10.2.3.3 Lab – Troubleshooting Basic Single-Area OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
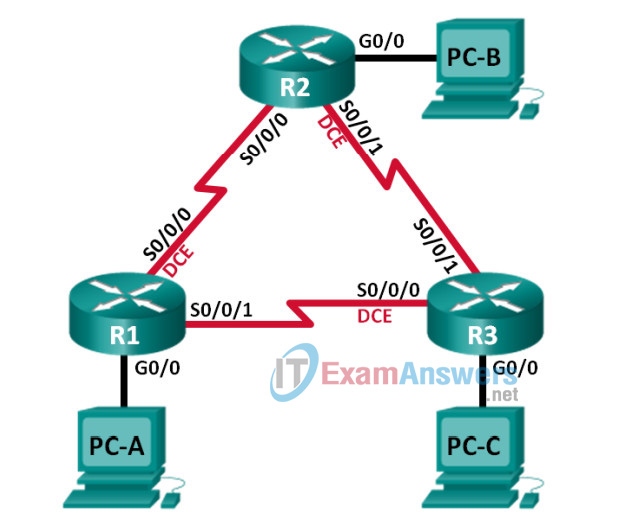
Addressing Table
| Device | OSPF Router ID |
Interface | IP Address | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 1.1.1.1 | G0/0 | 192.168.1.1/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1/64 FE80::1 link-local |
N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.12.1/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::1/64 FE80::1 link-local |
N/A | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.18.13.1/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::1/64 FE80::1 link-local |
N/A | ||
| R2 | 2.2.2.2 | G0/0 | 192.168.2.1/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::2/64 FE80::2 link-local |
N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.12.2/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::2/64 FE80::2 link-local |
N/A | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.23.1/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::2/64 FE80::2 link-local |
N/A | ||
| R3 | 3.3.3.3 | G0/0 | 192.168.3.1/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::3/64 FE80::3 link-local |
N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.13.2/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::3/64 FE80::3 link-local |
N/A | ||
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.23.2/30 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::3/64 FE80::3 link-local |
N/A | ||
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.3/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::A/64 |
192.168.1.1 FE80::1 |
|
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.2.3/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::B/64 |
192.168.2.1 FE80::2 |
|
| PC-C | NIC | 192.168.3.3/24 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::C/64 |
192.168.3.1 FE80::3 |
Objectives
Part 1: Build the Network and Load Device Configurations
Part 2: Troubleshoot Layer 3 Connectivity
Part 3: Troubleshoot OSPFv2
Part 4: Troubleshoot OSPFv3
Background / Scenario
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a link-state routing protocol for IP networks. OSPFv2 is defined for IPv4 networks, and OSPFv3 is defined for IPv6 networks. OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 are completely isolated routing protocols, changes in OSPFv2 do not affect OSPFv3 routing, and vice versa.
In this lab, a single-area OSPF network running OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 is experiencing problems. You have been assigned to find the problems with the network and correct them.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the routers have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 3 Routers (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable)
- 3 PCs (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology
Part 1: Build the Network and Load Device Configurations
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings on the PC hosts and routers.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Step 2: Configure PC hosts.
Step 3: Load router configurations.
Load the following configurations into the appropriate router. All routers have the same passwords. The privileged EXEC password is cisco. The password for console and vty access is class.
Router R1 Configuration:
conf t service password-encryption no ip domain lookup hostname R1 enable secret class line con 0 logging synchronous password cisco login line vty 0 password cisco login banner motd @Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!@ ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 passive-interface g0/0 interface g0/0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:a::1/64 ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local !ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 !no shutdown interface s0/0/0 clock rate 128000 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 !ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:12::1/64 ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 no shutdown interface s0/0/1 ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0 !ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:13::1/64 ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 no shutdown router ospf 1 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 129.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 !network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 passive-interface g0/0 !router-id 1.1.1.1 end
Router R2 Configuration:
conf t service password-encryption no ip domain lookup hostname R2 enable secret class line con 0 logging synchronous password cisco login line vty 0 password cisco login banner motd @Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!@ ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 !passive-interface g0/0 interface g0/0 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:B::2/64 ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local !no ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local !ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local !ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 no shutdown interface s0/0/0 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:12::2/64 ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 no shutdown interface s0/0/1 clock rate 128000 !ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:23::2/64 ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local !ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 no shutdown router ospf 1 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 !passive-interface g0/0 end
Router R3 Configuration:
conf t service password-encryption no ip domain lookup enable secret class hostname R3 line con 0 logging synchronous password cisco login line vty 0 password cisco login banner motd @Unauthorized Access is Prohibited!@ interface g0/0 !ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:c::3/64 ipv6 address fe80::3 link-local !ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 !no shutdown interface s0/0/0 clock rate 128000 ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252 !ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:13::3/64 ipv6 address fe80::3 link-local !ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 no shutdown interface s0/0/1 ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:23::3/64 ipv6 address fe80::3 link-local !ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 !no shutdown !ipv6 unicast-routing !ipv6 router ospf 1 !router-id 3.3.3.3 !passive-interface g0/0 router ospf 1 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 !network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 !network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 passive-interface g0/0 end
Part 2: Troubleshoot Layer 3 Connectivity
In Part 2, you will verify that Layer 3 connectivity is established on all interfaces. You will need to test both IPv4 and IPv6 connectivity for all device interfaces.
