Sections & Objectives
5.1 Modern Operating System
- Explain operating system requirements.
5.2 Operating System Installation
- Install a Microsoft Windows operating system.
5.3 Chapter Summary
5.1 Modern Operating Systems
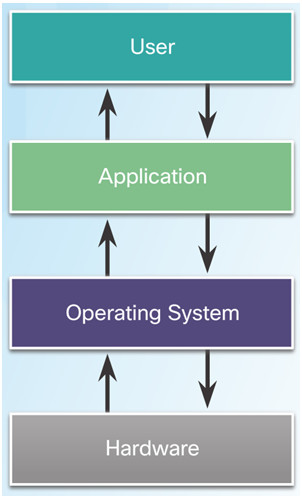
5.1.1 Operating System Terms and Characteristics
Terms
- Common terms describing operating systems include: multi-user, multitasking, multiprocessing and multithreading
Basic Functions of an Operating System (OS)
- Hardware Access
- File and Folder Management
- User Interface (CLI and GUI)
- Application Management
Processor Architecture
- Affects the performance of the computer.
- CPUs contain storage locations called registers.
- Registers can be 32-bits or 64-bits long.
5.1.2 Types of Operating Systems
Desktop Operating Systems
- Intended for use in SOHO environment.
- Supports a single user.
- Shares files and folders on a small network with limited security.
- Microsoft Windows, Apple Mac OS, and Linux are a few examples.
Network Operating Systems
- Contains features that increase functionality in a networked environment
- Supports multiple users.
- Provides increased security compared to desktop operating systems
5.1.3 Customer Requirements for an Operating System
OS Compatible Applications and Environments
Before recommending an OS, the technician must:
- Review budget constraints.
- Learn how the computer will be used.
- Determine which types of applications will be installed.
- Determine if a new computer needs to be purchased?
Minimum Hardware Requirements and Compatibility with the OS Platform
- The OS minimum requirements must be met for optimal operation.
- Some applications may also have specific hardware requirements.
- Upgrades may be necessary.
- RAM, hard drives, CPU, video card, motherboard are a few common upgradable components.
- Microsoft Compatibility Center can be a good resource.
5.1.4 Operating Systems Upgrade
Checking OS Compatibility
- New version of an OS brings new functionality and better performance.
- Support for older hardware may be dropped.
- New hardware may require latest OS versions.
- Make sure to check OS compatibility before upgrading the OS.
- Microsoft’s Upgrade Assistant and Upgrade Advisor can be helpful tools.
Windows OS Upgrades
- Upgrading Windows may be faster than performing a full install.
- The installed version of an OS determine the upgrades options.
- A full data backup is strongly recommended before upgrading.
Data Migration
- User data must be transferred after a new installation.
- User State Migration Tool and Windows Easy Transfer are tools designed to help the transfer process.
5.2 Operating System Installation
5.2.1 Storage Device Setup Procedures
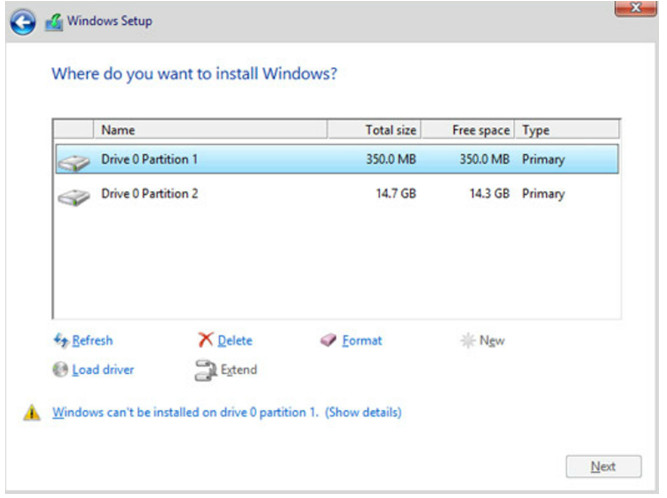
Storage Device Types
- Hard Disk Drives
- Flash Memory-Based Drives (USB Flash Drives, SSDs, SSHDs and eMMC)
Hard Drive Partitioning
- Logical divisions inside a disk.
