CCNA 2 Routing and Switching Essentials v5 Chapter 11: Network Address Translation for IPv4 – Check Your Understanding Questions Answers
1. Refer to the following output. Based on the output, which statement is true about the NAT configuration?

- Static NAT is configured.
- Dynamic NAT is configured.
- NAT Overload (PAT) is configured.
- NAT is configured incorrectly.
2. What is the default timeout value for NAT translations?
- One hour
- One day
- One week
- Indefinite
3. Match the characteristic to the NAT technique. Note that a technique can have more than one characteristic.
- Provides one-to-one fixed mappings of local and global addresses
- Assigns the translated address of IP hosts from a pool of public addresses
- Can map multiple addresses to a single address of an external interface
- Assigns unique source port numbers of an inside global address on a session- by-session basis
- Allows an external host to establish sessions with an internal host
_______ Dynamic NAT
_______ PAT
_______ Static NAT
| Assigns the translated address of IP hosts from a pool of public addresses. | Dynamic NAT |
| Can map multiple addresses to a single address of an external interface. Assigns unique source port numbers of an inside global address on a session- by-session basis. |
PAT |
| Provides one-to-one fixed mappings of local and global addresses. Allows an external host to establish sessions with an internal host. |
Static NAT |
4. Consider the following configuration:
R2(config)# ip nat inside source static 192.168.0.100 209.165.200.2 R2(config)# interface serial0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)# ip nat inside R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface serial0/1/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224 R2(config-if)# ip nat outside R2(config-if)# exit
Which host(s) will be translated by NAT?
- 10.1.1.2
- 192.168.0.100
- 209.165.200.2
- All hosts on the 10.1.1.0 network
- All hosts on the 192.168.0.0 network
5. Consider the following configuration:
R2(config)# ip nat pool nat-pool1 209.165.200.225 209.165.200.240 netmask 255.255.255.0 R2(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 pool nat-pool1 R2(config)# interface serial0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 R2(config-if)# ip nat inside R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# interface serial0/1/0 R2(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.1 255.255.255.224 R2(config-if)# ip nat outside R2(config-if)# exit R2(config)# access-list 1 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.31
Which addresses will be translated by NAT?
- 10.1.1.2 to 10.1.1.255
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.0.255
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.0.31
- 209.165.200.240 to 209.165.200.255
- Only host 10.1.1.2
- Only host 209.165.200.255
6. Consider the following topology.
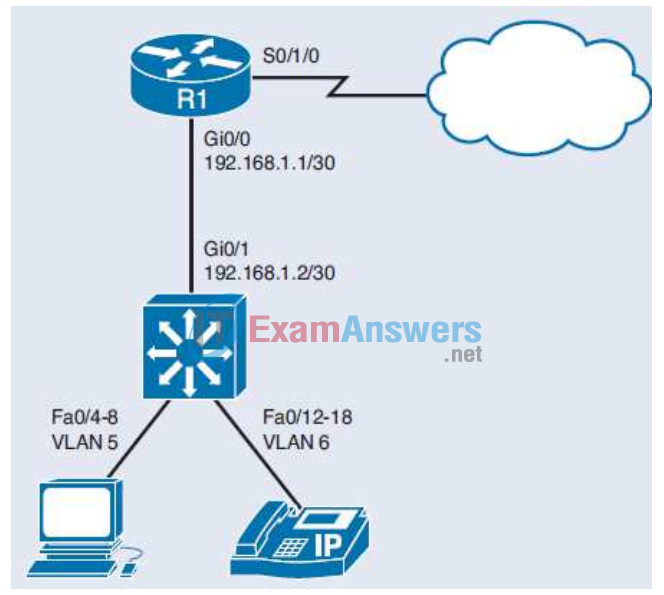
On which interface(s) would NAT be applied?
- Only S0/1/0
- Only Gi0/0
- Only on S0/1/0 and Gi0/0
- Only on Gi0/0 and Gi0/1
- Only on S0/1/0, Gi0/0, and Gi0/1
- On all interfaces
7. Which NAT solution allows external users to access an internal SFTP server on a network that uses private IP addresses?
- Dynamic NAT
- PAT
- Static NAT
- NAT overload
8. What are two disadvantages of NAT? (Choose two.)
- Uses too many legally registered addresses.
- Decreases the number of connections that can be used to the public network.
- Network device performance.
- End-to-end traceability is lost.
- Increased network costs.
- Increased provider costs.
9. What is the last step in configuring PAT with an address pool?
- Creating the access list
- Defining the address pool
- Binding the access list to the address pool
- Applying NAT to at least two interfaces
10. What parameter defines what internal addresses are translated by NAT?
- The access list
- The address pool
- The interface(s) that have the command ip nat inside applied
- The interface(s) that have the command ip nat outside applied
11. What is the effect of adding the keyword overload to a NAT configuration?
- More interfaces can participate in NAT.
- More internal address can be translated into one or more public addresses.
- The router is placed into stealth mode verifying that the address translation is not overtaxing the router hardware.
- Public IP addresses can be added to the NAT pool dynamically.
12. What is the most commonly deployed IPv6 NAT method recommended for all IPv6-based companies?
- NAT for IPv6
- IPv6 tunneling
- PAT for IPv6
- None of these
