Network Defense (NetDef) Course Final Exam Answers
Modules 1 – 11 of the Network Defense (NetDef) course Final Answers
1. What is a characteristic of a layered defense-in-depth security approach?
- When one device fails, another one takes over.
- One safeguard failure does not affect the effectiveness of other safeguards.
- Three or more devices are used.
- Routers are replaced with firewalls.
2. What device would be used as the third line of defense in a defense-in-depth approach?
- internal router
- edge router
- host
- firewall
3. Match the Security Onion tool with the description.
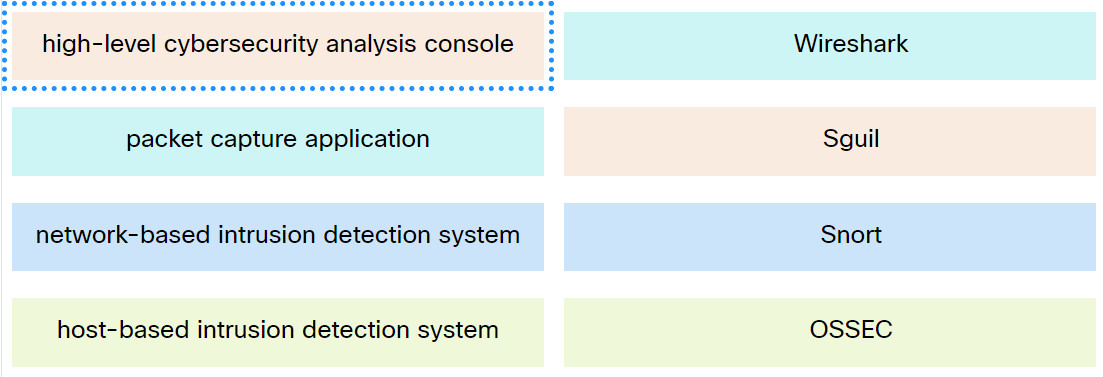
Network Defense (NetDef) Course Final Exam
4. Which wireless standard made AES and CCM mandatory?
- WEP
- WEP2
- WPA
- WPA2
5. In a comparison of biometric systems, what is the crossover error rate?
- rate of acceptability and rate of false negatives
- rate of rejection and rate of false negatives
- rate of false negatives and rate of false positives
- rate of false positives and rate of acceptability
6. What are two recommended steps to protect and secure a wireless network? (Choose two.)
- Use WPA2-AES encryption.
- Use the default SSID.
- Update firmware.
- Locate the wireless router where it is accessible to users.
- Enable remote management.
7. What is a feature of virtual LANs (VLANs)?
- A single collision domain is enabled on a switch that is shared between VLANs.
- Communication between different VLANs on the one switch is enabled by default.
- Switch port utilization is decreased because each port is only associated with one broadcast domain.
- Logical segmentation is provided by creating multiple broadcast domains on a single switch.
8. What is an example of privilege escalation attack?
- A DDoS attack is launched against a government server and causes the server to crash.
- A port scanning attack finds that the FTP service is running on a server that allows anonymous access.
- A threat actor sends an email to an IT manager to request the root access.
- A threat actor performs an access attack and gains the administrator password.
9. What is the principle behind the nondiscretionary access control model?
- It applies the strictest access control possible.
- It allows access based on attributes of the object be to accessed.
- It allows access decisions to be based on roles and responsibilities of a user within the organization.
- It allows users to control access to their data as owners of that data.
10. Which two features are included by both TACACS+ and RADIUS protocols? (Choose two.)
- utilization of transport layer protocols
- separate authentication and authorization processes
- password encryption
- 802.1X support
- SIP support
11. Refer to the exhibit. A router has an existing ACL that permits all traffic from the 172.16.0.0 network. The administrator attempts to add a new ACE to the ACL that denies packets from host 172.16.0.1 and receives the error message that is shown in the exhibit. What action can the administrator take to block packets from host 172.16.0.1 while still permitting all other traffic from the 172.16.0.0 network?

- Create a second access list denying the host and apply it to the same interface.
- Manually add the new deny ACE with a sequence number of 15.
- Manually add the new deny ACE with a sequence number of 5.
- Add a deny any any ACE to access-list 1.
12. Which command is used to activate an IPv6 ACL named ENG_ACL on an interface so that the router filters traffic prior to accessing the routing table?
