Lab 11.5.4 – Network Testing (Answers)
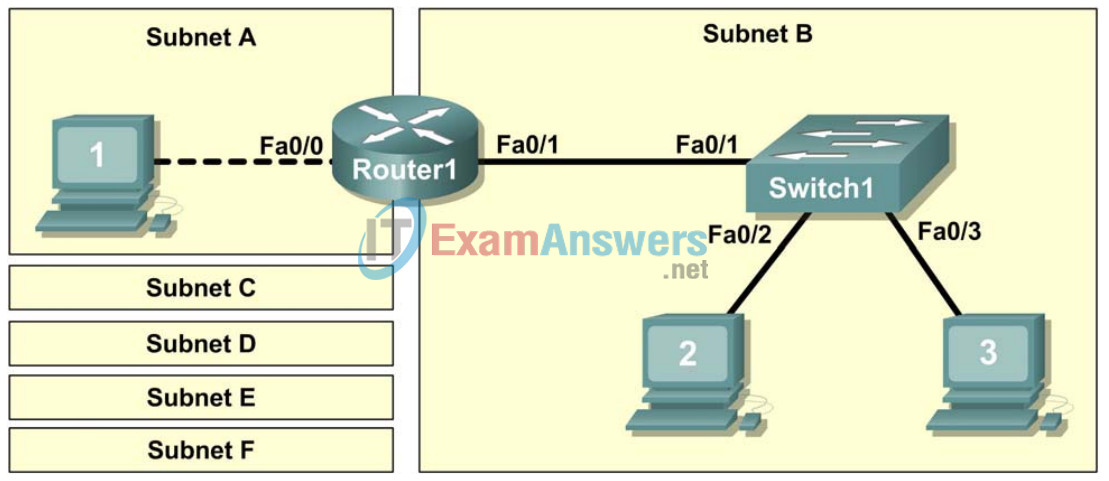
Topology Diagram
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
- Design the logical lab topology.
- Configure the physical lab topology.
- Configure the logical LAN topology.
- Verify LAN connectivity.
Background
Table 1. Equipment and Hardware for this Lab
| Hardware | Qty | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cisco Router | 1 | Part of CCNA Lab bundle |
| Cisco Switch | 1 | Part of CCNA Lab bundle |
| *Computer (Host) | 3 | Lab computer |
| CAT-5 or better straight-through UTP cables | 3 | Connects Router1, Host1, and Host2 to switch1 |
| CAT-5 crossover UTP cable | 1 | Connects Host 1 to Router1 |
| Console (rollover) cable | 1 | Connects Host1 to Router1 console |
Gather the necessary equipment and cables. To configure the lab, make sure the equipment listed in Table 1 is available.
Note to instructor: If you do not have a router that has two FastEthernet interfaces, consider configuring a loopback interface as an alternative to the FastEthernet 0/1. Another alternative would be to use two routers connected through a serial connection and use the FastEthernet interfaces from each router.
The Appendix contains Cisco IOS configuration syntax for this lab.
Scenario
In this lab, you will create a small network that requires connecting network devices and configuring host computers for basic network connectivity. SubnetA and SubnetB are subnets that are currently needed. SubnetC, SubnetD, SubnetE, and SubnetF are anticipated subnets, not yet connected to the network.
Note to instructor: To reinforce student cable identification, have several different types of cables available for the students. Mix crossover, straight-through, and rollover cables. Students should be able to identify the proper cable type based on a visual inspection.
Task 1: Design the Logical Lab Topology.
Given an IP address and mask of 172.20.0.0 / 24 (address / mask), design an IP addressing scheme that satisfies the following requirements:
| Subnet | Number of Hosts |
|---|---|
| SubnetA | As shown in topology diagram |
| SubnetB | Between 80 – 100 |
| SubnetC | Between 40 – 52 |
| SubnetD | Between 20 – 29 |
| SubnetE | 12 |
| SubnetF | 5 |
Note: Always start with the subnet with the largest number of hosts and work your way down. Therefore, you should start with SubnetB and finish with SubnetA.
Step 1: Design SubnetB address block.
Begin the logical network design by satisfying the requirement of SubnetB, which requires the largest block of IP addresses. Using binary numbers to create your subnet chart, pick the first address block that will support SubnetB.
1. Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetB:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.128 | 255.255.255.192 | 172.20.0.129 | 172.20.0.190 | 172.20.0.191 |
2. What is the bit mask in binary?
11111111.1111111.11111111.11000000
Step 3: Design SubnetD address block.