Step 1: Verify that the interfaces listed in the Addressing Table are active and configured with the correct IP address information.
a. Issue the show ip interface brief command on all routers to verify that the interfaces are in an up/up state. Record your findings.
_________________________________________________________
R1 – G0/0 is administratively down
R2 – S0/0/1 is down
R3 – G0/0 & S0/0/1 are administratively down
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.1.1 YES manual administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/0/0 192.168.12.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/0/1 192.168.13.1 YES manual up up
R2# show ip interface bri
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.2.1 YES manual up up
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/0/0 192.168.12.2 YES manual up up
Serial0/0/1 unassigned YES unset down down
R3# show ip interface bri
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
GigabitEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/0/0 192.168.3.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/0/1 192.168.23.2 YES manual administratively down down
b. Issue the show run interface command to verify IP address assignments on all router interfaces. Compare the interface IP addresses against the Addressing Table and verify the subnet mask assignments. For IPv6, verify that the link-local address has been assigned. Record your findings.
______________________________________________________
R1 – S0/0/0 & S0/0/1 incorrect subnet mask, should be 255.255.255.252
R2 – G0/0 incorrect IPv6 link local address, S0/0/1 no IPv4 address
R3 – G0/0 no IPv4 address, S0/0/0 incorrect IPv4 address
--R1 Intefaces --
R1# show run interface g0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 178 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1/64
end
R1# show run interface s0/0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 158 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::1/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
clock rate 2000000
end
R1# show run interface s0/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 138 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::1/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
end
--R2 Interfaces --
R2# show run interface g0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 168 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::2/64
end
R2# show run interface s0/0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 160 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::2/64
ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
end
R2# show run interface s0/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 133 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/1
no ip address
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::2/64
clock rate 128000
end
--R3 Interfaces --
R3# show run interface g0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 155 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::3/64
end
R3# show run interface s0/0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 159 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/0
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::3/64
clock rate 128000
end
R3# show run interface s0/0/1
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 150 bytes
!
interface Serial0/0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252
shutdown
ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::3/64
end
c. Resolve all problems that are found. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
______________________________________________________
R1(config)# interface g0/0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252
R1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252
R1(config-if)# end
R2(config)# interface g0/0
R2(config-if)# no ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
R2(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252
R2(config-if)# end
R3(config)# interface g0/0
R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)# no shutdown
R3(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
R3(config-if)# ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252
R3(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R3(config-if)# no shutdown
R3(config-if)# end
d. Using the ping command, verify that each router has network connectivity with the serial interfaces on the neighbor routers. Verify that the PCs can ping their default gateways. If problems still exist, continue troubleshooting Layer 3 issues.
Part 3: Troubleshoot OSPFv2
In Part 3, you will troubleshoot OSPFv2 problems and make the necessary changes needed to establish OSPFv2 routes and end-to-end IPv4 connectivity.
Note: LAN (G0/0) interfaces should not advertise OSPF routing information, but routes to these networks should be in the routing tables.
Step 1: Test IPv4 end-to-end connectivity.
From each PC host, ping the other PC hosts in the topology to verify end-to-end connectivity.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall before testing, to ping between PCs.
a. Ping from PC-A to PC-B. Were the pings successful? _____________No
b. Ping from PC-A to PC-C. Were the pings successful? _____________No
c. Ping from PC-B to PC-C. Were the pings successful? _____________No
Step 2: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv2 area 0 on R1.
a. Issue the show ip protocols command to verify that OSPF is running and that all networks are advertised in area 0. Verify that the router ID is set correctly. Record your findings.
