9.2.3.6 Packet Tracer – Implementing Static and Dynamic NAT (Instructor Version – Optional Lab)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide additional practice.
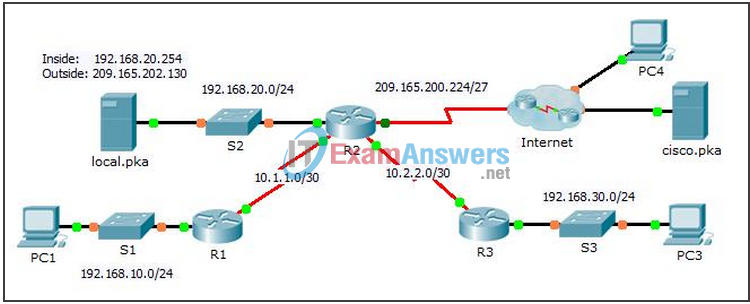
Topology
Objectives
- Part 1: Configure Dynamic NAT with PAT
- Part 2: Configure Static NAT
- Part 3: Verify NAT Implementation
Part 1: Configure Dynamic NAT with PAT
Step 1: Configure traffic that will be permitted for NAT translations.
On R2, configure a standard ACL named R2NAT that uses three statements to permit, in order, the following private address spaces:192.168.10.0/24, 192.168.20.0/24, and 192.168.30.0/24.
R2(config)# ip access-list standard R2NAT R2(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 R2(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.20.0 0.0.0.255 R2(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255
Step 2: Configure a pool of addresses for NAT.
Configure R2 with a NAT pool named R2POOL that uses the first address in the 209.165.202.128/30 address space. The second address is used for static NAT later in Part 2.
R2(config)# ip nat pool R2POOL 209.165.202.129 209.165.202.129 netmask 255.255.255.252
Step 3: Associate the named ACL with the NAT pool and enable PAT.
R2(config)# ip nat inside source list R2NAT pool R2POOL overload
Step 4: Configure the NAT interfaces.
Configure R2 interfaces with the appropriate inside and outside NAT commands.
R2(config)# inte fa0/0 R2(config-if)# ip nat inside R2(config-if)# inte s0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip nat inside R2(config-if)# inte s0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ip nat inside R2(config-if)# inte s0/1/0 R2(config-if)# ip nat outside
Part 2: Configure Static NAT
Refer to the Topology. Create a static NAT translation to map the local.pka inside address to its outside address.
R2(config)# ip nat inside source static 192.168.20.254 209.165.202.130
Part 3: Verify NAT Implementation
Step 1: Access services across the Internet.
a. From the web browser of PC1, or PC3, access the web page for cisco.pka.
b. From the web browser for PC4, access the web page for local.pka.
Step 2: View NAT translations.
View the NAT translations on R2.
R2# show ip nat translations

Hi great resource thank you. However the content remains locked even after liking the page on FB. Please advise as to how to unlock the content. Thanks!
Please reload your page