Objectives
The objective of the lab is to explore some of the functions of PowerShell.
Background / Scenario
PowerShell is a powerful automation tool. It is both a command console and a scripting language. In this lab, you will use the console to execute some of the commands that are available in both the command prompt and PowerShell. PowerShell also has functions that can create scripts to automate tasks and work together with the Windows Operating System.
Required Resources
- 1 Windows PC with PowerShell installed and Internet access
Step 1: Access PowerShell console.
a. Click Start. Search and select powershell.
b. Click Start. Search and select command prompt.
Step 2: Explore Command Prompt and PowerShell commands.
a. Enter dir at the prompt in both windows.
What are the outputs to the dir command?
Both windows provide a list of subdirectories and files, and associated information like type, file size, date and time of last write. In PowerShell, the attributes/modes are also shown.
b. Try another command that you have used in the command prompt, such as ping, cd, and ipconfig. What are the results?
The output in both windows are similar.
Step 3: Explore cmdlets.
a. PowerShell commands, cmdlets, are constructed in the form of verb-noun string. To identify the PowerShell command to list the subdirectories and files in a directory, enter Get-Alias dir at the PowerShell prompt.
PS C:\Users\CyberOpsUser> Get-Alias dir CommandType Name Version Source ----------- ---- ------- ------ Alias dir -> Get-ChildItem
What is the PowerShell command for dir?
Get-ChildItem
b. For more detailed information about cmdlets, navigate to https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee332526.aspx.
c. Close the Command Prompt window when done.
Step 4: Explore the netstat command using PowerShell.
a. At the PowerShell prompt, enter netstat -h to see the options available for the netstat command.
PS C:\Users\CyberOpsUser> netstat -h
Displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections.
NETSTAT [-a] [-b] [-e] [-f] [-n] [-o] [-p proto] [-r] [-s] [-x] [-t] [interval]
-a Displays all connections and listening ports.
-b Displays the executable involved in creating each connection or
listening port. In some cases well-known executables host
multiple independent components, and in these cases the
sequence of components involved in creating the connection
or listening port is displayed. In this case the executable
name is in [] at the bottom, on top is the component it called,
and so forth until TCP/IP was reached. Note that this option
can be time-consuming and will fail unless you have sufficient
permissions.
<some output omitted>
b. To display the routing table with the active routes, enter netstat -r at the prompt.
PS C:\Users\CyberOpsUser> netstat -r
===========================================================================
Interface List
3...08 00 27 a0 c3 53 ......Intel(R) PRO/1000 MT Desktop Adapter
10...08 00 27 26 c1 78 ......Intel(R) PRO/1000 MT Desktop Adapter #2
1...........................Software Loopback Interface 1
===========================================================================
IPv4 Route Table
===========================================================================
Active Routes:
Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.5 25
127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
127.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
169.254.0.0 255.255.0.0 On-link 169.254.181.151 281
169.254.181.151 255.255.255.255 On-link 169.254.181.151 281
169.254.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 169.254.181.151 281
192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 On-link 192.168.1.5 281
192.168.1.5 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.5 281
192.168.1.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.5 281
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 192.168.1.5 281
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 On-link 169.254.181.151 281
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 127.0.0.1 331
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 192.168.1.5 281
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 On-link 169.254.181.151 281
===========================================================================
Persistent Routes:
None
IPv6 Route Table
===========================================================================
Active Routes:
If Metric Network Destination Gateway
1 331 ::1/128 On-link
3 281 fe80::/64 On-link
10 281 fe80::/64 On-link
10 281 fe80::408b:14a4:7b64:b597/128
On-link
3 281 fe80::dd67:9e98:9ce0:51e/128
On-link
1 331 ff00::/8 On-link
3 281 ff00::/8 On-link
10 281 ff00::/8 On-link
===========================================================================
Persistent Routes:
None
What is the IPv4 gateway?
Answers will vary. The gateway is 192.168.1.1 in this example.
c. Open and run a second PowerShell with elevated privileges. Click Start. Search for PowerShell and right-click Windows PowerShell and select Run as administrator. Click Yes to allow this app to make changes to your device.

