Packet Tracer – Compare 2960 and 3560 (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
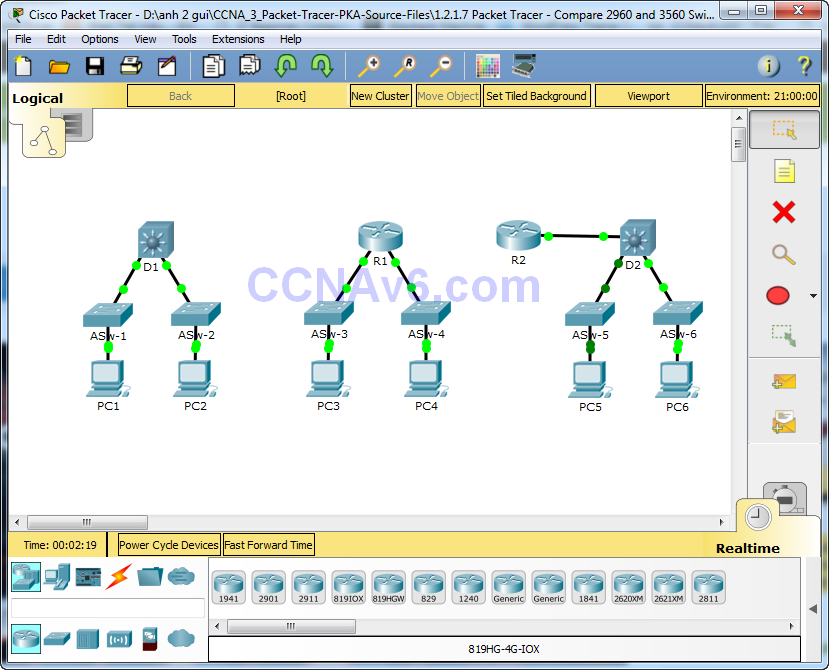
Topology
Objective
Part 1: Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches
Part 2: Compare a Layer 3 Switch and a Router
Background
In this activity, you will use various commands to examine three different switching topologies and compare the similarities and differences between the 2960 and 3560 switches. You will also compare the routing table of a 1941 router with a 3560 switch.
Part 1: Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches
a. Examine the physical aspects of D1 and ASw-1.
Each individual switch has how many physical interfaces?
How many Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces does each switch have?
24 Fast Ethernet and 2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
List the transmission speed of the Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on each switch.
The Fast Ethernet interfaces support speeds of 10/100mb/s, and the Gigabit Ethernet interfaces support speeds of up to 1000mb/s.
Are either of the two switches modular in design?
b. The interface of a 3560 switch can be configured as a Layer 3 interface by entering the no switchport command in interface configuration mode. This allows technicians to assign an IP address and subnet mask to the interface the same way it is configured on a router’s interface.
What is the difference between a Layer 2 switch and a Layer 3 switch?
A Layer 2 switch makes forwarding decisions based on L2 (MAC) addresses. Interfaces on Layer 3 switches can be configured with IP addresses. The switches can also be configured with routing protocols just like a router.
What is the difference between a switch’s physical interface and the VLAN interface?
A switch’s physical interface is used to physically connect end devices to the network. A switched virtual interface (SVI or VLAN) is used to configure the switch with an IP address so that it can be managed remotely.
On which layers do 2960 and 3560 switches operate?
The 2960 operates on Layer 2, and the 3560 operates on Layers 2 and 3.
Issue the show run command to examine the configurations of the D1 and ASw-1 switches. Do you notice any differences between them?
Yes, D1’s G0/1 and the G0/2 interfaces are configured with the no switchport command and show an IP address and mask configured on both Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. D1 has IP routing enabled.
Display the routing table on both switches using the show ip route command. Why do you think the command does not work on ASW-1, but works on D1?
It works on D1 because it functions on Layers 2 and 3, which allows it to function as a Layer 2 switch but at the same time, allows it to route packets and make forwarding decisions based on Layer 3 information (IP addresses) that conventional switches cannot.
Part 2: Compare a Layer 3 Switch and a Router
a. Up until recently, switches and routers have been separate and distinct devices. The term switch was set aside for hardware devices that function at Layer 2. Routers, on the other hand, are devices that make forwarding decisions based on Layer 3 information. They use routing protocols to share routing information and to communicate with other routers. Layer 3 switches, such as the 3560, can be configured to forward Layer 3 packets. Entering the ip routing command in global configuration mode allows Layer 3 switches to be configured with routing protocols, thereby possessing some of the same capabilities as a router. Although similar in some forms, switches are different than in many other aspects.
Open the Physical tab on D1 and R1. Do you notice any similarities between the two? Do you notice any differences between the two?
They both have a console port and both two Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. R1 is modular and can add various interfaces while D1 has only fixed interfaces. R1 has Serial and Asynchronous interfaces while D1 only has Ethernet interfaces. D1 can only use copper cables while R1 can use various connection types.
Issue the show run command and examine the configurations of R1 and D1. What differences do you see between the two?
R1 and D1 have the same IP addresses configured on them but on different interfaces. In order for the switch port to be assigned an IP address, technicians will have to issue the no switchport command.
Which command allows D1 to configure an IP address on one of its physical interfaces?
The no switchport command.
Use the show ip route command on both devices. Do you see any similarities or differences between the two tables?
The codes are the same except the router has an L code for local. This is a link that is configured on the physical interface of R1, while the switch does not have it. Both devices display the same networks in their routing tables.
Now, analyze the routing table of R2 and D2. What is evident now that was not in the configuration of R1 and D1?
They both have EIGRP configured and both are learning networks from one another.
b. Verify that each topology has full connectivity by completing the following tests:
· Ping from PC1 to PC2
· Ping from PC3 to PC4
· Ping from PC5 to PC6
In all three examples, each PC is on a different network. Which device is used to provide communication between networks?
Router or multilayer switch.
Why were we able to ping across networks without there being a router?
A multilayer switch can route between networks as long as it is configured with an IP address and has IP routing enabled. IP routing must also be enabled if you plan to run routing protocols such as EIGRP on the switch. The no switchport command must be enabled on the interface in order to assign an IP address and subnet mask on the switch’s physical interface.