8.2.1.5 Lab – Configure IP SLA ICMP Echo (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
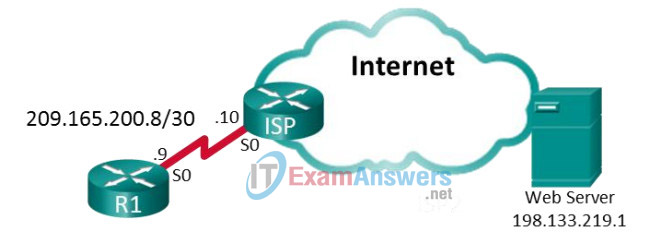
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | S0/0/0 | 209.165.200.9 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| ISP | S0/0/0 | 209.165.200.10 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| Lo0 | 198.133.219.1 | 255.255.255.255 | N/A |
Objectives
Part 1: Build the Network and Verify Connectivity
Part 2: Configure IP SLA ICMP Echo on R1
Part 3: Test and Monitor the IP SLA Operation
Background / Scenario
An outside vendor has been contracted to provide web services for your company. As the network administrator, you have been asked to monitor the vendor’s service. You decide to configure IP SLA to help with that task.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). The switches used are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 2 Router (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Serial cable as shown in the topology
Part 1: Build the Network and Verify Connectivity
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings, such as the interface IP addresses, static routing, device access, and passwords.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2: Initialize and reload the routers as necessary.
Step 3: Configure basic settings for R1.
a. Disable DNS lookup.
b. Configure the device name as shown in the topology.
c. Configure an IP address for the router as listed in the Addressing Table.
d. Assign class as the encrypted privileged EXEC mode password.
e. Assign cisco for the console and vty password, enable login.
f. Configure logging synchronous to prevent console messages from interrupting command entry.
g. Configure the default route for R1 to the ISP S0/0/0 IP address.
h. Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Step 4: Copy and paste the configuration to the ISP router.
The ISP router configuration is provided below. Copy and paste this configuration into the ISP router. Loopback 0 is being used to simulate the Web server shown in the Topology.
hostname ISP no ip domain lookup interface Loopback0 ip address 198.133.219.1 255.255.255.255 interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 209.165.200.10 255.255.255.252 no shut end
Step 5: Verify connectivity.
a. From R1, you should be able to ping the ISP Serial interface IP address. Were all pings successful?
___________Yes
If the pings are not successful, troubleshoot the basic device configurations before continuing.
b. From R1, you should be able to ping the Web Server IP address. Were all pings successful?
___________Yes
If the pings are not successful, troubleshoot the basic device configurations before continuing.
Part 2: Configure IP SLA ICMP Echo on R1
In Part 2, you configure an IP SLA ICMP Echo operation on R1. Use the following parameters for this operation:
- Operation-number: 22
- ICMP Echo Destination Address: 198.133.219.1
- Frequency: 20 seconds
- Schedule Start: Now
- Schedule Life time: Forever
Step 1: Create an IP SLA Operation.
R1(config)# ip sla 22
Step 2: Configure the ICMP Echo Operation.
R1(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 198.133.219.1
Step 3: Set the rate the IP SLA operation repeats.
R1(config-ip-sla-echo)# frequency 20
Step 4: Schedule the IP SLA ICMP Echo operation.
R1(config)# ip sla schedule 22 start-time now life forever
Step 5: Use show command to verify the IP SLA configuration.
R1# show ip sla configuration
IP SLAs Infrastructure Engine-III
Entry number: 22
Owner:
Tag:
Operation timeout (milliseconds): 5000
Type of operation to perform: icmp-echo
Target address/Source address: 198.133.219.1/0.0.0.0
Type Of Service parameter: 0x0
Request size (ARR data portion): 28
Verify data: No
Vrf Name:
Schedule:
Operation frequency (seconds): 20 (not considered if randomly scheduled)
Next Scheduled Start Time: Start Time already passed
Group Scheduled : FALSE
Randomly Scheduled : FALSE
Life (seconds): Forever
Entry Ageout (seconds): never
Recurring (Starting Everyday): FALSE
Status of entry (SNMP RowStatus): Active
Threshold (milliseconds): 5000
Distribution Statistics:
Number of statistic hours kept: 2
Number of statistic distribution buckets kept: 1
Statistic distribution interval (milliseconds): 20
Enhanced History:
History Statistics:
Number of history Lives kept: 0
Number of history Buckets kept: 15
History Filter Type: None
Part 3: Test and Monitor the IP SLA Operation
In Part 3, you will simulate an outage of web services. This can be done by an administratively shutdown of the loopback 0 interface on the ISP router. You will then display the IP SLA operation statistics to monitorthe effect of this test.
Step 1: Shutdown the loopback 0 interface on the ISP router.
ISP(config)# interface Lo0 ISP(config-if)# shutdown ISP(config-if)# *Nov 28 14:00:52.823: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to administratively down *Nov 28 14:00:53.823: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to down ISP(config-if)#
Note: Wait a few minutes before executing Step 2.
Step 2: Activate the loopback 0 interface on the ISP router.
R2(config-if)# no shutdown R2(config-if)# *Nov 28 14:04:23.263: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Loopback0, changed state to up *Nov 28 14:04:24.263: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up R2(config-if)#
Step 3: Issue the command used to display the IP SLA operation statistics on R1.
R1# show ip sla statistics
IPSLAs Latest Operation Statistics
IPSLA operation id: 22
Latest RTT: 1 milliseconds
Latest operation start time: 18:44:45 UTC Thu Jan 28 2016
Latest operation return code: OK
Number of successes: 103
Number of failures: 10
Operation time to live: Forever
Note: You should see a failure count greater than zero if you waited more than 20 seconds before re-activating the loopback 0 interface on the ISP router.
The IP SLA configured in Part 2 will run forever. How would you stop the IP SLA from running but still leave the IP SLA configured to use at a future time?
_______________________________________________________
R1(config)# no ip sla schedule 22
Reflection
Using the lab’s show ip sla statistics example, what does the failure count indicate about the Web Server?
_________________________________________________________
Answers will vary, but this number shows that the IP SLA ICMP Echo operation was not able to reach the Web Server 10 times since the start of the IP SLA monitoring operation. This can be interpreted that there has been approximately 3 minutes’ of interruptions in web services since Jan 28, 2016 6:45pm. However, it is not known if this was one long incident (approximately 3 minutes) or if it was multiple shorter incidents.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Interface Summary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. | ||||
Device Configs
Router R1
R1#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1577 bytes ! version 15.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 5 $1$papm$awGgHPitBMUA2.bImJtdp0 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! no ip domain lookup ip cef no ipv6 cef ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! redundancy ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 209.165.200.9 255.255.255.252 clock rate 2000000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.10 ! ip sla 22 icmp-echo 198.133.219.1 frequency 20 ip sla schedule 22 life forever start-time now ! control-plane ! line con 0 password cisco login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input none ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
Router ISP
ISP# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1360 bytes version 15.4 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname ISP ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! no ip domain lookup ip cef no ipv6 cef ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! cts logging verbose ! redundancy ! interface Loopback0 ip address 198.133.219.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 209.165.200.10 255.255.255.252 ! interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown clock rate 125000 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! line con 0 line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 login transport input none ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
