Chapter 5 – Sections & Objectives
- 5.1 Basic Switch Configuration
- Configure initial settings on a Cisco switch.
- Configure switch ports to meet network requirements.
- 5.2 Switch Security: Management and Implementation
- Configure the management virtual interface on a switch.
- Configure the port security feature to restrict network access.
5.1 Basic Switch Configuration
5.1.1 Configure a Switch with Initial Settings
Switch Boot Sequence
- Power-on self test (POST).
- Run boot loader software.
- Boot loader performs low-level CPU initialization.
- Boot loader initializes the flash file system.
- Boot loader locates and loads a default IOS operating system software image into memory and passes control of the switch over to the IOS.
To find a suitable Cisco IOS image, the switch goes through the following steps:
- Step 1. It attempts to automatically boot by using information in the BOOT environment variable.
- Step 2. If this variable is not set, the switch performs a top-to-bottom search through the flash file system. It loads and executes the first executable file, if it can.
- Step 3. The IOS software then initializes the interfaces using the Cisco IOS commands found in the configuration file and startup configuration, which is stored in NVRAM.
Note: The boot system command can be used to set the BOOT environment variable. Use the show boot command to see to what the current IOS boot file is set.
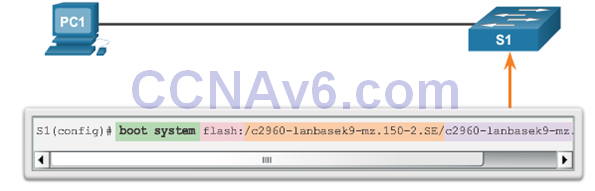

Recovering From a System Crash
- The boot loader can also be used to manage the switch if the IOS cannot be loaded.
- The boot loader can be accessed through a console connection by:
- 1.Connecting a PC by console cable to the switch console port. Unplug the switch power cord.
- 2.Reconnecting the power cord to the switch and press and hold the Mode button.
- 3.The System LED turns briefly amber and then solid green. Release the Mode button.
- The boot loader switch: prompt appears in the terminal emulation software on the PC.
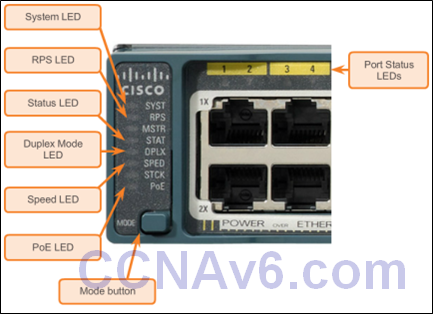
Switch LED Indicators
- Each port on Cisco Catalyst switches have status LED indicator lights.
- By default, these LED lights reflect port activity, but they can also provide other information about the switch through the Mode button.
- The following modes are available on Cisco Catalyst 2960 switches:
- System LED
- Redundant Power System (RPS) LED
- Port Status LED
- Port Duplex LED
- Port Speed LED
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) Mode LED
Preparing for Basic Switch Management
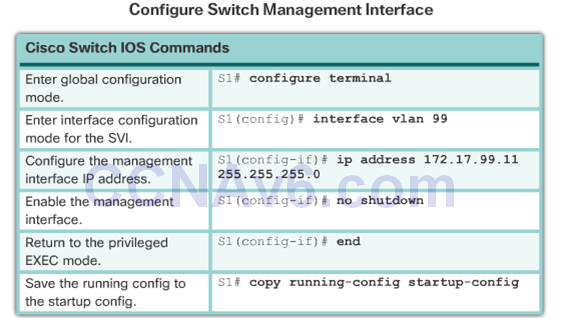
- To remotely manage a Cisco switch, it must be configured to access the network.
- A console cable is used to connect a PC to the console port of a switch for configuration.