- ipv6 traffic-filter ENG_ACL in
- ipv6 traffic-filter ENG_ACL out
- ipv6 access-class ENG_ACL out
- ipv6 access-class ENG_ACL in
13. In which configuration would an outbound ACL placement be preferred over an inbound ACL placement?
- when the ACL is applied to an outbound interface to filter packets coming from multiple inbound interfaces before the packets exit the interface
- when an outbound ACL is closer to the source of the traffic flow
- when an interface is filtered by an outbound ACL and the network attached to the interface is the source network being filtered within the ACL
- when a router has more than one ACL
14. What are two differences between stateful and stateless firewalls? (Choose two.)
- A stateless firewall is able to filter sessions that use dynamic port negotiations while a stateful firewall cannot.
- A stateless firewall will examine each packet individually while a stateful firewall observes the state of a connection.
- stateless firewall provides more stringent control over security than a stateful firewall.
- A stateless firewall will provide more logging information than a stateful firewall.
- A stateful firewall will prevent spoofing by determining whether packets belong to an existing connection while a stateless firewall follows pre-configured rule sets.
15. Which statement describes a typical security policy for a DMZ firewall configuration?
- Traffic that originates from the inside interface is generally blocked entirely or very selectively permitted to the outside interface.
- Traffic that originates from the DMZ interface is selectively permitted to the outside interface.
- Return traffic from the inside that is associated with traffic originating from the outside is permitted to traverse from the inside interface to the outside interface.
- Traffic that originates from the outside interface is permitted to traverse the firewall to the inside interface with few or no restrictions.
- Return traffic from the outside that is associated with traffic originating from the inside is permitted to traverse from the outside interface to the DMZ interface.
16. Which type of firewall makes use of a proxy server to connect to remote servers on behalf of clients?
- stateless firewall
- application gateway firewall
- stateful firewall
- packet filtering firewall
17. What is the result in the self zone if a router is the source or destination of traffic?
- Only traffic that is destined for the router is permitted.
- Only traffic that originates in the router is permitted.
- No traffic is permitted.
- All traffic is permitted.
18. Designing a ZPF requires several steps. Which step involves dictating the number of devices between most-secure and least-secure zones and determining redundant devices?
- identify subsets within zones and merge traffic requirements
- design the physical infrastructure
- establish policies between zones
- determine the zones
19. Which statement describes Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall operation?
- The pass action works in only one direction.
- Router management interfaces must be manually assigned to the self zone.
- Service policies are applied in interface configuration mode.
- A router interface can belong to multiple zones.
20. Which cloud security domain describes controls related to securing the data itself?
- Data Security and Encryption
- Application Security
- Security as a Service
- Infrastructure Security
21. Which two advantages in security controls are provided by software-defined networks (SDN) over traditional network security solutions? (Choose two.)
- offer more security features than hardware firewalls
- easier insertion into the traffic path
- apply to assets based on more flexible criteria than hardware firewalls
- easier network isolation without constraints of physical hardware
- higher performance than hardware firewalls
22. What is the function of SDKs in application development?
- to provide a repository of code to reduce time and cost of application development
- to maintain data integrity and identify malicious input
- to store precompiled SQL statements that execute tasks
- to verify software can run under required security settings
- to prevent software from being reverse engineered by replacing sensitive data with fictional data
23. A company is using a public cloud provider to host its software development and distribution processes. What two cloud resources is the company solely responsible for in the shared security responsibility model? (Choose two.)
- network control
- customer endpoints
- application
- data
- identity management
24. A company implements a security policy that ensures that a file sent from the headquarters office to the branch office can only be opened with a predetermined code. This code is changed every day. Which two algorithms can be used to achieve this task? (Choose two.)
- MD5
- AES
- SHA-1
- HMAC
- 3DES
25. What are two methods to maintain certificate revocation status? (Choose two.)
- CRL
- OCSP
- subordinate CA
- LDAP
- DNS
26. Before data is sent out for analysis, which technique can be used to replace sensitive data in nonproduction environments to protect the underlying information?
- steganography
- steganalysis
- software obfuscation
- data masking substitution
27. Which technology would be used to create the server logs generated by network devices and reviewed by an entry level network person who works the night shift at a data center?
- ACL
- VPN
- NAT
- syslog
28. Which two application layer protocols manage the exchange of messages between a client with a web browser and a remote web server? (Choose two.)
- HTTPS
- DNS
- HTML
- DHCP
- HTTP
29. How can IMAP be a security threat to a company?
- It can be used to encode stolen data and send to a threat actor.
- An email can be used to bring malware to a host.
- Encrypted data is decrypted.
- Someone inadvertently clicks on a hidden iFrame.