d. The netstat command can also display the processes associated with the active TCP connections. Enter the netstat -abno at the prompt.
PS C:\Windows\system32> netstat -abno Active Connections Proto Local Address Foreign Address State PID TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 756 RpcSs [svchost.exe] TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4 Can not obtain ownership information TCP 0.0.0.0:49664 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 444 Can not obtain ownership information TCP 0.0.0.0:49665 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 440 Schedule [svchost.exe] TCP 0.0.0.0:49666 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 304 EventLog [svchost.exe] TCP 0.0.0.0:49667 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1856 [spoolsv.exe] TCP 0.0.0.0:49668 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 544 <some output omitted>
e. Open the Task Manager. Navigate to the Details tab. Click the PID heading so the PID are in order.
f. Select one of the PIDs from the results of netstat -abno. PID 756 is used in this example.
g. Locate the selected PID in the Task Manager. Right-click the selected PID in the Task Manager to open the Properties dialog box for more information.
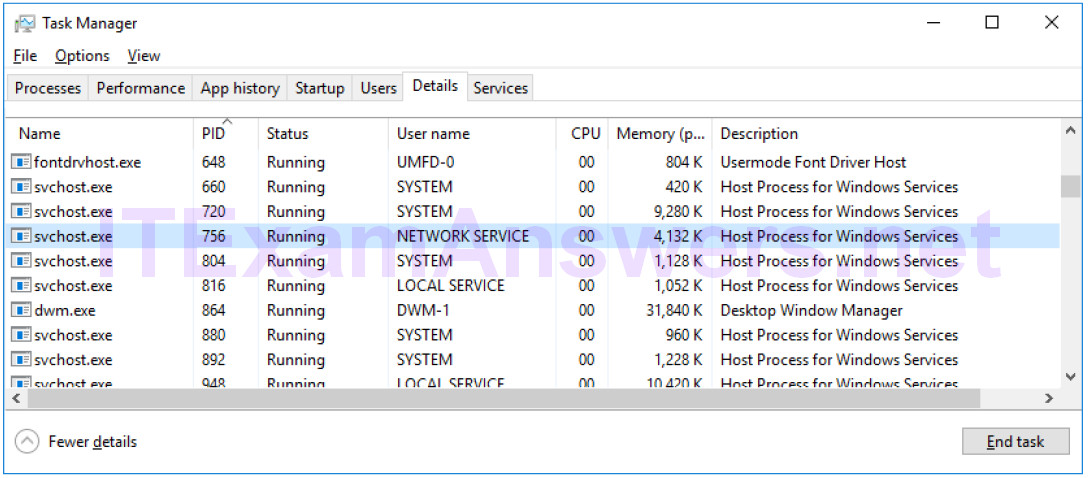
What information can you get from the Details tab and the Properties dialog box for your selected PID?
PID 756 is associated with svchost.exe process. The user for this process is NETWORK SERVICE and it is using 4132K of memory.
Step 5: Empty recycle bin using PowerShell.
PowerShell commands can simplify management of a large computer network. For example, if you wanted to implement a new security solution on all servers in the network you could use a PowerShell command or script to implement and verify that the services are running. You can also run PowerShell commands to simplify actions that would take multiple steps to execute using Windows graphical desktop tools.
a. Open the Recycle Bin. Verify that there are items that can be deleted permanently from your PC. If not, restore those files.
b. If there are no files in the Recycle Bin, create a few files, such as text file using Notepad, and place them into the Recycle Bin.
c. In a PowerShell console, enter clear-recyclebin at the prompt.
PS C:\Users\CyberOpsUser> clear-recyclebin Confirm Are you sure you want to perform this action? Performing the operation "Clear-RecycleBin" on target "All of the contents of the Recycle Bin". [Y] Yes [A] Yes to All [N] No [L] No to All [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "Y"): y
What happened to the files in the Recycle Bin?
The files in the Recycle Bin are deleted permanently.
Reflection
PowerShell was developed for task automation and configuration management. Using the Internet, research commands that you could use to simplify your tasks as a security analyst. Record your findings.
Answers will vary.
