CCNA 2 Routing and Switching Essentials v5 Chapter 4: Routing Concepts – Check Your Understanding Questions Answers
1. Which two statements correctly describe the components of a router? (Choose two.)
- RAM permanently stores the configuration file used during the boot sequence.
- ROM contains diagnostics executed on hardware modules.
- NVRAM stores a backup copy of the IOS used during the boot sequence.
- Flash memory does not lose its contents during a reboot.
- ROM contains the most current and most complete version of the IOS.
- Flash contains boot system commands to identify the location of the IOS.
2. Which three statements describe features of Cisco devices that perform routing? (Choose three.)
- The IP address of a LAN interface on a Layer 3 device provides the default gateway for hosts connected to that LAN.
- A routing protocol must be enabled in order for a Layer 3 device to build a routing table.
- Routing tables are volatile. When power is removed from a Layer 3 device, the routing table ceases to exist.
- A routing table is automatically created for directly connected, active LAN and WAN interfaces.
- A directly connected Layer 3 interface must be manually added to the routing table in order for routing to be enabled on that interface.
3. What address and prefix length is used when configuring an IPv6 default static route?
- ::/0
- ::1/128
- 0.0.0.0/0
- FF02::1/8
4. What is the purpose of a routing protocol?
- It is used to build and maintain ARP tables.
- It provides a method for segmenting and reassembling data packets.
- It allows an administrator to devise an addressing scheme for the network.
- It allows a router to share information about known networks with other routers.
- It provides a procedure for encoding and decoding data into bits for packet forwarding.
5. Which tasks can be accomplished by using the command history feature? (Choose two.)
- View a list of commands entered in a previous session.
- Recall up to 15 command lines by default.
- Set the command history buffer size.
- Recall previously entered commands.
- Save command lines in a log file for future reference.
6. During the process of encapsulation, how does the PC determine if the packet is destined for a host on a remote network?
- By checking the ARP cache for the destination host MAC address
- By querying the DNS server for the information of the destination host
- By sending a broadcast to the local LAN segment to see if there is any response
- By performing the AND operation on the destination IP address and its own subnet mask
7. When a router learns that multiple paths are available to a destination network from the same routing protocol, which factor is considered by a router to choose the best path to forward a packet?
- The lowest metric
- The order of paths on the routing table
- The fastest bandwidth of exiting interfaces
- The reliability value of the neighboring routers
8. Which two statements describe characteristics of load balancing? (Choose two.)
- Load balancing occurs when a router sends the same packet to different destination networks.
- Load balancing occurs when the same number of packets is sent over static and dynamic routes.
- Load balancing allows a router to forward packets over multiple paths to the same destination network.
- Unequal cost load balancing is supported by EIGRP.
- If multiple paths with different metrics to a destination exist, the router cannot support load balancing.
9. What is a Gateway of Last Resort?
- The IP address of another router
- The IP address of the Internet provider
- A term to describe a default gateway on a host device
- Where dropped packets are sent
10. Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the router port that is shown?
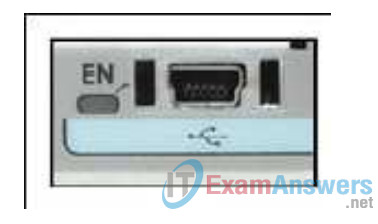
- To back up the IOS
- To configure the router
- To run an IOS from an alternative location
- To connect to a port on a switch
11. What code is used in the routing table to identify routes learned through EIGRP?
- C
- D
- L
- O
- S
12. Which two statements describe static routes? (Choose two.)
- They are created in interface configuration mode.
- They require manual reconfiguration to accommodate network changes.
- They automatically become the default gateway of the router.
- They are identified in the routing table with the prefix S.
- They are automatically updated whenever an interface is reconfigured or shut down.
13. The output of the show ip route command contains the following entry:
S 10.2.0.0 [1/0] via 172.16.2.2.
What value is indicated by the 1 in the [1/0] portion of the output?
- Metric
- Number of hops
- Administrative distance
- Interface ID through which the network can be reached