_____________________________________________________
Router ID is incorrectly configured. The router ID should be 1.1.1.1, not 192.168.13.1. The network 129.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 statement is incorrect. The network statement should be for 192.168.12.0/30.
R1# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 192.168.13.1
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
129.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 110)
b. Make the necessary changes to the configuration on R1 based on the output from the show ip protocols command. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
________________________________________________________
R1(config)# router ospf 1
R1(config-router)# no network 129.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
R1(config-router)# router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)# end
c. Issue the clear ip ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ip protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ip ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks assigned to area 0.
R1# show ip ospf interface brief
Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C
Se0/0/0 1 0 192.168.12.1/30 64 P2P 1/1
Se0/0/1 1 0 192.168.13.1/30 64 P2P 0/0
Gi0/0 1 0 192.168.1.1/24 1 DR 0/0
f. Issue the show ip ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that G0/0 is a passive interface.
Note: This information is also in the show ip protocols command.
R1# show ip ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 192.168.1.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 1.1.1.1, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 1.1.1.1, Interface address 192.168.1.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R1. List any additional changes made to R1. If no problems were found on the device, then respond with “no problems were found”.
_____________________________________________________
No problems were found
Instructor Note: The passive interface command was configured correctly in the original configs.
Step 3: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv2 area 0 on R2.
a. Issue the show ip protocols command to verify that OSPF is running and that all networks are being advertised in area 0. Verify that the router ID is set correctly. Record your findings.
_____________________________________________________
Router ID is incorrect 192.168.12.2. The correct router ID is 2.2.2.2.
R2# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 192.168.12.2
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
1.1.1.1 110 00:16:38
192.168.13.1 110 00:17:01
Distance: (default is 110)
b. Make the necessary changes to the configuration on R2 based on the output from the show ip protocols command. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
_______________________________________________________
R2(config)# router ospf 1
R2(config-router)# router-id 2.2.2.2
c. Issue the clear ip ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ip protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ip ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks assigned to area 0.
R2# sh ip ospf interface brief Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C Se0/0/1 1 0 192.168.23.1/30 64 P2P 0/0 Se0/0/0 1 0 192.168.12.2/30 64 P2P 1/1 Gi0/0 1 0 192.168.2.1/24 1 DR 0/0
f. Issue the show ip ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that G0/0 is a passive interface.
Note: This information is also available from the show ip protocols command.
R2# show ip ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 192.168.2.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 2.2.2.2, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 2.2.2.2, Interface address 192.168.2.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
Hello due in 00:00:00
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R2. List any additional changes made to R2. If no problems were found on the device, then respond with “no problems were found”.
_____________________________________________________
R2(config)# router ospf 1
R2(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0
Step 4: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv2 area 0 on R3.
a. Issue the show ip protocols command to verify that OSPF is running and that all networks are being advertised in area 0. Verify that the router ID is set correctly as well. Record your findings.
_______________________________________________________
The router ID, 192.168.13.1 is incorrectly configured. The correct router ID for R3 is 3.3.3.3. The network statements for 192.168.13.0/30 and 192.168.23.0/30 are missing.
R3# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 192.168.13.1
Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
Passive Interface(s):
GigabitEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 110)
b. Make the necessary changes to the configuration on R3 based on the output from the show ip protocols command. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
________________________________________________________
R3(config)# router ospf 1
R3(config-router)# network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
R3(config-router)# network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0
R3(config-router)# router-id 3.3.3.3
c. Issue the clear ip ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ip protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ip ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks assigned to area 0.
R3# show ip ospf interface brief
Interface PID Area IP Address/Mask Cost State Nbrs F/C
Se0/0/1 1 0 192.168.23.2/30 64 P2P 1/1
Se0/0/0 1 0 192.168.13.2/30 64 P2P 1/1
Gi0/0 1 0 192.168.3.1/24 1 DR 0/0
f. Issue the show ip ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that G0/0 is a passive interface.
Note: This information is also in the show ip protocols command.