30. Refer to the exhibit. Which technology generated the event log?
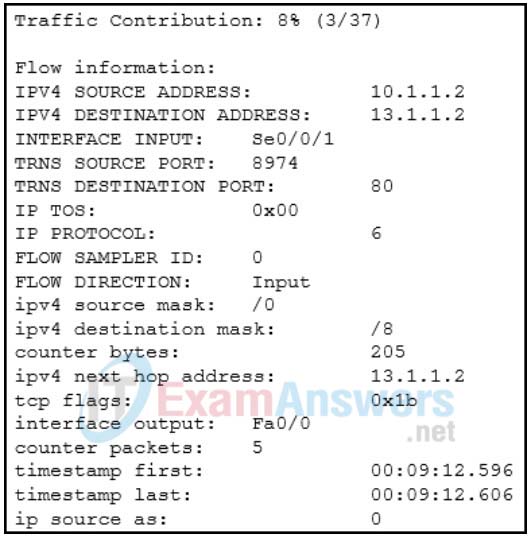
- web proxy
- syslog
- Netflow
- Wireshark
31. Which two tools have a GUI interface and can be used to view and analyze full packet captures? (Choose two.)
- Wireshark
- Splunk
- Cisco Prime Network Analysis Module
- nfdump
- tcpdump
32. Which information can be provided by the Cisco NetFlow utility?
- source and destination UDP port mapping
- security and user account restrictions
- peak usage times and traffic routing
- IDS and IPS capabilities
33. A network administrator is reviewing server alerts because of reports of network slowness. The administrator confirms that an alert was an actual security incident. What is the security alert classification of this type of scenario?
- false positive
- true negative
- true positive
- false negative
34. A network administrator is trying to download a valid file from an internal server. However, the process triggers an alert on a NMS tool. What condition describes this alert?
- false positive
- true positive
- false negative
- true negative
35. What is indicated by a Snort signature ID that is below 3464?
- This is a custom signature developed by the organization to address locally observed rules.
- The SID was created by Sourcefire and distributed under a GPL agreement.
- The SID was created by the Snort community and is maintained in Community Rules.
- The SID was created by members of EmergingThreats.
36. A network administrator is setting up a web server for a small advertising office and is concerned with data availability. The administrator wishes to implement disk fault tolerance using the minimum number of disks required. Which RAID level should the administrator choose?
- RAID 5
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 6
37. Which three security services are provided by digital signatures? (Choose three.)
- authenticates the source
- guarantees data has not changed in transit
- provides data encryption
- provides nonrepudiation using HMAC functions
- provides confidentiality of digitally signed data
- authenticates the destination
38. A company is deploying a customer service web application on AWS. A network administrator is installing and configuring a VM instance. Which three actions should the administrator take to protect the VM? (Choose three.)
- Disable unneeded ports and services.
- Enforce account management policies.
- Configure RAID to ensure storage fault tolerance.
- Plan subnet placement.
- Deploy an advanced firewall appliance.
- Install an IPS appliance in the VM.
39. What is the purpose of mobile device management (MDM) software?
- It is used to create a security policy.
- It is used to identify potential mobile device vulnerabilities.
- It is used by threat actors to penetrate the system.
- It is used to implement security policies, setting, and software configurations on mobile devices.
40. Which protocol would be used to provide security for employees that access systems remotely from home?
- Telnet
- WPA
- SSH
- SCP
41. A company has a file server that shares a folder named Public. The network security policy specifies that the Public folder is assigned Read-Only rights to anyone who can log into the server while the Edit rights are assigned only to the network admin group. Which component is addressed in the AAA network service framework?
- automation
- authorization
- accounting
- authentication
42. To facilitate the troubleshooting process, which inbound ICMP message should be permitted on an outside interface?
- echo request
- echo reply
- time-stamp reply
- time-stamp request
- router advertisement
43. Which two statements describe the effect of the access control list wildcard mask 0.0.0.15? (Choose two.)
- The last four bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
- The first 32 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
- The first 28 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
- The first 28 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
- The last five bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
- The last four bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
44. When implementing components into an enterprise network, what is the purpose of a firewall?
- A firewall is a system that stores vast quantities of sensitive and business-critical information.
- A firewall is a system that enforces an access control policy between internal corporate networks and external networks.
- A firewall is a system that is designed to secure, monitor, and manage mobile devices, including corporate-owned devices and employee-owned devices.
- A firewall is a system that inspects network traffic and makes forwarding decisions based solely on Layer 2 Ethernet MAC addresses.
45. Which ICMP message type should be stopped inbound?
- unreachable
- source quench
- echo-reply
- echo
46. When ACLs are configured to block IP address spoofing and DoS flood attacks, which ICMP message should be allowed both inbound and outbound?
