2.1.4.6 Packet Tracer – Navigating the IOS (Instructor Version – Optional Packet Tracer)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or to provide additional practice.
Topology
2.1.4.6 Packet Tracer – Navigating the IOS
Objectives
- Part 1: Establish Basic Connections, Access the CLI, and Explore Help
- Part 2: Explore EXEC Modes
- Part 3: Set the Clock
Background
In this activity, you will practice skills necessary for navigating the Cisco IOS, such as different user access modes, various configuration modes, and common commands used on a regular basis. You will also practice accessing the context-sensitive Help by configuring the clock command.
Part 1: Establish Basic Connections, Access the CLI, and Explore Help
In Part 1 of this activity, you will connect a PC to a switch using a console connection and explore various command modes and Help features.
Step 1: Connect PC1 to S1 using a console cable.
a. Click the Connections icon (the one that looks like a lightning bolt) in the lower left corner of the Packet Tracer window.
b. Select the light blue Console cable by clicking it. The mouse pointer will change to what appears to be a connector with a cable dangling from it.
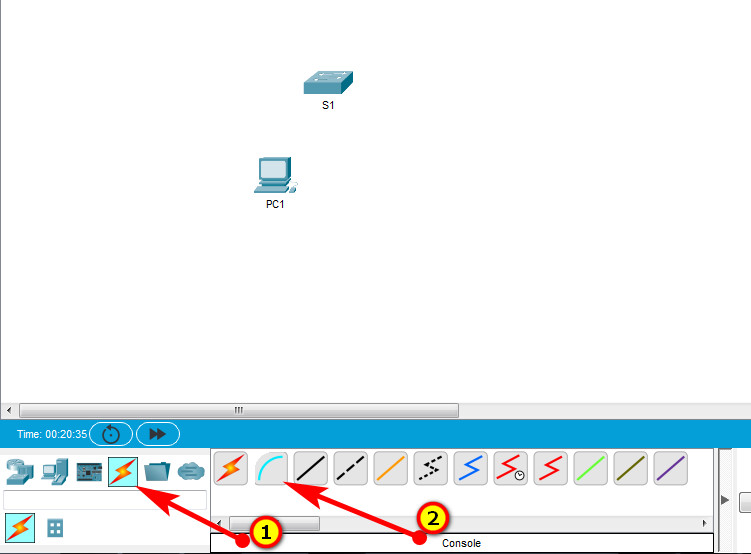
c. Click PC1. A window displays an option for an RS-232 connection.
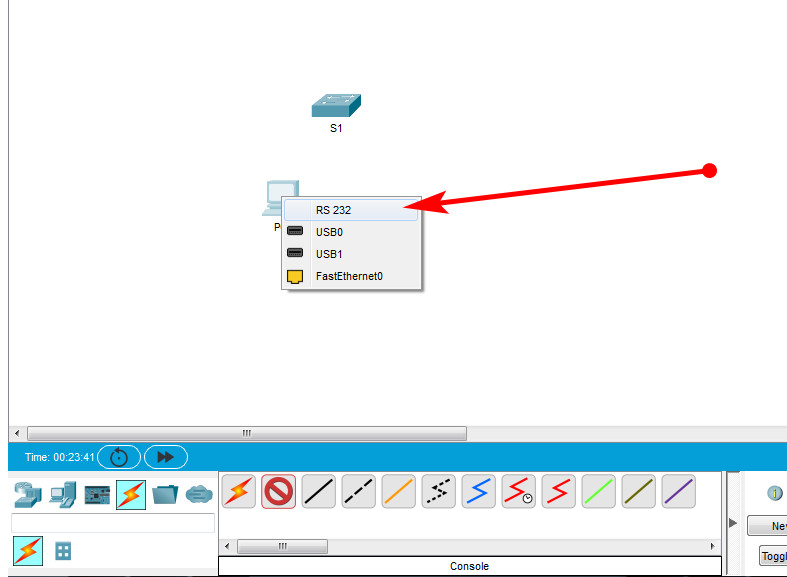
d. Drag the other end of the console connection to the S1 switch and click the switch to access the connection list.
e. Select the Console port to complete the connection.
Step 2: Establish a terminal session with S1.
a. Click PC1 and then select the Desktop tab.
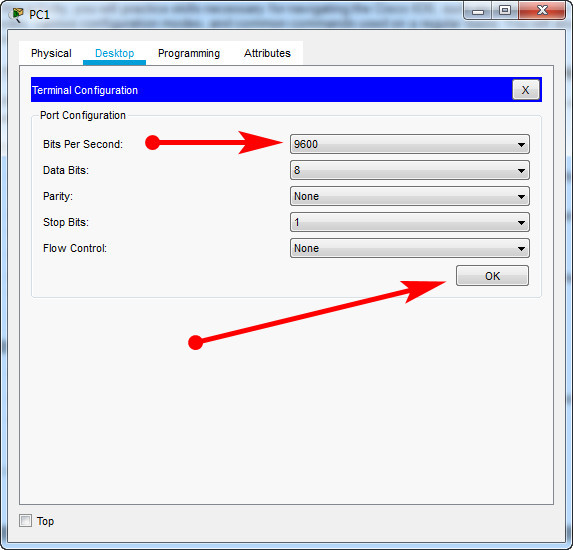
b. Click the Terminal application icon. Verify that the Port Configuration default settings are correct.
