Chapter 8 – Sections & Objectives
- 8.1 DHCPv4
- Explain how DHCPv4 operates in a small- to medium-sized business network.
- Configure a router as a DHCPv4 server.
- Configure a router as a DHCPv4 client.
- Troubleshoot a DHCP configuration for IPv4 in a switched network.
- 8.2 DHCPv6
- Explain the operation of DHCPv6.
- Configure stateless DHCPv6 for a small to medium-sized business.
- Configure stateful DHCPv6 for a small to medium-sized business.
- Troubleshoot a DHCP configuration for IPv6 in a switched network.
8.1 DHCPv4
8.1.1 DHCPv4 Operation
Introducing DHCPv4
- DHCPv4:
- assigns IPv4 addresses and other network configuration information dynamically
- useful and timesaving tool for network administrators
- dynamically assigns, or leases, an IPv4 address from a pool of addresses
- A Cisco router can be configured to provide DHCPv4 services.
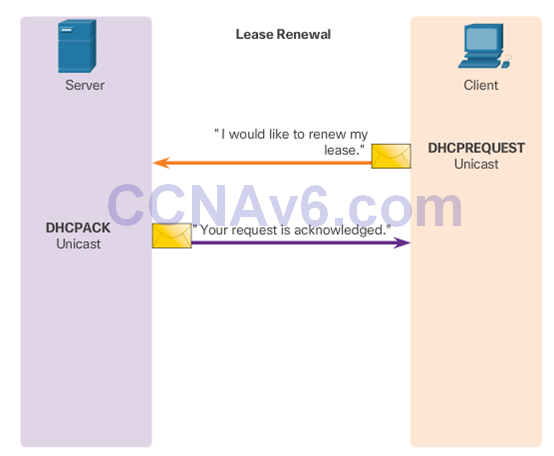
- Administrators configure DHCPv4 servers so that leases expire. Then the client must ask for another address, although the client is typically reassigned the same address.
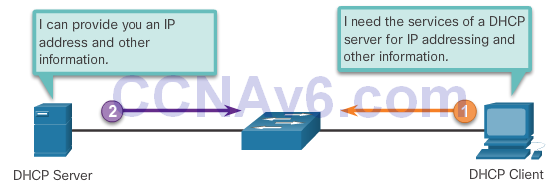
DHCPv4 Operation