- Proper partitioning is crucial for a correct boot process.
- MBR and GPT are the two most popular partition scheme standards.
File Systems
- File systems define how data is written within a partition.
- Different OSs, support different file systems.
- FAT32, NTFS, exFAT, CCFS and NFS are common file systems supported by Windows-based OSs.
OS Installation with Default Settings
- The installer program applies the most common settings.
- Preferred by inexperienced users.
- Allows for very little customization.
- Windows allows for granular customization after the default setting installation is complete.
Account Creation
- User accounts allow multiple users to share a computer.
- Common Windows account types are Administrator, Standard, and Guest.
Finalize the Installation
- Use Windows Update to check for updates after the installation is complete.
- Use Device Manager to verify that all hardware was properly installed.
5.2.2 Custom Installation Options
Disk Cloning
- Good solution to speed up bulk installations
- Uses a single OS installation as base system to create multiple clone systems.
Other Installation Methods
- Windows has several different types of Custom Installations including network installation and image-based installation.
- Other types of Custom Installations include Windows Advanced Startup Options, Refresh your PC (Windows 8.x only), System Restore, Upgrade, Repair installation, Remote network installation, Recovery partition, and Refresh/restore.
Network Installation
- Relies on a network connection to deploy the installation files.
- Network Installation methods include Remote Network Installation and Unattended Installation.
Restore, Refresh, and Recover
- Some tools are also used to perform Custom Installations
- These tools include Windows System Restore, Windows Refresh your PC, and Windows Recovery Partition.
System Recovery Options
- Used to recover after a system failure.
- Popular recovery tools are:
- Windows Advanced Startup Options (Win 8.x)
- System Recovery Options (Windows 7 & Vista)
- Factory Recovery Partition
5.2.3 Boot Sequence and Registry Files
Windows Boot Process
- Common boot steps are: POST execution, locating and loading CMOS configurations, locating and loading bootloaders, locating and loading the OS.
- Windows Boot Loader and Windows Boot Manager are programs used to manage Windows startup.
Startup Modes
- Windows Startup Modes allow for troubleshooting when Windows fails to start.
- Windows Startup Modes include: Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking, Safe Mode with Command Prompt and Last Known Good Configuration.
Windows Registry
- All Windows settings are stored as key-values pairs in the Windows Registry
- Extreme caution must be taken when working with the Registry.
5.2.4 Multiboot
Multiboot Procedures
- It is possible to install multiple OSs in one computer.
- BOOTMGR manages multiple versions of Windows installed on a single computer.
Disk Management Utility
- Many tasks can be accomplished through Disk Management Utility, including: view drive status, extend partitions, split partitions, assign drive letters, add drives and add arrays.
Partitions
- Logical divisions created inside a drive to host file systems.
- Partitions can be extended or shrunk using the Disk Management Utility
Drive Mapping or Drive Letter Assignment
- In Windows, assigning letters to name physical or logical drives is called drive mapping or drive letter assignment.
- Disk Management Utility can also be used to manage drive letter assignment.
5.2.5 Disk Directories
Directory Structures
- Designed to store files and folders.
- A disk must be initialized and formatted if Windows cannot recognize its file systems.
- Formatting a disk or partition creates a file system.
- Formatted disks or partitions must be mounted before use.
User and System File Locations
- System files are files critical to the OS operation.
- User files are files belonging to a user and of little significance to the OS.

Attributes
- File extensions identify file types in Windows and must adhere to Windows Naming Convention.
- File attributes define how files can be handled.
- Common file attributes are READ, ARCHIVE, SYSTEM and HIDDEN.
Application, File, and Folder Properties
- Right-click on a file, application or folder to see its properties.
- Application and File Properties are different than Folder Properties.
5.3 Chapter Summary
This chapter introduced computer operating systems. As a technician, you should be skilled at installing Windows® operating systems. The following concepts from this chapter are important to remember:
- Several different operating systems are available, and you must consider the customer’s needs and environment when choosing an OS.
- The main steps in setting up a customer’s computer include preparing the drive, installing the OS, creating user accounts, and configuring installation options.
