CCNA 2 Routing and Switching Essentials v5 Chapter 3: VLANs – Check Your Understanding Questions Answers
1. What is the difference between an access port and a trunk port?
- A trunk port belongs to a single VLAN; an access port provides access for
multiple VLANs between switches. - An access port can have a native VLAN, but a trunk port cannot.
- An access port can have only one device attached.
- Multiple VLANs traverse a trunk port, but an access port can belong to a single VLAN.
2. Switch S1 and Switch S2 are both configured with ports in the Faculty, Students, Voice, Guest, Printing, and Admin VLANs. Each VLAN contains 12 users. How many subnets are needed to address the VLANs?
- 1
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
- 12
- 24
3. What mechanism is used to achieve the separation between different VLANs as they cross a trunk link?
- VLAN tagging using 802.1Q protocol
- VLAN tagging using 802.1p protocol
- VLAN multiplexing
- VLAN set as a native VLAN
4. What are two options to consider when configuring a trunk link between two switches? (Choose two.)
- The switchport nonegotiate command must be configured for trunks that use DTP.
- Port security cannot be configured on the trunk interfaces.
- The native VLAN must be the same on both ends of the trunk.
- Different encapsulation types can be configured on both ends of the trunk link.
- Trunk ports can be configured only on Gigabit Ethernet interfaces.
5. A 24-port switch has been configured to support three VLANs named Sales, Marketing, and Finance. Each VLAN spans four ports on the switch. The network administrator has deleted the Marketing VLAN from the switch. What two statements describe the status of the ports associated with this VLAN? (Choose two.)
- The ports are inactive.
- The ports are administratively disabled.
- The ports will become trunks to carry data from all remaining VLANs.
- The ports will remain part of the Marketing VLAN until reassigned to another VLAN.
- The ports were released from the Marketing VLAN and automatically reassigned to VLAN 1.
6. Which three statements are true about hosts that are configured in the same VLAN? (Choose three.)
- Hosts in the same VLAN must be on the same IP subnet.
- Hosts in different VLANs can communicate with the aid of only the Layer 2 switch.
- Hosts in the same VLAN share the same broadcast domain.
- Hosts in the same VLAN share the same collision domain.
- Hosts in the same VLAN comply with the same security policy.
- Hosts in the same VLAN must be on the same physical segment.
7. Refer to the exhibit. Host PC3 is unable to transfer data because it does not have the MAC address of the destination host. If PC3 sends out an ARP request broadcast, which of the other hosts will see the message?
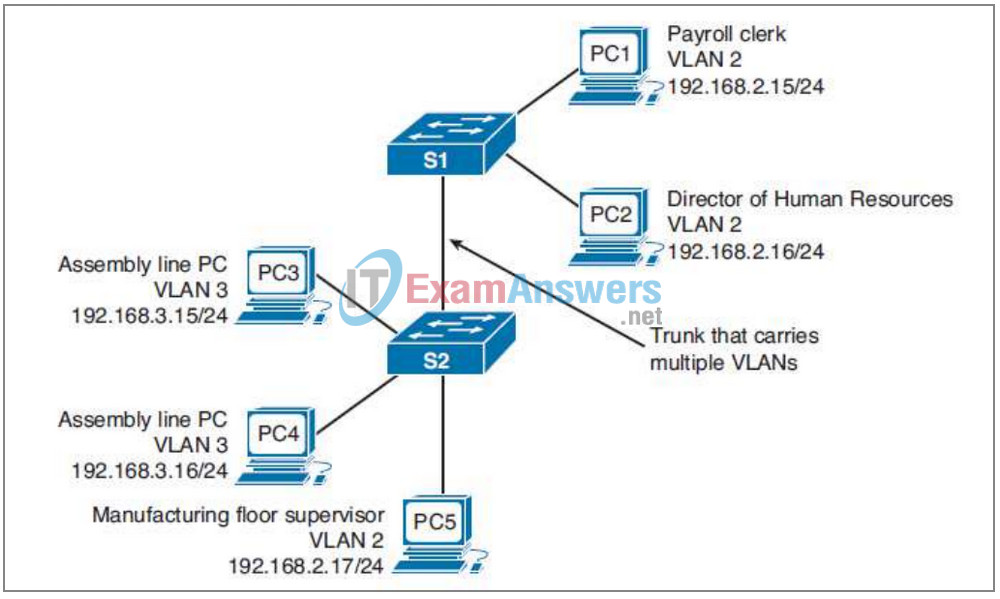
- Only PC3
- Only PC4
- Only PC4 and PC5
- PC1, PC2, PC4, and PC5
- PC1, PC2, PC3, PC4, and PC5
8. With each listed characteristic on the right, indicate in the blank on the left whether it reflects a normal range VLAN, an extended range VLAN, or VLAN 1. Use N for normal range VLAN, E for extended range VLAN, and 1 for VLAN 1.