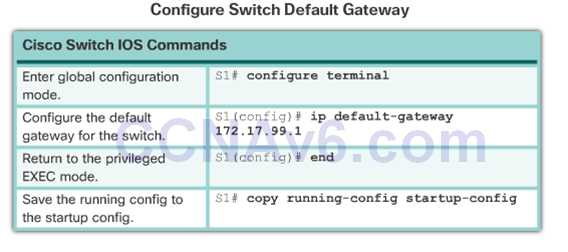
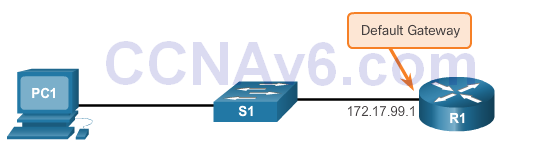
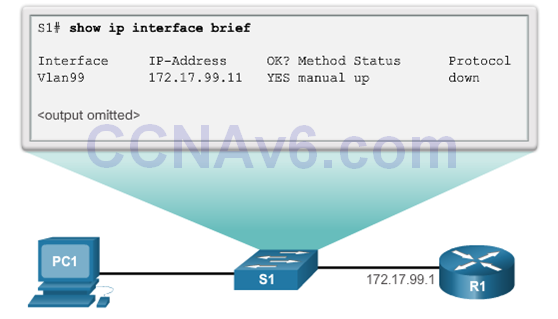
- The IP information (address, subnet mask, gateway) is to be assigned to a switch virtual interface (SVI).
- If managing the switch from a remote network, a default gateway must also be configured.
- Although these IP settings allow remote management and remote access to the switch, they do not allow the switch to route Layer 3 packets.
Configuring Switch Management Access
![]()
5.1.2 Configure Switch Ports
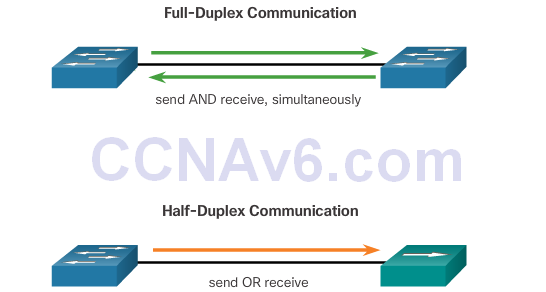
Duplex Communication
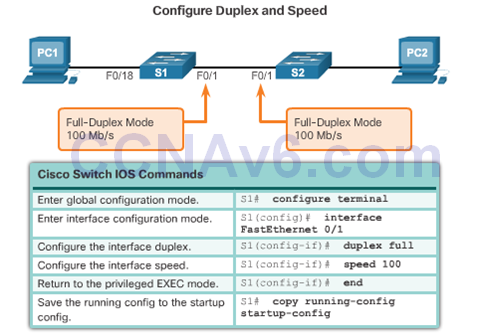
Configure Switch Ports at the Physical Layer
Auto-MDIX
- Certain cable types (straight-through or crossover) were historically required when connecting devices.
- The automatic medium-dependent interface crossover (auto-MDIX) feature eliminates this problem.