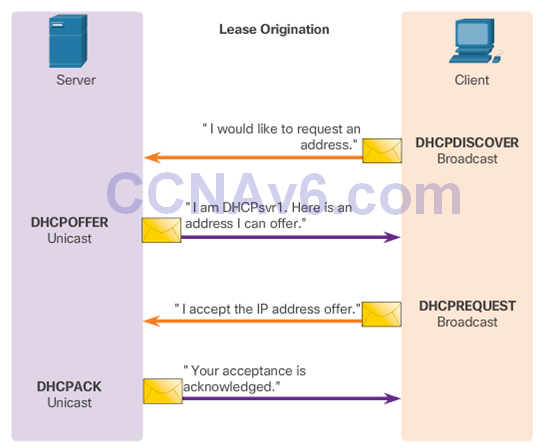
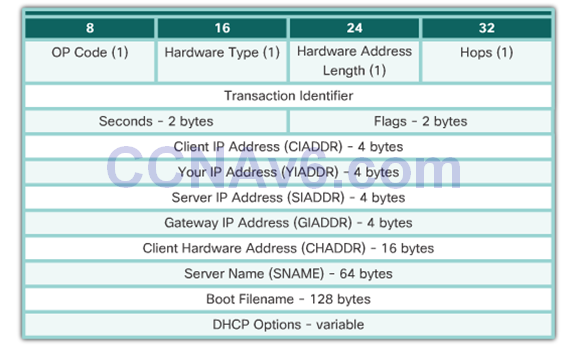
DHCPv4 Message Format
DHCPv4 Discover and Offer Messages
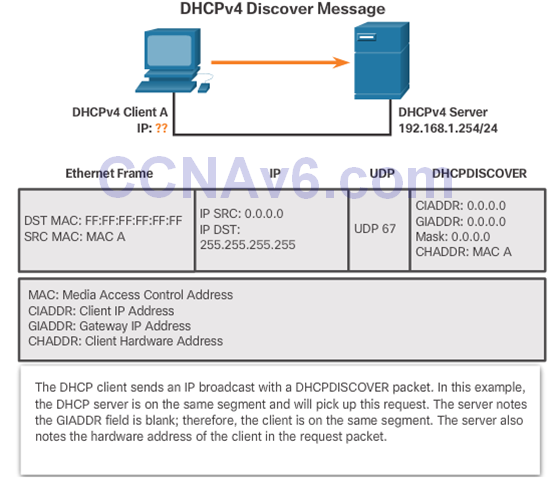
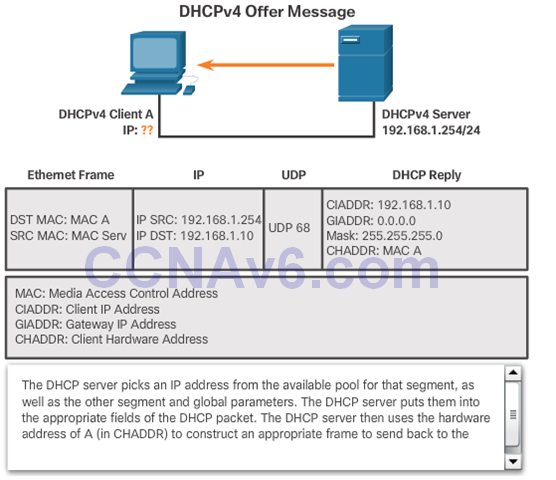
8.1.2 Configure DHCPv4 Server
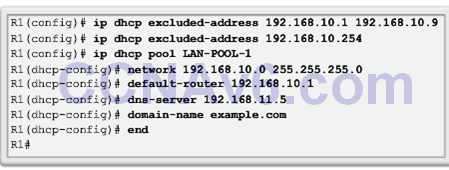
Configure a Basic DHCPv4 Server
- A Cisco router running the Cisco IOS software can be configured to act as a DHCPv4 server. To set up DHCP:
- Exclude addresses from the pool
- Set up the DHCP pool name.
- Define the range of addresses and subnet mask. Use the default-router command for the default gateway. Optional parameters that can be included in the pool – dns server, domain-name.
- To disable DHCP, use the no service dhcp command.
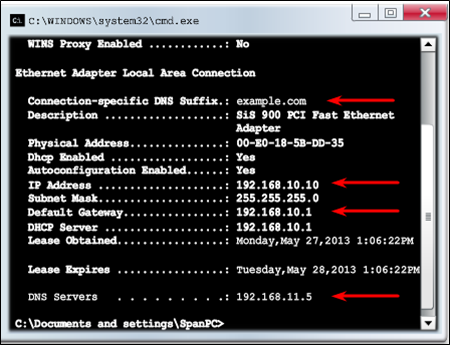
Verifying DHCPv4
- Commands to verify DHCP:
- show running-config | section dhcp
- show ip dhcp binding
- show ip dhcp server statistics
- On the PC, issue the ipconfig /all command.
DHCPv4 Relay
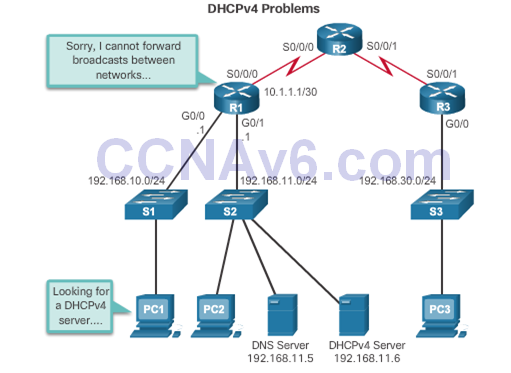
- Using an IP helper address enables a router to forward DHCPv4 broadcasts to the DHCPv4 server. Acting as a relay.