Satisfy the requirement of SubnetD, the next largest IP address block. Using binary numbers to create your subnet chart, pick the next available address block that will support SubnetD.
1. Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetD:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.192 | 255.255.255.224 | 172.20.0.193 | 172.20.0.222 | 172.20.0.223 |
2. What is the bit mask in binary?
11111111.1111111.11111111.11100000
Step 4: Design SubnetE address block.
Satisfy the requirement of SubnetE, the next largest IP address block. Using binary numbers to create your subnet chart, pick the next available address block that will support SubnetE.
1. Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetE:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.224 | 255.255.255.240 | 172.20.0.225 | 172.20.0.238 | 172.20.0.239 |
2. What is the bit mask in binary?
11111111.1111111.11111111.11110000
Step 5: Design SubnetF address block.
Satisfy the requirement of SubnetF, the next largest IP address block. Using binary numbers to create your subnet chart, pick the next available address block that will support SubnetF.
1. Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetF:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.240 | 255.255.255.248 | 172.20.0.241 | 172.20.0.246 | 172.20.0.247 |
2. What is the bit mask in binary?
11111111.1111111.11111111.11111000
Step 6: Design SubnetA address block.
Satisfy the requirement of SubnetA, the smallest IP address block. Using binary numbers to create your subnet chart, pick the next available address block that will support SubnetA.
1. Fill in the following table with IP address information for SubnetA:
| Network Address | Mask | First Host Address | Last Host Address | Broadcast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.20.0.248 | 255.255.255.252 | 172.20.0.249 | 172.20.0.250 | 172.20.0.251 |
2. What is the bit mask in binary?
11111111.1111111.11111111.11111100
Task 2: Configure the Physical Lab Topology.
Step 1: Physically connect lab devices.
1. Cable the network devices as shown in Figure 1. Pay special attention to the crossover cable required between Host1 and Router1.

Figure 1. Cabling the Network
2. If not already enabled, turn power on to all devices.
Step 2: Visually inspect network connections.
After cabling the network devices, take a moment to verify the connections. Attention to detail now will minimize the time required to troubleshoot Layer 1 connectivity issues later.
Task 3: Configure the Logical Topology.
Step 1: Document logical network settings.
On SubnetA, Host1 will use the first IP address in the subnet. Router1, interface Fa0/0, will use the last host address. On SubnetB, host computers will use the first and second IP addresses in the subnet, respectively. Router1, interface Fa0/1, will use the last network host address.
To properly route Layer 2 frames between LAN devices, Switch1 does not require Layer 3 configuration. The IP address assigned to Switch 1, interface VLAN 1, is used to establish Layer 3 connectivity between external devices and the switch. Without an IP address, upper-layer protocols such as TELNET and HTTP will not work. The default gateway address permits the switch to respond to protocol requests from devices on distant networks. For example, the IP gateway address extends Layer 3 connectivity beyond Subnet B. Switch1 will use the next-to-last host address.
Write down the IP address information for each device:
| Device | Subnet | IP Address | Mask | Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Host1 | 172.20.0.248 | 172.20.0.249 | 255.255.255.252 | 172.20.0.250 |
| Router1-Fa0/0 | 172.20.0.248 | 172.20.0.250 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| Host2 | 172.20.0.0 | 172.20.0.1 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.20.0.126 |
| Host3 | 172.20.0.0 | 172.20.0.2 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.20.0.126 |
| Switch1 | 172.20.0.0 | 172.20.0.125 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.20.0.126 |
| Router1-Fa0/1 | 172.20.0.0 | 172.20.0.126 | 255.255.255.128 | N/A |
Step 2: Configure host computers.
1. On each computer, in turn, click Start > Control Panel > Network Connections. Right-click the LAN icon, and choose Properties. On the General tab, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and then click the, Properties button.
2. Verify that the Host1 Layer 3 IP address is on a different subnet than Host2 and Host3. Configure each host computer using the IP address information recorded in Step 1.
3. Verify proper configuration of each host computer with the ipconfig command and fill in the following table:
| Device | IP Address | Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| Host1 | 172.20.0.249 | 255.255.255.252 | 172.20.0.250 |
| Host2 | 172.20.0.1 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.20.0.126 |
| Host3 | 172.20.0.2 | 255.255.255.128 | 172.20.0.126 |
Step 3: Configure Router1.