- source quench
- echo
- unreachable
- echo reply
47. What are two elements that form the PRI value in a syslog message? (Choose two.)
- header
- timestamp
- facility
- severity
- hostname
48. Which two options are network security monitoring approaches that use advanced analytic techniques to analyze network telemetry data? (Choose two.)
- NBAD
- NBA
- IPFIX
- Snorby
- Sguil
- NetFlow
49. What is a characteristic of a probabilistic analysis in an alert evaluation?
- each event an inevitable result of antecedent causes
- random variables that create difficulty in knowing the outcome of any given event with certainty
- precise methods that yield the same result every time by relying on predefined conditions
- analysis of applications that conform to application/networking standards
50. Match the security policy with the description.
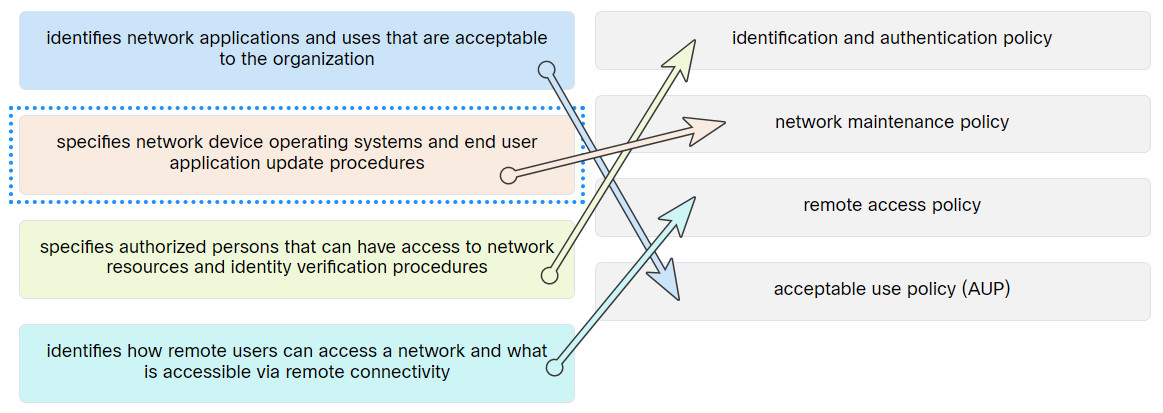
51. What are two physical security precautions that a business can take to protect its computers and systems? (Choose two.)
- Replace software firewalls with hardware firewalls.
- Perform daily data backups.
- Ensure that all operating system and antivirus software is up to date.
- Lock doors to telecommunications rooms.
- Implement biometric authentication.
52. Which hashing technology requires keys to be exchanged?
- salting
- AES
- MD5
- HMAC
53. The IT department is tasked to implement a system that controls what a user can and cannot do on the corporate network. Which process should be implemented to meet the requirement?
- a set of attributes that describes user access rights
- observations to be provided to all employees
- a biometric fingerprint reader
- user login auditing
54. Which two keywords can be used in an access control list to replace a wildcard mask or address and wildcard mask pair? (Choose two.)
- any
- gt
- some
- all
- host
- most
55. What is the function of the pass action on a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall?
- tracking the state of connections between zones
- inspecting traffic between zones for traffic control
- logging of rejected or dropped packets
- forwarding traffic from one zone to another
56. Which statement describes the threat to a public cloud due to a poor cloud security architecture strategy?
- when a cloud customer does not have full visibility into the cloud services
- when user accounts or access privileges are not properly secured and are hijacked by threat actors
- when a cloud customer employee, contractor, or business partner maliciously or unintentionally compromise the cloud service
- when the shared security responsibilities between a cloud customer and cloud provider are not implemented correctly
57. A company is developing a security policy for secure communication. In the exchange of critical messages between a headquarters office and a branch office, a hash value should only be recalculated with a predetermined code, thus ensuring the validity of data source. Which aspect of secure communications is addressed?
- origin authentication
- data integrity
- non-repudiation
- data confidentiality
58. Which Windows log contains information about installations of software, including Windows updates?
- security logs
- application logs
- setup logs
- system logs
59. For network systems, which management system addresses the inventory and control of hardware and software configurations?
- vulnerability management
- risk management
- asset management
- configuration management
60. What are two uses of an access control list? (Choose two.)
- ACLs can permit or deny traffic based upon the MAC address originating on the router.
- Standard ACLs can restrict access to specific applications and ports.
- ACLs can control which areas a host can access on a network.
- ACLs assist the router in determining the best path to a destination.
- ACLs provide a basic level of security for network access.
61. When implementing a ZPF, what is the default security setting when forwarding traffic between two interfaces in the same zone?
- Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is not subject to any policy and passes freely.
- Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is blocked.
- Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is selectively forwarded based on Layer 3 information.
- Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is selectively forwarded based on the default policy restrictions.
62. You have been asked to implement a data integrity program to protect data files that need to be electronically downloaded by the sales staff. You have decided to use the strongest hashing algorithm available on your systems. Which hash algorithm would you select?
- AES
- SHA-1
- SHA-256
- MD5
63. What is the purpose of a digital certificate?
- It authenticates a website and establishes a secure connection to exchange confidential data.
- It guarantees that a website has not been hacked.
- It ensures that the person who is gaining access to a network device is authorized.
- It provides proof that data has a traditional signature attached.
64. Which network logs contain information that a security analyst can use to determine if packets received from the web are in response to legitimate requests or are part of an exploit?
- NetFlow logs
- content filter logs
- NBAR logs
- proxy logs
65. Why can ACLs give a false sense of security if overly relied upon as a network security technology?
- ACLs can be applied to network interfaces in one direction only.
- ACLs only log denied traffic, not permitted traffic.
- Packets are permitted by default when ACL statements don’t match.
- Attackers can determine which IP addresses, protocols, and ports are allowed by ACLs.
66. Why must a network administrator consider more security features in addition to firewalls to achieve the best possible network security?
- Experienced firewall specialists may not always be available, requiring the deployment of less complex security technologies.
- Firewalls are expensive to implement, given that there are less expensive security technologies.
- Firewall configuration often takes too much time, and network technicians are more effective if deployed in other security areas.
- Firewalls typically do not stop intrusions from hosts within a network or zone.
67. What is one of the first actions performed on Internet-connected smart devices before being put into service?
- Connect the device to the network and download firmware updates.
- Change the default administrator credentials.
- Install the device in a physically secure environment.
- Configure the device to communicate with a central server
68. What is an example of transaction data recorded by a network security monitoring tool?
- source and destination port numbers of two network endpoints
- requests and replies between the two network endpoints
- source and destination IP addresses of two network endpoints
- the IP code for the protocol in use
69. Which two statements describe the effects of the access control list wildcard mask 0.0.0.31? (Choose two.)
- The first 27 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
- The first 31 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
- The last 5 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
- The last 5 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
- The last 27 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
- The first 31 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
70. A cybersecurity analyst is going to verify security alerts using the Security Onion. Which tool should the analyst visit first?
- Bro
- ELK
- CapME
- Sguil
71. Which term describes the ability of a web server to keep a log of the users who access the server, as well as the length of time they use it?
- assigning permissions
- authentication
- accounting
- authorization
72. An investigator finds a USB drive at a crime scene and wants to present it as evidence in court. The investigator takes the USB drive and creates a forensic image of it and takes a hash of both the original USB device and the image that was created. What is the investigator attempting to prove about the USB drive when the evidence is submitted in court?
- The data is all there.
- An exact copy cannot be made of a device.
- The investigator found a USB drive and was able to make a copy of it.
- The data in the image is an exact copy and nothing has been altered by the process.
73. Refer to the exhibit. A security analyst is reviewing an alert message generated by Snort. What does the number 2100498 in the message indicate?

- the message length in bits
- the Snort rule that is triggered
- the session number of the message
- the id of the user that triggers the alert
74. What does it indicate if the timestamp in the HEADER section of a syslog message is preceded by a period or asterisk symbol?
- The timestamp represents the round trip duration value.
- The syslog message indicates the time an email is received.
- The syslog message should be treated with high priority.
- There is a problem associated with NTP.
75. A SOHO office is using a public cloud provider to host their website. The IT technician is choosing an approach to protect transaction data between the website and visitors from the internet. Which type of encryption key management method should the technician choose?
- public key encryption
- private key encryption
- secret key encryption
- shared-secret key encryption
76. What are two benefits offered by a zone-based policy firewall on a Cisco router? (Choose two.)
- Any interface can be configured with both a ZPF and an IOS Classic Firewall.
- Policies are applied to unidirectional traffic between zones.
- Virtual and physical interfaces are put in different zones to enhance security.
- Policies are defined exclusively with ACLs.
- Policies provide scalability because they are easy to read and troubleshoot.
77. Why could network Syslog servers be a target for threat actors?
- Syslog servers are usually not installed behind a firewall.
- Syslog servers contain configurations and passwords for all devices on the network.
- Syslog data could be encrypted by the attacker and used as ransomware.
- Syslog servers could contain information that could lead to the detection of an exploit by a hacker.
78. What effect does the use of hashing have on stored passwords?
- Less digital storage is required for user credentials that include hashed passwords.
- Enforces the use of complex passwords.
- The recovery of forgotten passwords is faster.