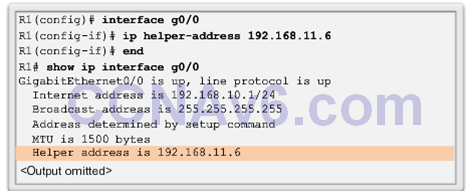
8.1.3 Configure DHCPv4 Client
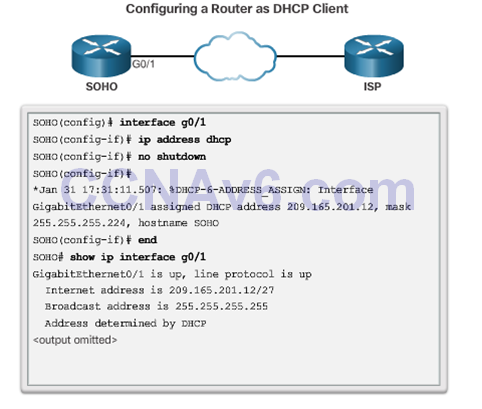
Configuring a Router as a DHCPv4 client
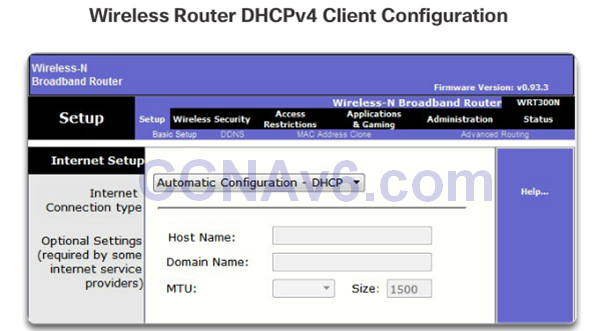
Configuring a Wireless Router as a DHCPv4 Client
8.1.4 Troubleshooting DHCPv4
Troubleshooting Tasks
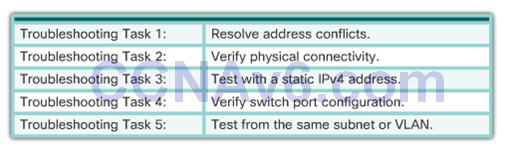
Verify Router DHCPv4 Configuration
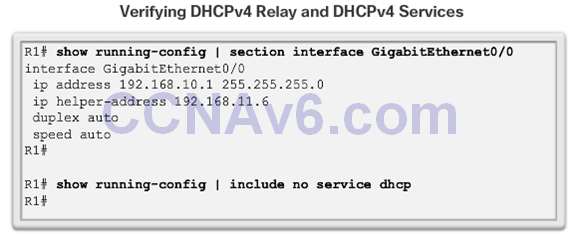
Debugging DHCPv4
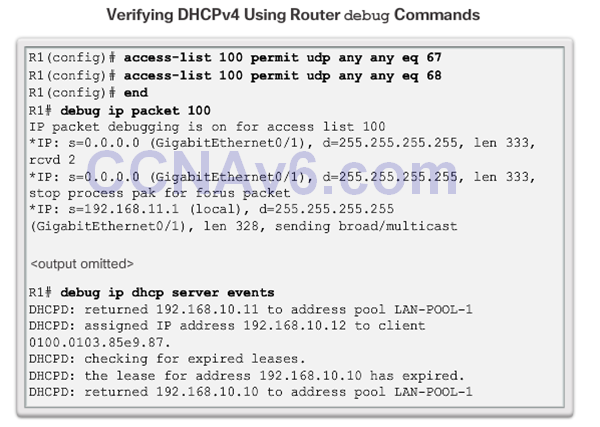
- The figure shows an extended ACL permitting only packets with UDP destination ports of 67 or 68. These are the typical ports used by DHCPv4 clients and servers when sending DHCPv4 messages. The extended ACL is used with the debug ip packetcommand to display only DHCPv4 messages.