- When auto-MDIX is enabled, the interface automatically detects and appropriately configures the connection.
- When using auto-MDIX on an interface, the interface speed and duplex must be set to auto.
![]()
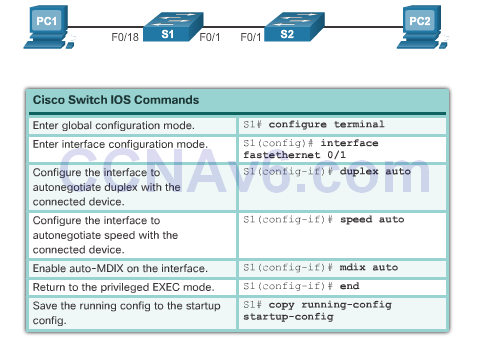
![]()
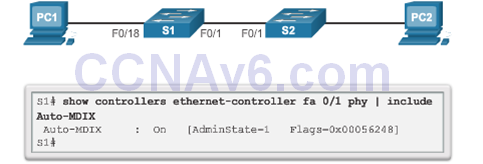
Verifying Switch Port Configuration
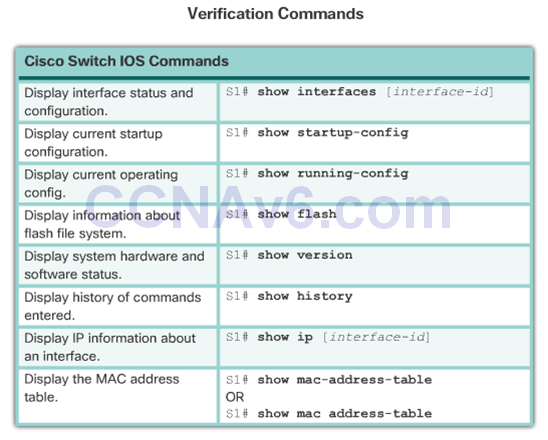
Network Access Layer Issue
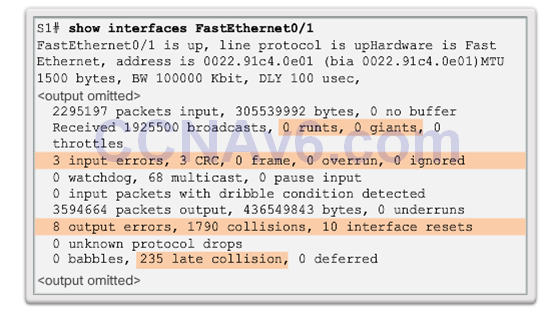
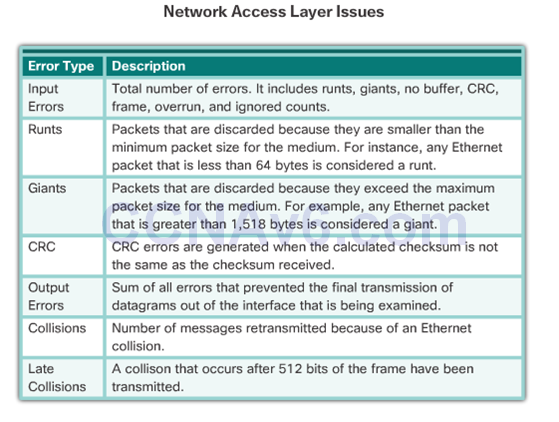
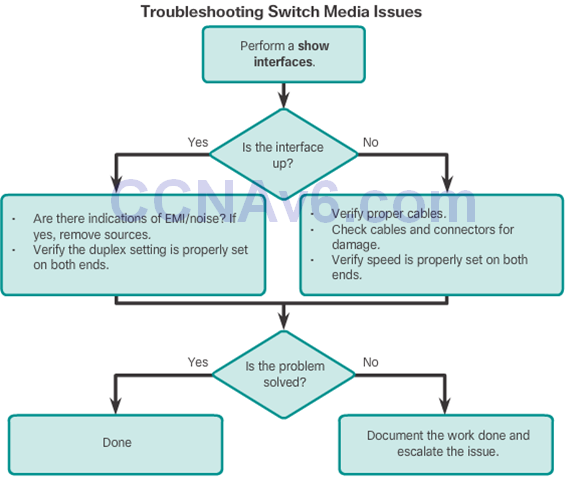
Troubleshooting Network Access Layer Issues
5.2 Switch Security: Management and Implementation
5.2.1 Secure Remote Access
SSH Operation
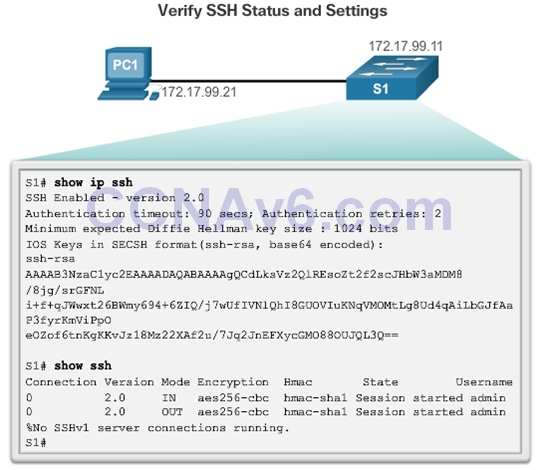
- Secure Shell (SSH) is a protocol that provides a secure (encrypted), command-line based connection to a remote device.
- Because of strong encryption features, SSH should replace Telnet for management connections.
- SSH uses TCP port 22, by default.