R3# show ip ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Internet Address 192.168.3.1/24, Area 0, Attached via Network Statement
Process ID 1, Router ID 3.3.3.3, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Topology-MTID Cost Disabled Shutdown Topology Name
0 1 no no Base
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 3.3.3.3, Interface address 192.168.3.1
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
oob-resync timeout 40
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS)
Cisco NSF helper support enabled
IETF NSF helper support enabled
Index 1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R3. List any additional changes made to R3. If no problems were found on the device, then respond with “no problems were found”.
_______________________________________________________
No problems were found
Instructor Note: The passive interface command was configured correctly in the original configuration.
Step 5: Verify OSPF neighbor information.
a. Issue the show ip ospf neighbor command on all routers to view the OSPF neighbor information.
R1# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
2.2.2.2 0 FULL/ - 00:00:38 192.168.12.2 Serial0/0/0
3.3.3.3 0 FULL/ - 00:00:36 192.168.13.2 Serial0/0/1
R2# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
3.3.3.3 0 FULL/ - 00:00:33 192.168.23.2 Serial0/0/1
1.1.1.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:35 192.168.12.1 Serial0/0/0
R3# show ip ospf neighbor
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface
2.2.2.2 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 192.168.23.1 Serial0/0/1
1.1.1.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 192.168.13.1 Serial0/0/0
Step 6: Verify OSPFv2 Routing Information.
a. Issue the show ip route ospf command to verify that each router has OSPFv2 routes to all non-adjoining networks.
R1# show ip route ospf
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
O 192.168.2.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.12.2, 00:26:56, Serial0/0/0
O 192.168.3.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.13.2, 00:12:20, Serial0/0/1
192.168.23.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 192.168.23.0 [110/128] via 192.168.13.2, 00:12:20, Serial0/0/1
[110/128] via 192.168.12.2, 00:26:56, Serial0/0/0
R2# show ip route ospf
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.12.1, 00:32:23, Serial0/0/0
O 192.168.3.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.23.2, 00:17:47, Serial0/0/1
192.168.13.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 192.168.13.0 [110/128] via 192.168.23.2, 00:17:47, Serial0/0/1
[110/128] via 192.168.12.1, 00:32:23, Serial0/0/0
R3# show ip route ospf
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override
Gateway of last resort is not set
O 192.168.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.13.1, 00:14:12, Serial0/0/0
O 192.168.2.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.23.1, 00:14:12, Serial0/0/1
192.168.12.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 192.168.12.0 [110/128] via 192.168.23.1, 00:14:12, Serial0/0/1
[110/128] via 192.168.13.1, 00:14:12, Serial0/0/0
Are all OSPFv2 routes available? _______yes
If any OSPFv2 routes are missing, what is missing?
______________________________________________________
All OSPFv2 routes are present.
b. If any routing information is missing, resolve these issues.
Instructor Note: All problems should have been resolved.
Step 7: Verify IPv4 end-to-end connectivity.
From each PC, verify that IPv4 end-to-end connectivity exists. PCs should be able to ping the other PC hosts in the topology. If IPv4 end-to-end connectivity does not exist, then continue troubleshooting to resolve any remaining issues.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall to ping between PCs.
Part 4: Troubleshoot OSPFv3
In Part 4, you will troubleshoot OSPFv3 problems and make the necessary changes needed to establish OSPFv3 routes and end-to-end IPv6 connectivity.
Note: LAN (G0/0) interfaces should not advertise OSPFv3 routing information, but routes to these networks should be contained in the routing tables.
Step 1: Test IPv6 end-to-end connectivity.
From each PC host, ping the IPv6 addresses of the other PC hosts in the topology to verify IPv6 end-to-end connectivity.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall to ping between PCs.
Step 2: Verify that IPv6 unicast routing has been enabled on all routers.
a. An easy way to verify that IPv6 routing has been enabled on a router is to use the show run | section ipv6 unicast command. By adding this pipe (|) section to the show run command, the ipv6 unica-strouting command displays if IPv6 routing has been enabled.
Note: The show run command can also be issued without any pipe, and then a manual search for the ipv6 unicast-routing command can be done.
Issue the command on each router. Record your findings.
______________________________________________________
R3 does not have ipv6 unicast routing enabled.
R1# show run | section ipv6 unicast ipv6 unicast-routing R2# show run | section ipv6 unicast ipv6 unicast-routing R3# show run | section ipv6 unicast R3#
b. If IPv6 unicast routing is not enabled on one or more routers, enable it now. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
______________________________________________________
R3(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
Step 3: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv3 area 0 on R1.
a. Issue the show ipv6 protocols command and verify that the router ID is correct. Also verify that the expected interfaces are displayed under area 0.