8.2 DHCPv6
8.2.1 SLAAC and DHCPv6
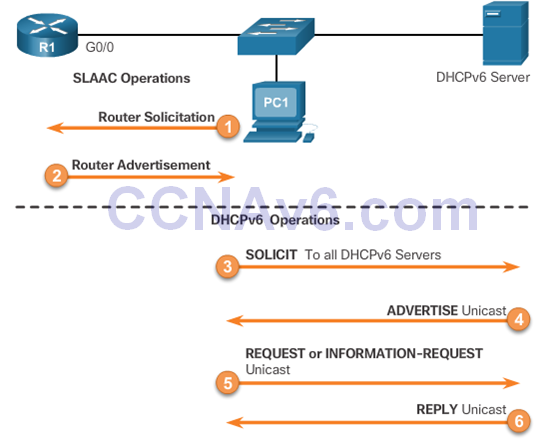
Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC)
- SLAAC uses ICMPv6 Router Solicitation and Router Advertisement messages to provide addressing and other configuration information that would normally be provided by a DHCP server:
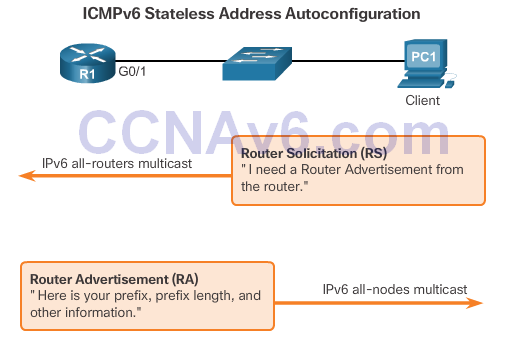
SLAAC Operation
- A router must have IPv6 routing enabled before it can send RA messages: Router(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
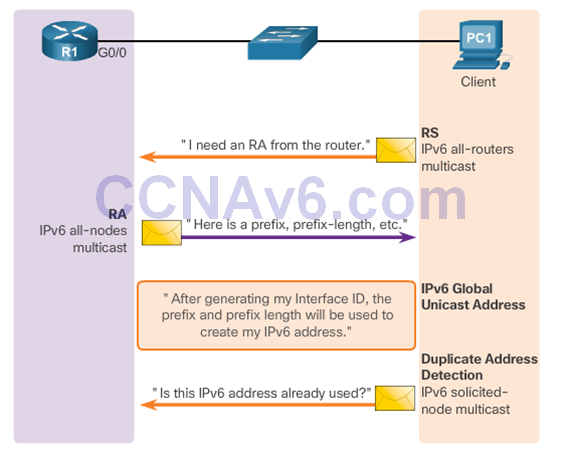
SLAAC and DHCPv6
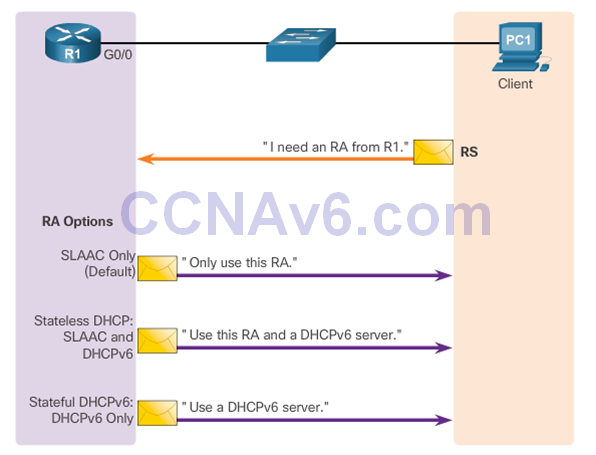
SLAAC Option
- SLAAC is the default option on Cisco routers. Both the M flag and the O flag are set to 0 in the RA, as shown in the figure.