- The password cannot be restored from the stored unique hash.
79. What is used by an application layer gateway to connect to remote servers on behalf of clients?
- packet filter
- stateful firewall
- intrusion detection system
- proxy server
80. Which component of the zero trust security model focuses on secure access when an API, a microservice, or a container is accessing a database within an application?
- workplace
- workload
- workflow
- workforce
81. Match the security concept to the description.
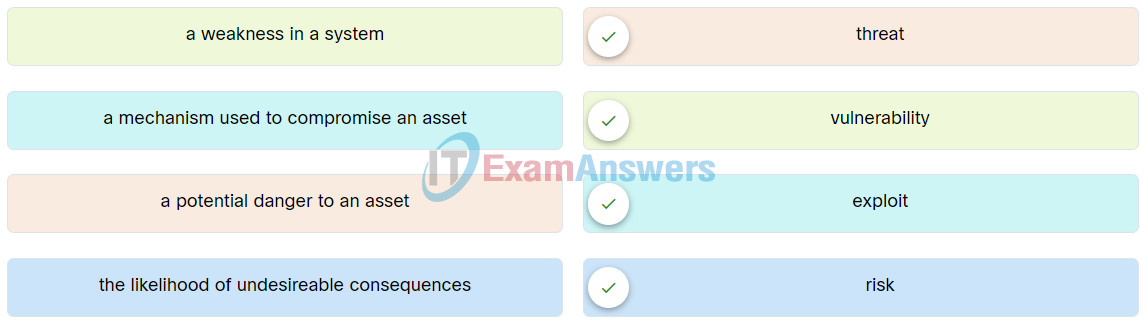
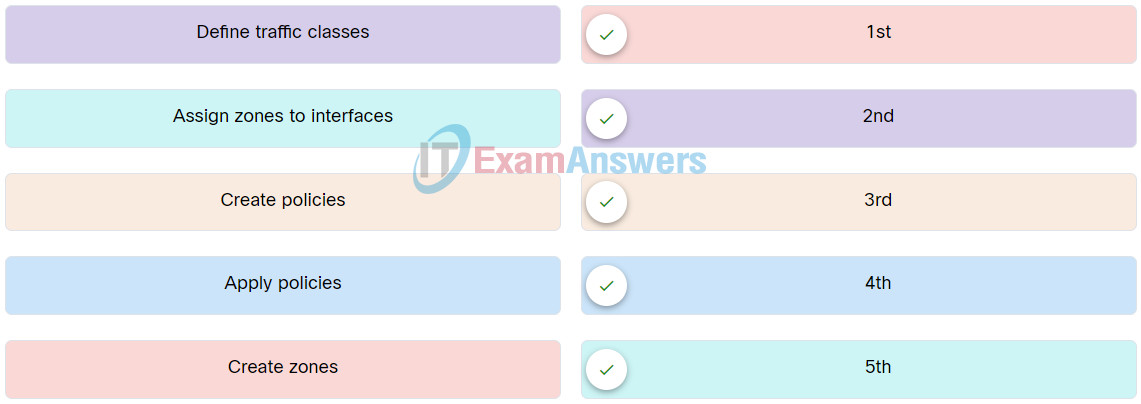
82. Place the steps for configuring zone-based policy (ZPF) firewalls in order from first to last.
83. In a hierarchical CA topology, where can a subordinate CA obtain a certificate for itself?
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA at the same level
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA at a higher level
- from the root CA or from self-generation
- from the root CA only
- from the root CA or another subordinate CA anywhere in the tree

Which network logs contain information that a security analyst can use to determine if packets received from the web are in response to legitimate requests or are part of an exploit?
NetFlow logs
content filter logs
NBAR logs
proxy logs
Thank you for sharing.
Why can ACLs give a false sense of security if overly relied upon as a network security technology?
ACLs can be applied to network interfaces in one direction only.
ACLs only log denied traffic, not permitted traffic.
Packets are permitted by default when ACL statements don’t match.
Attackers can determine which IP addresses, protocols, and ports are allowed by ACLs.
Why must a network administrator consider more security features in addition to firewalls to achieve the best possible network security?
Experienced firewall specialists may not always be available, requiring the deployment of less complex security technologies.
Firewalls are expensive to implement, given that there are less expensive security technologies.
Firewall configuration often takes too much time, and network technicians are more effective if deployed in other security areas.
Firewalls typically do not stop intrusions from hosts within a network or zone.
What is one of the first actions performed on Internet-connected smart devices before being put into service?
Connect the device to the network and download firmware updates.
Change the default administrator credentials.
Install the device in a physically secure environment.