- Telnet uses TCP port 23.
- A version of the IOS software, including cryptographic (encrypted) features and capabilities, is required to enable SSH on Catalyst 2960 switches.
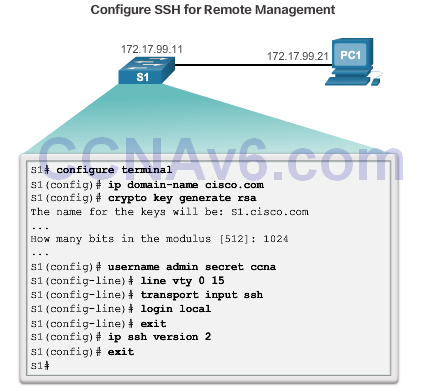
Configuring SSH
- Verify SHH Support – show ip ssh
- Configure the IP domain.
- Generate RSA key pairs.
- Configure user authentication.
- Configure the vty lines.
- Enable SSH version 2.
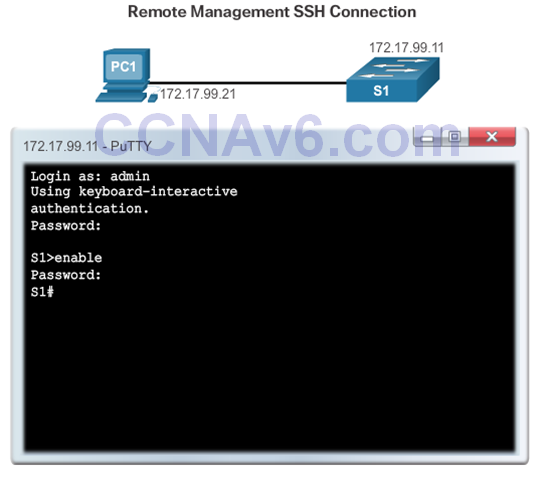
Verifying SSH
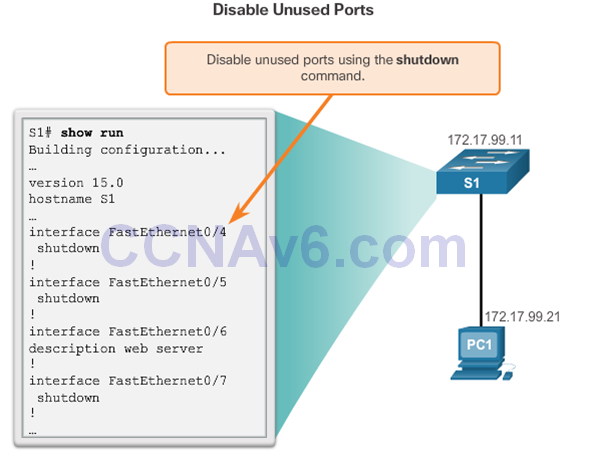
Secure Unused Ports
5.2.2 – Switch Port Security
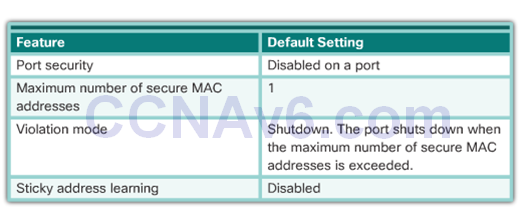
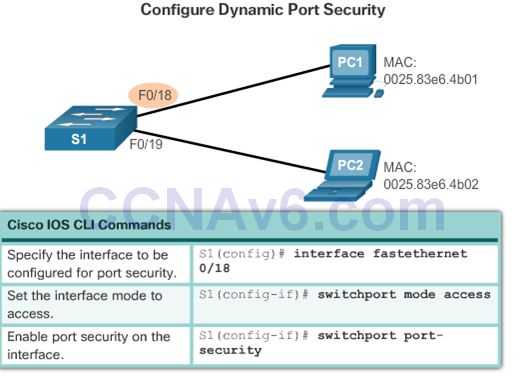
Port Security: Operation
- The MAC addresses of legitimate devices are allowed access, while other MAC addresses are denied.
- Any additional attempts to connect by unknown MAC addresses generate a security violation.