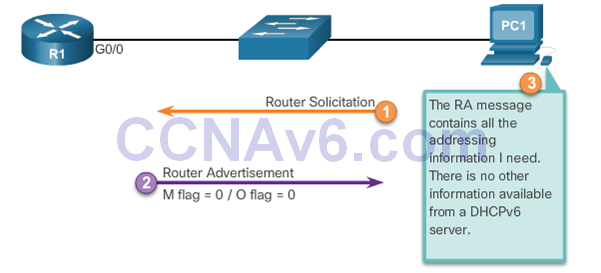
Stateless DHCPv6 Option
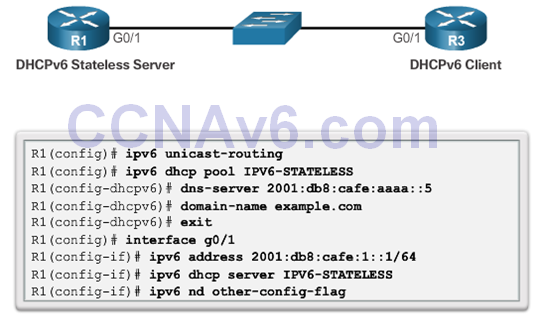
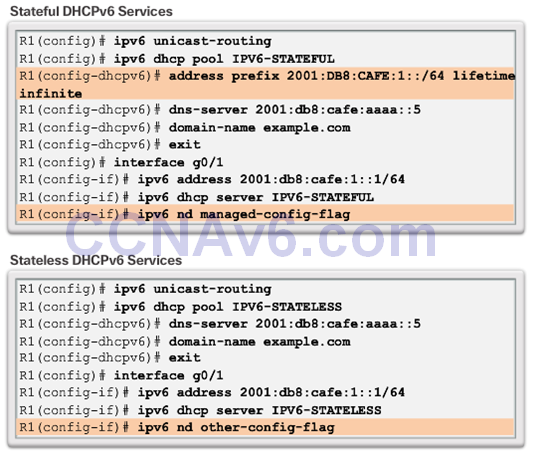
- To modify the RA message sent on the interface of a router to indicate stateless DHCPv6, use the following command: Router(config-if)#ipv6 nd other-config-flag
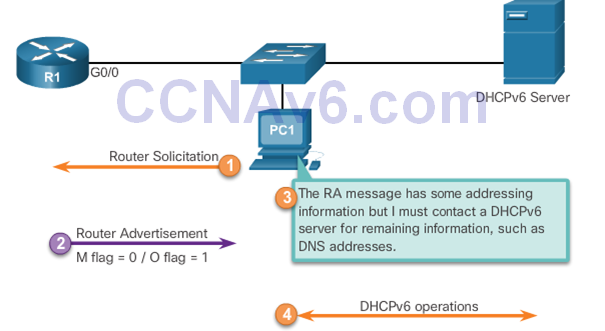
- This option is the most similar to DHCPv4. In this case, the RA message informs the client not to use the information in the RA message. All addressing information and configuration information must be obtained from a stateful DHCPv6 server. Router(config-if)# ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
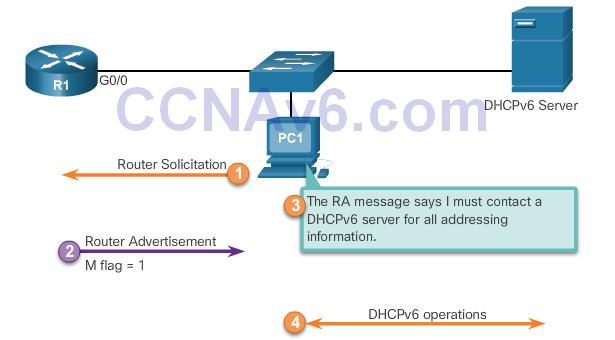
DHCPv6 Operations
- If stateless or stateful DHCPv6 is indicated in the RA message, then the device begins DHCPv6 client/server communications.