Note: If no output is generated from this command, then the OSPFv3 process has not been configured.
Record your findings.
_____________________________________________________
Router ID is correct. The network for G0/0 interface is advertised in the OSPFv3 process.
R1# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Router ID 1.1.1.1
Number of areas: 1 normal, 0 stub, 0 nssa
Interfaces (Area 0):
Serial0/0/1
Serial0/0/0
Redistribution:
None
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
b. Make the necessary configuration changes to R1. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
_______________________________________________________
R1(config)# interface g0/0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
c. Issue the clear ipv6 ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ipv6 protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks assigned to area 0.
f. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that this interface is set not to advertise OSPFv3 routes.
R1# show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Link Local Address FE80::1, Interface ID 3
Area 0, Process ID 1, Instance ID 0, Router ID 1.1.1.1
Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State WAITING, Priority 1
No designated router on this network
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Wait time before Designated router selection 00:00:23
Graceful restart helper support enabled
Index 1/3/3, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R1. List any additional changes made to R1. If no problems were found on the device, then respond with “no problems were found”.
_____________________________________________________
No problems were found, G0/0 is already a passive OSPFv3 interface.
Step 4: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv3 area 0 on R2.
a. Issue the show ipv6 protocols command and verify the router ID is correct. Also verify that the expected interfaces display under area 0.
Note: If no output is generated from this command, then the OSPFv3 process has not been configured.
Record your findings.
_____________________________________________________
Router ID is correct, interfaces G0/0 & S0/0/1 are missing
R2# show ipv6 protocols
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "connected"
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ospf 1"
Router ID 2.2.2.2
Number of areas: 1 normal, 0 stub, 0 nssa
Interfaces (Area 0):
Serial0/0/0
Redistribution:
None
IPv6 Routing Protocol is "ND"
b. Make the necessary configuration changes to R2. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
________________________________________________________
R2(config)# interface g0/0
R2(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
R2(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R2(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
c. Issue the clear ipv6 ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ipv6 protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks assigned to area 0.
f. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that this interface is not set to advertise OSPFv3 routes.
R2# show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Link Local Address FE80::2, Interface ID 3
Area 0, Process ID 1, Instance ID 0, Router ID 2.2.2.2
Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State WAITING, Priority 1
No designated router on this network
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
Hello due in 00:00:04
Wait time before Designated router selection 00:00:05
Graceful restart helper support enabled
Index 1/2/2, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. List any additional changes made to R2. If no problems were found on the device, then respond with “no problems were found”.
______________________________________________________
R2(config)# ipv6 router ospf 1
R2(config-rtr)# passive-interface g0/0
Step 5: Verify that all interfaces are assigned to OSPFv3 area 0 on R3.
a. Issue the show ipv6 protocols command and verify that the router ID is correct. Also verify that the expected interfaces display under area 0.
Note: If no output is generated from this command, then the OSPFv3 process has not been configured.
Record your findings.
_______________________________________________________
OSPFv3 has not been configured on this router.
R3# show ipv6 protocols
b. Make the necessary configuration changes to R3. Record the commands used to correct the issues.
_______________________________________________________
R3(config)# ipv6 router ospf 1
R3(config-rtr)# router-id 3.3.3.3
R3(config-rtr)# passive-interface g0/0
R3(config-rtr)# interface g0/0
R3(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
R3(config-if)# interface s0/0/0
R3(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
R3(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R3(config-if)# ipv6 ospf 1 area 0
c. Issue the clear ipv6 ospf process command if necessary.
d. Re-issue the show ipv6 protocols command to verify that your changes had the desired effect.
e. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface brief command to verify that all interfaces are listed as OSPF networks assigned to area 0.
f. Issue the show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0 command to verify that this interface is set not to advertise OSPFv3 routes.
R3# show ipv6 ospf interface g0/0
GigabitEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
Link Local Address FE80::3, Interface ID 3
Area 0, Process ID 1, Instance ID 0, Router ID 3.3.3.3
Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1
Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1
Designated Router (ID) 3.3.3.3, local address FE80::3
No backup designated router on this network
Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5
No Hellos (Passive interface)
Graceful restart helper support enabled
Index 1/1/1, flood queue length 0
Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0)/0x0(0)
Last flood scan length is 0, maximum is 0
Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec
Neighbor Count is 0, Adjacent neighbor count is 0
Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s)
g. Resolve any problems discovered on R3. List any additional changes made to R3. If no problems were found on the device, then respond with “no problems were found”.