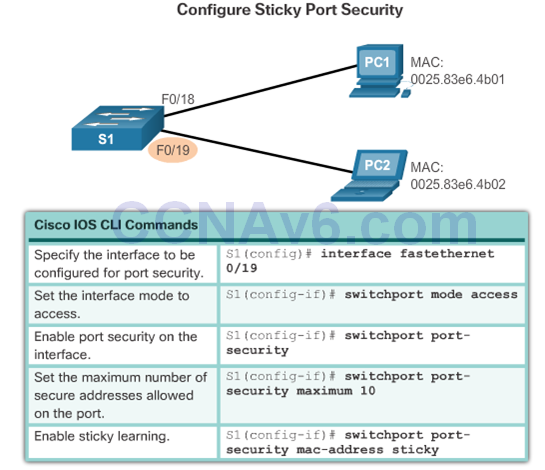
- Secure MAC addresses can be configured in a number of ways:
- Static secure MAC addresses – manually configured and added to running configuration – switchport port-security mac-address mac-address
- Dynamic secure MAC addresses – removed when switch restarts
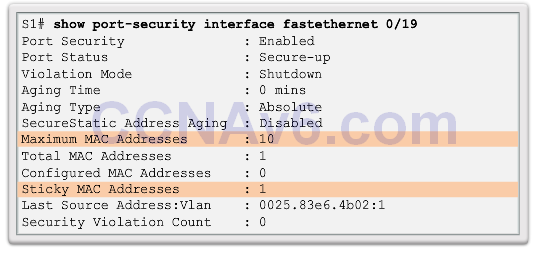
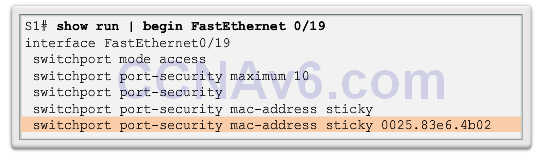
- Sticky secure MAC addresses – added to running configuration and learned dynamically – switchport port-security mac-address stickyinterface configuration mode command
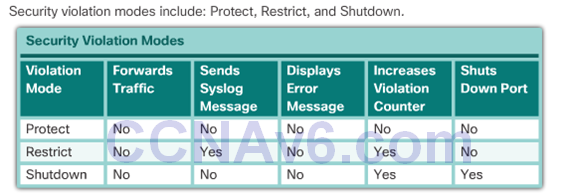
Port Security: Violation Modes
- IOS considers a security violation when:
- The maximum number of secure MAC addresses for that interface have been added to the CAM, and a station whose MAC address is not in the address table attempts to access the interface.
- There are three possible actions to take when a violation is detected:
- Protect – no notification received
- Restrict – notification received of security violation
- Shutdown
- switchport port-security violation {protect |restrict |shutdown} interface configuration mode command
Port Security: Configuring
Port Security: Verifying
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
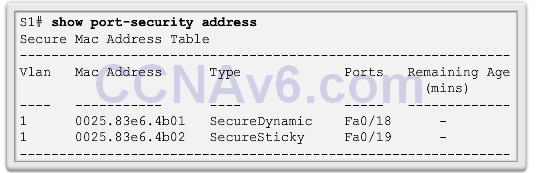
Ports in Error Disabled State
- A port security violation can put a switch in error disabled state.
- A port in error disabled is effectively shutdown.
- The switch communicates these events through console messages.
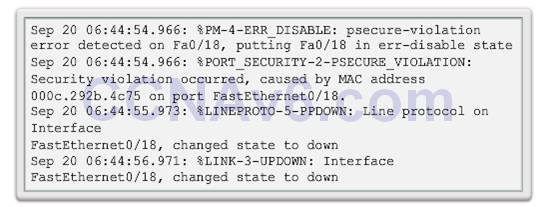
- The show interface command also reveals a switch port on error disabled state.