8.2.2 Stateless DHCPv6
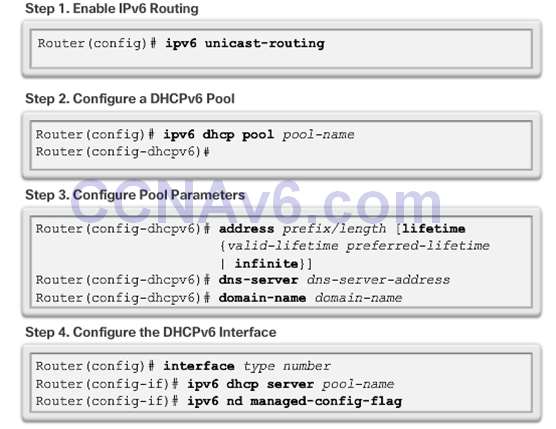
Configuring a Router as a Stateless DHCPv6 Server
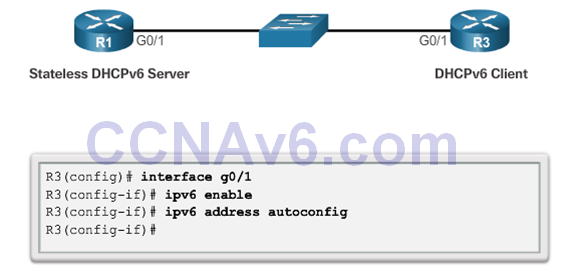
Configuring a Router as a Stateless DHCPv6 Client
Verifying Stateless DHCPv6
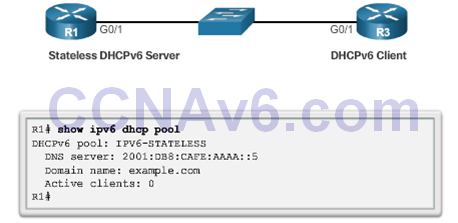
- Verify the stateless DHCP client using the following commands:
- show ipv6 interface
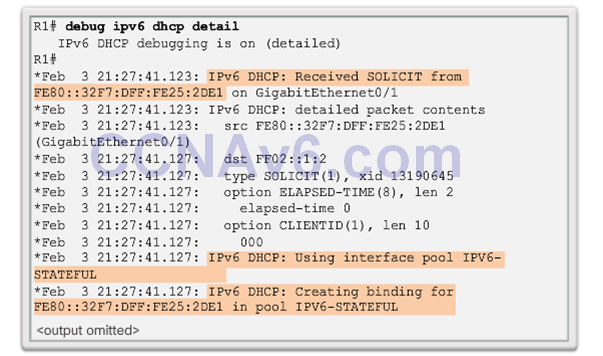
- debug ipv6 dhcp detail
8.2.3 Stateful DHCPv6 Server
Configuring a Router as a Stateful DHCPv6 Server
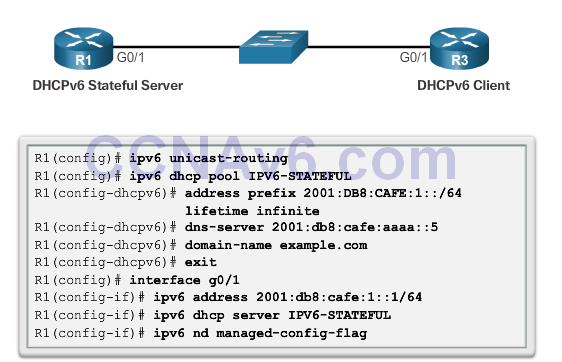
Configuring a Router as a Stateful DHCPv6 Client
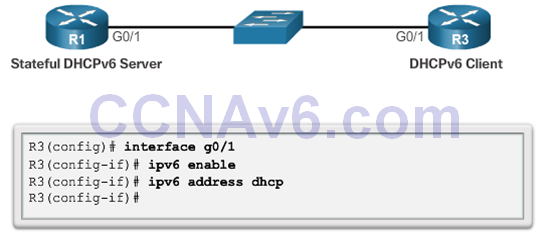
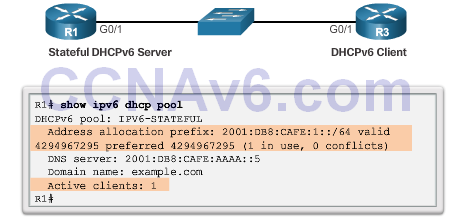
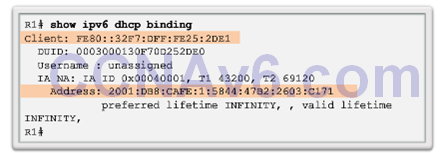
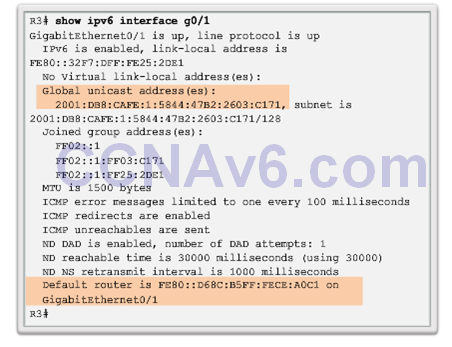
Verifying Stateful DHCPv6
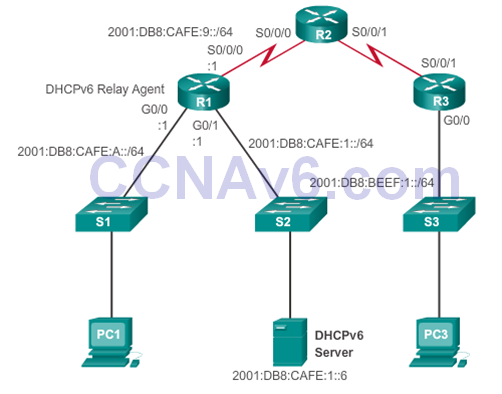
Configuring a Router as a DHCPv6 Relay Agent

8.2.4 Troubleshooting DHCPv6
Troubleshooting Tasks

Verify Router DHCPv6 Configuration
Debugging DHCPv6
8.3 Summary
Explain how DHCPv4 operates in a small- to medium-sized business network.
Configure a router as a DHCPv4 server.
Configure a router as a DHCPv4 client.
Troubleshoot a DHCP configuration for IPv4 in a switched network.
Explain the operation of DHCPv6.
Configure stateless DHCPv6 for a small to medium-sized business.
Configure stateful DHCPv6 for a small to medium-sized business.
Troubleshoot a DHCP configuration for IPv6 in a switched network.
Section 8.1
Terms and Commands
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- DHCP Discover (DHCPDISCOVER)