______________________________________________________
No problems were found as long as G0/0 was configured as a passive OSPFv3 interface in Step 5b.
Step 6: Verify that all routers have correct neighbor adjacency information.
a. Issue the show ipv6 ospf neighbor command to verify that adjacencies have formed between neighboring routers.
R1# show ipv6 ospf neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process ID 1)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
3.3.3.3 0 FULL/ - 00:00:34 6 Serial0/0/1
2.2.2.2 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 6 Serial0/0/0
R2# sh ipv6 ospf neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (2.2.2.2) (Process ID 1)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
3.3.3.3 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 7 Serial0/0/1
1.1.1.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:30 6 Serial0/0/0
R3# sh ipv6 ospf neighbor
OSPFv3 Router with ID (3.3.3.3) (Process ID 1)
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Interface ID Interface
2.2.2.2 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 7 Serial0/0/1
1.1.1.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:37 7 Serial0/0/0
b. Resolve any OSPFv3 adjacency issues that still exist.
Instructor Note: All adjacency issues should have been resolved in earlier steps.
Step 7: Verify OSPFv3 routing information.
a. Issue the show ipv6 route ospf command, and verify that OSPFv3 routes exist to all non-adjoining networks.
R1# show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 10 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::3, Serial0/0/1
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::/64 [110/128]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/0
via FE80::3, Serial0/0/1
R2# show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 10 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::1, Serial0/0/0
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::3, Serial0/0/1
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::/64 [110/128]
via FE80::1, Serial0/0/0
via FE80::3, Serial0/0/1
R3# show ipv6 route ospf
IPv6 Routing Table - default - 10 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
B - BGP, R - RIP, I1 - ISIS L1, I2 - ISIS L2
IA - ISIS interarea, IS - ISIS summary, D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external
ND - ND Default, NDp - ND Prefix, DCE - Destination, NDr - Redirect
O - OSPF Intra, OI - OSPF Inter, OE1 - OSPF ext 1, OE2 - OSPF ext 2
ON1 - OSPF NSSA ext 1, ON2 - OSPF NSSA ext 2
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::1, Serial0/0/0
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::/64 [110/65]
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/1
O 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::/64 [110/128]
via FE80::1, Serial0/0/0
via FE80::2, Serial0/0/1
Are all OSPFv3 routes available? ________yes
If any OSPFv3 routes are missing, what is missing?
____________________________________________________
All OSPFv3 routes are present.
b. Resolve any routing issues that still exist.
Instructor Note: All OSPFv3 routes issues should have been resolved.
Step 8: Verify IPv6 end-to-end connectivity.
From each PC, verify that IPv6 end-to-end connectivity exists. PCs should be able to ping each interface on the network. If IPv6 end-to-end connectivity does not exist, then continue troubleshooting to resolve remaining issues.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall to ping between PCs.
Reflection
Why would you troubleshoot OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 separately?
________________________________________________________
OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 do not share routing information and their configuration is completely independent.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Interface Summary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. | ||||
Device Configs – Final
Router R1
R1#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2010 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! ip cef ! no ip domain lookup ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:A::1/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::1/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 clock rate 128000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::1/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ! router ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^CUnauthorized Access is Prohibited!^C ! line con 0 password 7 060506324F41 logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 password 7 00071A150754 login transport input all line vty 1 4 login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
Router R2
R2#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2010 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname R2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! ip cef ! no ip domain lookup ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:B::2/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:12::2/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::2/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 clock rate 128000 ! router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 network 192.168.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^CUnauthorized Access is Prohibited!^C ! line con 0 password 7 094F471A1A0A logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 password 7 14141B180F0B login transport input all line vty 1 4 login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
Router R3
R3#sh run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2049 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname R3 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! ip cef ! no ip domain lookup ipv6 unicast-routing ipv6 cef multilink bundle-name authenticated ! ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:C::3/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:13::3/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 clock rate 128000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252 ipv6 address FE80::3 link-local ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:23::3/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ! router ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^CUnauthorized Access is Prohibited!^C ! line con 0 password 7 02050D480809 logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 password 7 104D000A0618 login transport input all line vty 1 4 login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