![]()
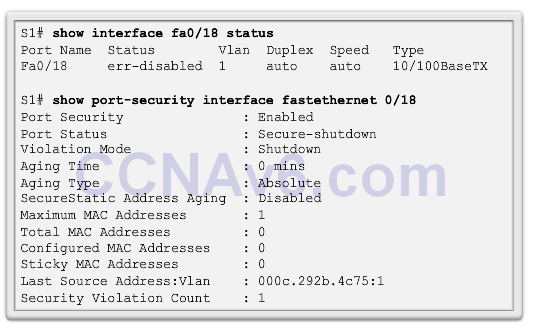
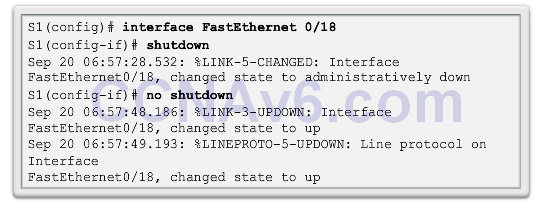
- A shutdown or no shutdown interface configuration mode command must be issued to re-enable the port.
![]()
5.3 Chapter Summary
- Cisco LAN switch boot sequence.
- Cisco LAN switch LED modes.
- How to remotely access and manage a Cisco LAN switch through a secure connection.
- Cisco LAN switch port duplex modes.
- Cisco LAN switch port security, violation modes, and actions.
- Best practices for switched networks.
- When a Cisco LAN switch is first powered on it goes through the following boot sequence:
- First, the switch loads a power-on self-test (POST) program stored in ROM. POST checks the CPU subsystem. It tests the CPU, DRAM, and the portion of the flash device that makes up the flash file system.
- Next, the switch loads the boot loader software. The boot loader is a small program stored in ROM and is run immediately after POST successfully completes.
- The boot loader performs low-level CPU initialization. It initializes the CPU registers, which control where physical memory is mapped, the quantity of memory, and its speed.
- The boot loader initializes the flash file system on the system board.
- Finally, the boot loader locates and loads a default IOS operating system software image into memory and gives control of the switch over to the IOS.
- If the Cisco IOS files are missing or damaged, the boot loader program can be used to reload or recover from the problem.
- The operational status of the switch is displayed by a series of LEDs on the front panel. These LEDs display such things as port status, duplex, and speed.
- An IP address is configured on the SVI of the management VLAN to allow for remote configuration of the device. A default gateway belonging to the management VLAN must be configured on the switch using the ip default-gateway command. If the default gateway is not properly configured, remote management is not possible.
- It is recommended that Secure Shell (SSH) be used to provide a secure (encrypted) management connection to a remote device to prevent the sniffing of unencrypted user names and passwords, which is possible when using protocols such as Telnet.
- One of the advantages of a switch is that it allows full-duplex communication between devices, effectively doubling the communication rate. Although it is possible to specify the speed and duplex settings of a switch interface, it is recommended that the switch be allowed to set these parameters automatically to avoid errors.
- Port security is only one defense against network compromise.
Section 5.1
Terms and Commands
- Power on Self-test (POST)
- Boot loader
- BOOT environment variable
- boot system
- show boot
- Mode button
- System LED
- boot loader switch:
- dir flash:
- System LED
- Redundant Power System (RPS) LED
- Port Status LED
- Port Duplex LED
- Port Speed LED
- Power Over Ethernet (POE) LED
- Switch virtual interface (SVI)
- VLAN
- Full-duplex
- Half-duplex
- Auto-mdix
- interface vlan 99
- ip default-gateway
- show ip interface brief
- duplex auto
- speed auto
- mdix auto
- show interfaces
- Input errors
- Runts
- Giants
- CRC Error
- Output errors
- Collisions
- Late Collisions
Section 5.2
Terms and Commands
- Secure Shell (SSH)
- show ip ssh version 2
- crypto key generate rsa
- crypto key zeroize rsa
- Username usernamesecret password
- transport input ssh
- login local
- show ip ssh
- Static Secure MAC Address
- Dynamic Secure MAC Address
- Sticky Secure MAC Address
- show port-security
- show port-security mac-address
- show port-security mac-address sticky
- show port-security interface
- Protect
- Restrict
- Shutdown
- switchport port-security violation{protect | restrict | shutdown}
- Switchport port-security maximum #
- show port-security interface interface-id
- show port-security address
- Secure-shutdown
Download Slide PowerPoint (pptx):