- DHCP Offer (DHCPOFFER)
- DHCP Request (DHCPREQUEST)
- DHCP Acknowledgment (DHCPACK)
- Operation (OP) Code
- Hardware Address Length
- Hops
- Transaction Identifier
- ip dhcp excluded-address
- ip dhcp pool pool-name
- default-router
- dns-server
- domain-name domain
- lease
- netbios-name-server
- no service dhcp
- show running-config | section dhcp
- show ip dhcp binding
- show ip dhcp server statistics
- ip helper-address
- ip address dhcp
- show ip dhcp conflict
- debug ip packet
- debug ip dhcp server events
Section 8.2
Terms and Commands
- Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC)
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (Stateful DHCPv6)
- Router Advertisement (RA) message
- Stateless DHCPv6 Option (Router Advertisement and DHCPv6)
- Stateful DHCPv6 (DHCPv6 only)
- Stateless DHCPv6 client
- Stateful DHCPv6 client
- DHCPv6 SOLICIT
- DHCPv6 ADVERTISE
- DHCPv6 REQUEST
- no ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
- no ipv6 nd other-config-flag
- ipv6 nd other-config-flag
- ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
- ipv6 dhcp server pool-name
- ipv6 enable
- ipv6 address autoconfig
- show ipv6 dhcp pool
- show ipv6 interface type number
- debug ipv6 dhcp detail
- address prefix
- ipv6 dhcp server pool-name
- ipv6 dhcp pool pool-name
- ipv6 enable
- ipv6 address dhcp
- show ipv6 dhcp binding
- ipv6 dhcp relay destination ipv6_address
- show ipv6 dhcp interface type number
Download Slide PowerPoint (pptx):