Configure the device to communicate with a central server
What is an example of transaction data recorded by a network security monitoring tool?
source and destination port numbers of two network endpoints
requests and replies between the two network endpoints
source and destination IP addresses of two network endpoints
the IP code for the protocol in use
Which two statements describe the effects of the access control list wildcard mask 0.0.0.31? (Choose two.)
The first 27 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
The first 31 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
The last 5 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
The last 5 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
The last 27 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
The first 31 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
Which statement describes the threat to a public cloud due to a poor cloud security architecture strategy?
when a cloud customer employee, contractor, or business partner maliciously or unintentionally compromise the cloud service
when the shared security responsibilities between a cloud customer and cloud provider are not implemented correctly
when user accounts or access privileges are not properly secured and are hijacked by threat actors
when a cloud customer does not have full visibility into the cloud services
When implementing components into an enterprise network, what is the purpose of a firewall?
A firewall is a system that inspects network traffic and makes forwarding decisions based solely on Layer 2 Ethernet MAC addresses.
A firewall is a system that enforces an access control policy between internal corporate networks and external networks.
A firewall is a system that stores vast quantities of sensitive and business-critical information.
A firewall is a system that is designed to secure, monitor, and manage mobile devices, including corporate-owned devices and employee-owned devices.
What is a characteristic of a probabilistic analysis in an alert evaluation?
random variables that create difficulty in knowing the outcome of any given event with certainty
analysis of applications that conform to application/networking standards
precise methods that yield the same result every time by relying on predefined conditions
each event an inevitable result of antecedent causes
A cybersecurity analyst is going to verify security alerts using the Security Onion. Which tool should the analyst visit first?
Bro
ELK
CapME
Sguil
Which term describes the ability of a web server to keep a log of the users who access the server, as well as the length of time they use it?
assigning permissions
authentication
accounting
authorization
Which hashing technology requires keys to be exchanged?
salting
MD5
AES
HMAC
An investigator finds a USB drive at a crime scene and wants to present it as evidence in court. The investigator takes the USB drive and creates a forensic image of it and takes a hash of both the original USB device and the image that was created. What is the investigator attempting to prove about the USB drive when the evidence is submitted in court?
The data is all there.
An exact copy cannot be made of a device.
The investigator found a USB drive and was able to make a copy of it.
The data in the image is an exact copy and nothing has been altered by the process.
Which ICMP message type should be stopped inbound?
echo
echo-reply
source quench
unreachable
To facilitate the troubleshooting process, which inbound ICMP message should be permitted on an outside interface?
router advertisement
echo request
time-stamp reply
echo reply
time-stamp request
Refer to the exhibit. A security analyst is reviewing an alert message generated by Snort. What does the number 2100498 in the message indicate?
the message length in bits
*** the Snort rule that is triggered
the session number of the message
the id of the user that triggers the alert
I added. Thank you.
What does it indicate if the timestamp in the HEADER section of a syslog message is preceded by a period or asterisk symbol?
The timestamp represents the round trip duration value.
The syslog message indicates the time an email is received.
The syslog message should be treated with high priority.
*** There is a problem associated with NTP.
What are two elements that form the PRI value in a syslog message? (Choose two.)
header
hostname
*** severity
timestamp
*** facility
What is the purpose of a digital certificate?
It guarantees that a website has not been hacked.
*** It authenticates a website and establishes a secure connection to exchange confidential data.
It ensures that the person who is gaining access to a network device is authorized.
It provides proof that data has a traditional signature attached.
A SOHO office is using a public cloud provider to host their website. The IT technician is choosing an approach to protect transaction data between the website and visitors from the internet. Which type of encryption key management method should the technician choose?
*** public key encryption
private key encryption
secret key encryption
shared-secret key encryption
What is the function of the pass action on a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall?
*** forwarding traffic from one zone to another
tracking the state of connections between zones
logging of rejected or dropped packets
inspecting traffic between zones for traffic control
What are two benefits offered by a zone-based policy firewall on a Cisco router? (Choose two.)
Any interface can be configured with both a ZPF and an IOS Classic Firewall.
*** Policies are applied to unidirectional traffic between zones.
Virtual and physical interfaces are put in different zones to enhance security.
Policies are defined exclusively with ACLs.
*** Policies provide scalability because they are easy to read and troubleshoot.
When implementing components into an enterprise network, what is the purpose of a firewall?
*** A firewall is a system that enforces an access control policy between internal corporate networks and external networks.
A firewall is a system that is designed to secure, monitor, and manage mobile devices, including corporate-owned devices and employee-owned devices.
A firewall is a system that stores vast quantities of sensitive and business-critical information.
