policy firewall zone is system-defined and applies to traffic destined for the router or originating from the router?
- inside zone
- outside zone
- system zone
- local zone
- self zone
Explanation: Zone-based policy firewalls typically have the private (internal or trusted) zone, the public (external or untrusted) zone, and the default self zone, which does not require any interfaces. The private or internal zone is commonly used for internal LANs. The public zone would include the interfaces that connect to an external (outside the business) interface.
16. Which cloud security domain covers cloud-specific aspects of infrastructure security and foundations for operating securely in the cloud?
- Application Security
- Data Security and Encryption
- Management Plane and Business Continuity
- Infrastructure Security
Explanation: The Security Guidance for Critical Areas of Focus in Cloud Computing v4 document developed by the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) covers 14 domains of cloud security. Some of these domains are:
- Infrastructure Security – describes cloud-specific aspects of infrastructure security and the foundation for operating securely in the cloud.
- Data Security and Encryption – describes those controls related to securing the data itself, of which encryption is one of the most important.
- Application Security – provides guidance on how to securely build and deploy applications in cloud computing environments, specifically for PaaS and IaaS.
- Management Plane and Business Continuity – describes the need to secure the cloud computing management plane and business continuity and disaster recovery procedures.
17. Which technique can be used to leverage virtual network topologies to run smaller and more isolated networks without incurring additional hardware costs?
- shadow IT
- microsegmentation
- fog computing
- edge computing
Explanation: Microsegmentation (also referred to as hypersegregation) leverages virtual network topologies to run smaller and more isolated networks without incurring additional hardware costs. Microsegmentation techniques allow for more granular control of security for traffic and workflows within the cloud.
18. Which algorithm is used with symmetric encryption to provide confidentiality?
Explanation: Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a symmetric encryption algorithm. MD5 is a hashing algorithm while RSA and ECC are asymmetric encryption algorithms.
19. In which phase of application development is new software verified to run under the required security settings?
- testing
- staging
- developing
- provisioning
Explanation: In the staging phase developers test the application in a staging environment to verify that software runs under the required security settings.
20. What is the description of VM sprawl?
- The demand for VMs is greater than the ability to create VMs.
- When a process breaks out of the VM and interacts with the host operating system.
- VMs are spread over too large of a geographic area.
- There are more VMs than can be effectively managed.
Explanation: VM Sprawl occurs when an organization has more VMs on the network than it can effectively control and manage.
21. Which measure can a security analyst take to perform effective security monitoring against network traffic encrypted by SSL technology?
- Use a Syslog server to capture network traffic.
- Require remote access connections through IPsec VPN.
- Deploy a Cisco ASA.
- Deploy a Cisco SSL Appliance.
Explanation: Deploy a Cisco SSL Appliance to decrypt SSL traffic and send it to intrusion prevention system (IPS) appliances to identify risks normally hidden by SSL.
22. What technology has a function of using trusted third-party protocols to issue credentials that are accepted as an authoritative identity?
- hashing algorithms
- PKI certificates
- symmetric keys
- digital signatures
Explanation: Digital certificates are used to prove the authenticity and integrity of PKI certificates, but a PKI Certificate Authority is a trusted third-party entity that issues PKI certificates. PKI certificates are public information and are used to provide authenticity, confidentiality, integrity, and nonrepudiation services that can scale to large requirements.
23. Match the description with the correct term.
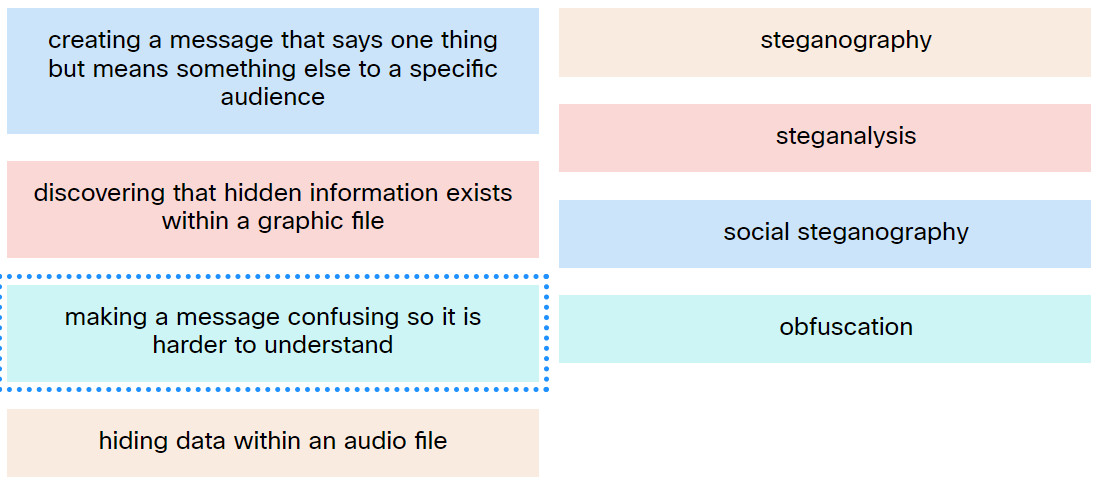
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
| Creating a message that says one thing but means something else to a specific audience |
Social steganography |
| Making a message confusing so it is harder to understand |
Obfuscation |
| Hiding data within an audio file |
Steganography |
| Discovering that hidden information exists within a graphic file |
Steganalysis |
24. Which method tries all possible passwords until a match is found?
- cloud
- cryptographic
- birthday
- brute force
- rainbow tables
- dictionary
Explanation: Two common methods of cracking hashes are dictionary and brute force. Given time, the brute force method will always crack a password.
25. An IT enterprise is recommending the use of PKI applications to securely exchange information between the employees. In which two cases might an organization use PKI applications to securely exchange information between users? (Choose two.)
- file and directory access permission
- HTTPS web service
- local NTP server
- 802.1x authentication
- FTP transfers
Explanation: The Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a third party-system referred to as a certificate authority or CA. The PKI is the framework used to securely exchange information between parties. Common PKI applications are as follows:
SSL/TLS certificate-based peer authentication
Secure network traffic using IPsec VPNs
HTTPS Web traffic
Control access to the network using 802.1x authentication
Secure email using the S/MIME protocol
Secure instant messaging
Approve and authorize applications with Code Signing
Protect user data with the Encryption File System (EFS)
Implement two-factor authentication with smart cards
Securing USB storage devices