______ 1–1005
______ 1006–4094
______ Stored in vlan.dat
______ Default management VLAN
______ Default native VLAN
______ All ports are a member of by default
______ Stored in running configuration file
9. Refer to the following configuration. Host 1 is connected to interface Fa0/4 with IP address 192.168.1.22/28. Host 2 is connected to interface Fa0/5 with IP address 192.168.1.33/28. Host 3 is connected to interface F0/6 with IP address 192.168.1.30/28. Select the three statements that describe the success of pinging from one host to another. (Choose three.)
Switch(config)# vlan 10 Switch(config-vlan)# name Faculty Switch(config-vlan)# vlan 20 Switch(config-vlan)# name Staff Switch(config-vlan)# interface range fa0/4 , fa0/6 Switch(config-if-range)# switchport mode access Switch(config-if-range)# switchport access vlan 10 Switch(config-if-range)# interface fa0/5 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access Switch(config-if)# switchport access vlan 20
- Host 1 can ping Host 2.
- Host 1 cannot ping Host 2.
- Host 1 can ping Host 3.
- Host 1 cannot ping Host 3.
- Host 2 can ping Host 3.
- Host 2 cannot ping Host 3.
10. Which three options accurately associate the Catalyst switch command with the result? (Choose three.)
- show vlan id vlan-id: displays information about a specific VLAN.
- show vlan: displays detailed information about all VLANs on the switch.
- show vlan brief: displays detailed information about all VLANs on the switch.
- show interfaces fa0/1 switchport: displays information about a specific port.
- show interfaces fa0/1: displays VLAN information about a specific port.
11. Match the commands with the correct descriptions.
______ switchport mode trunk
______ switchport mode dynamic desirable
______ switchport nonegotiate
______ switchport mode access
- Configures the port to negotiate a trunk
- Configures the trunk to not send DTP packets
- Configures the port as a permanent 802.1Q trunk
- Disables trunk mode
12. Match the problem definition with the correct problem description.
______ Native VLAN mismatch
______ Trunk mode mismatch
______ Incorrect VLAN list
______ VLAN subnet conflict
- Both switches are configured to dynamic auto and will not negotiate a link.
- Not all the VLANs needed are allowed to traverse a trunk.
- PCs on the same VLAN are not sharing the same address space.
- The VLAN configured for untagged frames is not the same on two switches connected by a trunk.
13. The ______ protocol is an industry standard for trunking.
14. Which Layer 2 security issue sends a frame destined for one VLAN to a different VLAN by adding more than one VLAN ID to the header?
- Double-tagging
- Switch spoofing
- PVLAN edge
- Plaintext vty access
15. Which two design considerations are best practices for switch VLAN design? (Choose two.)
- Unused ports should be left to the default configuration.
- The native VLAN should be an unused VLAN.
- All unused ports should be configured as a part of the black hole VLAN.
- All unused ports should be configured as a part of the native VLAN.
- A server should always be configured as a protected port.
- The management VLAN should be a VLAN not used by any type of user traffic.
- Disable DTP messages.