A firewall is a system that inspects network traffic and makes forwarding decisions based solely on Layer 2 Ethernet MAC addresses.
When implementing a ZPF, what is the default security setting when forwarding traffic between two interfaces in the same zone?
Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is selectively forwarded based on the default policy restrictions.
*** Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is not subject to any policy and passes freely.
Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is blocked.
Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is selectively forwarded based on Layer 3 information.
Which two statements describe the effect of the access control list wildcard mask 0.0.0.15? (Choose two.)
The last four bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
The first 32 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
*** The first 28 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
The first 28 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
The last five bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
*** The last four bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
To facilitate the troubleshooting process, which inbound ICMP message should be permitted on an outside interface?
*** echo reply
echo request
time-stamp request
router advertisement
time-stamp reply
Which term describes the ability of a web server to keep a log of the users who access the server, as well as the length of time they use it?
authentication
assigning permissions
*** accounting
authorization
The IT department is tasked to implement a system that controls what a user can and cannot do on the corporate network. Which process should be implemented to meet the requirement?
*** a set of attributes that describes user access rights
a biometric fingerprint reader
user login auditing
observations to be provided to all employees
An investigator finds a USB drive at a crime scene and wants to present it as evidence in court. The investigator takes the USB drive and creates a forensic image of it and takes a hash of both the original USB device and the image that was created. What is the investigator attempting to prove about the USB drive when the evidence is submitted in court?
The data is all there.
*** The data in the image is an exact copy and nothing has been altered by the process.
The investigator found a USB drive and was able to make a copy of it.
An exact copy cannot be made of a device.
What is one of the first actions performed on Internet-connected smart devices before being put into service?
Configure the device to communicate with a central server.
Install the device in a physically secure environment.
Connect the device to the network and download firmware updates.
Change the default administrator credentials.
Thank you for sharing.
Why could network Syslog servers be a target for threat actors?
Syslog servers are usually not installed behind a firewall.
Syslog servers contain configurations and passwords for all devices on the network.
Syslog data could be encrypted by the attacker and used as ransomware.
Syslog servers could contain information that could lead to the detection of an exploit by a hacker.
What is an example of transaction data recorded by a network security monitoring tool?
source and destination IP addresses of two network endpoints
requests and replies between the two network endpoints
the IP code for the protocol in use
source and destination port numbers of two network endpoints
What effect does the use of hashing have on stored passwords?
Less digital storage is required for user credentials that include hashed passwords.
Enforces the use of complex passwords.
The recovery of forgotten passwords is faster.
The password cannot be restored from the stored unique hash.
What is used by an application layer gateway to connect to remote servers on behalf of clients?
packet filter
stateful firewall
intrusion detection system
proxy server
Which two statements describe the effects of the access control list wildcard mask 0.0.0.31? (Choose two.)
The last 27 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
The last 5 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
The first 31 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
The first 27 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
The first 31 bits of a supplied IP address will be matched.
The last 5 bits of a supplied IP address will be ignored.
A SOHO office is using a public cloud provider to host their website. The IT technician is choosing an approach to protect transaction data between the website and visitors from the internet. Which type of encryption key management method should the technician choose?
shared-secret key encryption
secret key encryption
public key encryption
private key encryption
When implementing a ZPF, what is the default security setting when forwarding traffic between two interfaces in the same zone?
Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is blocked.
Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is not subject to any policy and passes freely.
Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is selectively forwarded based on Layer 3 information.
Traffic between interfaces in the same zone is selectively forwarded based on the default policy restrictions.
Which component of the zero trust security model focuses on secure access when an API, a microservice, or a container is accessing a database within an application?
workplace
workload
workflow
workforce
What is a characteristic of a probabilistic analysis in an alert evaluation?
random variables that create difficulty in knowing the outcome of any given event with certainty
each event an inevitable result of antecedent causes
precise methods that yield the same result every time by relying on predefined conditions
analysis of applications that conform to application/networking standards
What is the function of the pass action on a Cisco IOS Zone-Based Policy Firewall?
tracking the state of connections between zones
logging of rejected or dropped packets
forwarding traffic from one zone to another
inspecting traffic between zones for traffic control
A company is deploying a customer service web application on AWS. A network administrator is installing and configuring a VM instance. Which three actions should the administrator take to protect the VM? (Choose three.)
I added. Thank you.
Which three security services are provided by digital signatures? (Choose three.)
Thank you for sharing.
A network administrator is setting up a web server for a small advertising office and is concerned with data availability. The administrator wishes to implement disk fault tolerance using the minimum number of disks required. Which RAID level should the administrator choose?
RAID 1
RAID 0
RAID 5
RAID 6
Thank you for sharing.