What is the setting for bits per second?
c. Click OK.
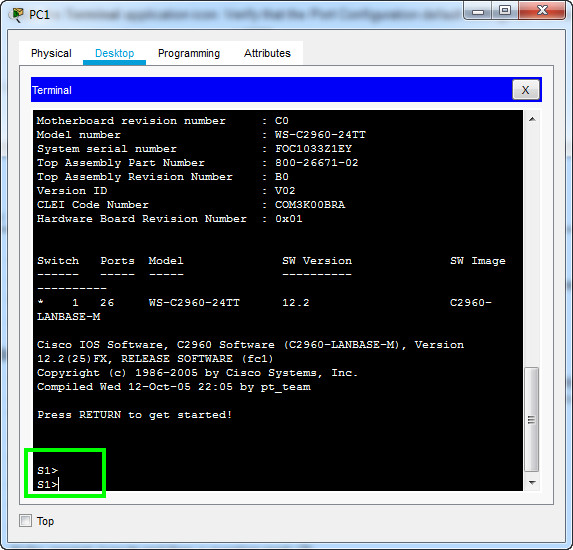
d. The screen that appears may have several messages displayed. Somewhere on the screen there should be a Press RETURN to get started! message. Press ENTER.
What is the prompt displayed on the screen?
Step 3: Explore the IOS Help.
a. The IOS can provide help for commands depending on the level accessed. The prompt currently displayed is called User EXEC, and the device is waiting for a command. The most basic form of help is to type a question mark (?) at the prompt to display a list of commands.
S1> ?
Which command begins with the letter ‘C’?
b. At the prompt, type t and then a question mark (?).
S1> t?
Which commands are displayed?
c. At the prompt, type te and then a question mark (?).
S1> te?
Which commands are displayed?
This type of help is known as context-sensitive Help. It provides more information as the commands are expanded.
Part 2: Explore EXEC Modes
In Part 2 of this activity, you will switch to privileged EXEC mode and issue additional commands.
Step 1: Enter privileged EXEC mode.
a. At the prompt, type the question mark (?).
S1> ?
What information is displayed that describes the enable command?
b. Type en and press the Tab key.
S1> en
What displays after pressing the Tab key?
This is called command completion (or tab completion). When part of a command is typed, the Tab key can be used to complete the partial command. If the characters typed are enough to make the command unique, as in the case of the enable command, the remaining portion of the command is displayed.
What would happen if you typed te
c. Enter the enable command and press ENTER. How does the prompt change?
d. When prompted, type the question mark (?).
S1# ?
One command starts with the letter ‘C’ in user EXEC mode. How many commands are displayed now that privileged EXEC mode is active? (Hint: you could type c? to list just the commands beginning with ‘C’.)
Step 2: Enter Global Configuration mode.
a. When in privileged EXEC mode, one of the commands starting with the letter ‘C’ is configure. Type either the full command or enough of the command to make it unique. Press the
S1# configure
What is the message that is displayed?
b. Press Enter to accept the default parameter that is enclosed in brackets [terminal].
How does the prompt change?
c. This is called global configuration mode. This mode will be explored further in upcoming activities and labs. For now, return to privileged EXEC mode by typing end, exit, or Ctrl-Z.
S1(config)# exit S1#
Part 3: Set the Clock
Step 1: Use the clock command.
a. Use the clock command to further explore Help and command syntax. Type show clock at the privileged EXEC prompt.
S1# show clock
What information is displayed? What is the year that is displayed?
b. Use the context-sensitive Help and the clock command to set the time on the switch to the current time. Enter the command clock and press ENTER.
S1# clock
What information is displayed?
c. The “% Incomplete command” message is returned by the IOS. This indicates that the clock command needs more parameters. Any time more information is needed, help can be provided by typing a space after the command and the question mark (?).
S1# clock ?
What information is displayed?
d. Set the clock using the clock set command. Proceed through the command one step at a time.
S1# clock set ?
What information is being requested?
What would have been displayed if only the
clock set command had been entered, and no request for help was made by using the question mark?e. Based on the information requested by issuing the
clock set ? command, enter a time of 3:00 p.m. by using the 24-hour format of 15:00:00. Check to see if more parameters are needed.
S1# clock set 15:00:00 ?
The output returns a request for more information:
<1-31> Day of the month MONTH Month of the year
f. Attempt to set the date to 01/31/2035 using the format requested. It may be necessary to request additional help using the context-sensitive Help to complete the process. When finished, issue the show clock command to display the clock setting. The resulting command output should display as:
S1# show clock *15:0:4.869 UTC Tue Jan 31 2035
g. If you were not successful, try the following command to obtain the output above:
S1# clock set 15:00:00 31 Jan 2035
Step 2: Explore additional command messages.
a. The IOS provides various outputs for incorrect or incomplete commands. Continue to use the clock command to explore additional messages that may be encountered as you learn to use the IOS.
b. Issue the following command and record the messages:
S1# cl
What information was returned?
S1# clock
What information was returned?
S1# clock set 25:00:00
What information was returned?
S1# clock set 15:00:00 32
What information was returned?
