6.6.3 Packet Tracer – Ping Answers
Topology
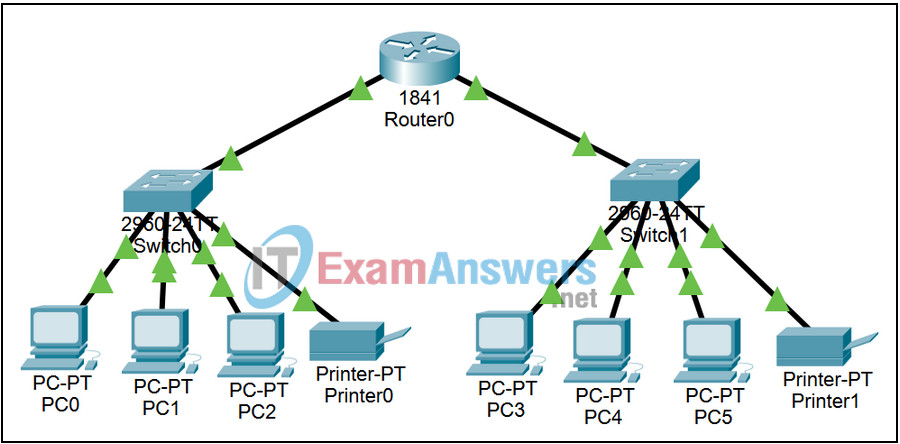
Learning Objectives
- Observe the operation of a ping when testing the local TCP/IP protocol stack
- Observe the operation of a ping when pinging the local default gateway
- Observe the operation of a ping when pinging a remote host on a different segment
Introduction:
In this activity you will use the ping command to test the local stack, ping the gateway, and ping a remote host.
Note: If you experience a delay in the switch links turning from amber to green, toggling between Realtime and Simulation modes 3 or 4 times will speed up the process.
Task 1: Test the local TCP/IP protocol stack.
Step 1. Enter Simulation mode.
Click the Simulation tab to enter Simulation mode. We want to capture only ICMP events. In the Event List Filters section, click the Edit Filters button. Select only ICMP events.
Step 2. Ping the local loopback.
From the command prompt of PC0, issue the command ping 127.0.0.1 and press the Enter key. Minimize the command prompt window, the first packet should appear.
Step 3. Examine the first packet.
Examine the first packet that appears in the Event List by clicking on the colored Info square for that packet.
Step 4. Step through the simulation.
Click the Capture / Forward button once. The first ICMP packet is returned to PC0 Observe the process and examine the events. Click the Reset Simulation button.
Task 2: Test reaching the local default gateway.
Step 1. Ping in Realtime mode.
Click the Realtime tab to enter Realtime mode. From the command prompt of PC0, issue the command ping 10.0.0.254 and press the Enter key. Observe the results.
Step 2. Ping in Simulation mode.
Click the Simulation tab to enter Simulation mode. From the command prompt of PC0, issue the command ping 10.0.0.254 and press the Enter key. Minimize the command prompt window. The first packet should appear.
Step 3. Examine the first packet
Examine the first packet that appears in the Event List by clicking on the colored Info square for that packet.
Step 4. Step through the simulation.
Click the Capture / Forward button repeatedly until the first ICMP echo reply packet is returned successfully to PC0 and observe the process. Examine the packet via the PDU Information window at various points along its journey. Click the Reset Simulation button.
For extra detail regarding this process, click Power Cycle Devices in the lower left of the interface and switch between Realtime and Simulation modes up to 4 times to clear the Spanning Tree Protocol. All link lights will be green. Select ARP and ICMP from the Event List Filters list, and reissue the initial ping command as described in Step 2. Click the Capture / Forward button repeatedly until the first ICMP echo reply packet is returned successfully to PC0 and observe the process. Examine the packet via the PDU Information window at various points along its journey. You will see in this interaction the role of the Address Resolution Protocol (covered in Chapter 9) in this interaction. When finished, click the Reset Simulation button.
Task 3: Test reaching a remote host.
Step 1. Ping the remote host.
From the command prompt of PC0, issue the command ping 10.0.1.1 and press the Enter key. Minimize the command prompt window. The first packet should appear.
Step 2. Examine the first packet
Examine the first packet that appears in the Event List by clicking on the colored Info square for that packet.
Step 3. Step through the simulation
Click the Capture / Forward button repeatedly until the first ICMP echo reply packet is returned successfully to PC0 and observe the process. Examine the packet via the PDU Information window at various points along its journey.