1. From the Windows taskbar, start the HyperTerminal program by clicking Start > Programs > Accessories > Communications > HyperTerminal. Configure HyperTerminal for access to Router1. Configuration for Router1 includes the following tasks:
| Tasks (Refer to the Appendix for help with commands) |
|---|
| Specify Router name: Router1 |
| Specify an encrypted privileged EXEC password: cisco |
| Specify a console access password: class |
| Specify a telnet access password: class |
| Configure the MOTD banner |
| Configure Router1 interface Fa0/0: • Set the description • Set the Layer 3 address • Issue no shutdown |
| Configure Router1 interface Fa0/1: • Set the description • Set the Layer 3 address • Issue no shutdown |
2. Save the configuration in NVRAM.
3. Display the contents of RAM: show running-config
4. Write the configuration specifications below:
Hostname: Router1
Enable secret password: cisco
Console access password: class
Telnet access password: class
MOTD banner: Answers will vary
5. Display configuration information for interface Fa0/0: show interface Fa0/0
FastEthernet 0/0 status (up / down): should be up
Line protocol: should be up
MAC Address: Answers will vary
6. Display configuration information for interface Fa0/1: show interface Fa0/1
FastEthernet 0/0 status (up / down): should be up
Line protocol: should be up
MAC Address: Answers will vary
7. Display brief IP address information about each interface: show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/0 answers will vary YES manual up up FastEthernet0/1 answers will vary YES manual up up
8. Take corrective action with any problems, and retest.
Step 4: Configure Switch1.
1. Move the console cable from Router1 to Switch1.
2. Press Enter until a response is received.
3. Configuration for Switch1 includes the following tasks:
| Tasks (Refer to the Appendix for help with commands) |
|---|
| Specify Switch name- Switch1 |
| Specify an encrypted privileged exec password- cisco |
| Specify a console access password- class |
| Specify a telnet access password- class |
| Configure the MOTD banner |
| Configure Switch1 interface Fa0/1: Set the description |
| Configure Switch1 interface Fa0/2: Set the description |
| Configure Switch1 interface Fa0/3: Set the description |
| Configure management VLAN 1 IP address: • Set the description • Set the Layer 3 address • Issue no shutdown |
| Configure default IP gateway address |
4. Display the contents of RAM: show running-config
5. Write the configuration specifications below:
Hostname: Switch1
Enable secret password: cisco
Console access password: class
Telnet access password: class
MOTD banner: Answers will vary
Interface VLAN 1: Answers will vary
Default IP gateway address: Answers will vary
6. Display configuration information for interface VLAN 1: show interface vlan1
VLAN 1 status (up / down): should be up
Line protocol: should be up
Task 4: Verify Network Connectivity.
Step 1: Use the ping command to verify network connectivity.
Network connectivity can be verified with the ping command. It is very important that connectivity exists throughout the network. Corrective action must be taken if there is a failure.
1. Use the following table to methodically verify connectivity with each network device:
| From | To | IP Address | Ping results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Host1 | LocalHost (127.0.0.1) | 127.0.0.1 | Should be success. |
| Host1 | NIC IP address | 172.20.0.249 | Should be success. |
| Host1 | Gateway (Router1, Fa0/0) | 172.20.0.250 | Should be success. |
| Host1 | Router1, Fa0/1 | 172.20.0.126 | Should be success. |
| Host1 | Switch1 | 172.20.0.125 | Should be success. |
| Host1 | Host2 | 172.20.0.1 | Should be success. |
| Host1 | Host3 | 172.20.0.2 | Should be success. |
| Host2 | LocalHost (127.0.0.1) | 127.0.0.1 | Should be success. |
| Host2 | NIC IP address | 172.20.0.1 | Should be success. |
| Host2 | Host3 | 172.20.0.2 | Should be success. |
| Host2 | Switch1 | 172.20.0.125 | Should be success. |
| Host2 | Gateway (Router1, Fa0/1) | 172.20.0.126 | Should be success. |
| Host2 | Router1, Fa0/0 | 172.20.0.250 | Should be success. |
| Host2 | Host1 | 172.20.0.249 | Should be success. |
| Host3 | LocalHost (127.0.0.1) | 127.0.0.1 | Should be success. |
| Host3 | NIC IP address | 172.20.0.2 | Should be success. |
| Host3 | Host2 | 172.20.0.1 | Should be success. |
| Host3 | Switch1 | 172.20.0.125 | Should be success. |
| Host3 | Gateway (Router1, Fa0/1) | 172.20.0.126 | Should be success. |
| Host3 | Router1, Fa0/0 | 172.20.0.250 | Should be success. |
| Host3 | Host1 | 172.20.0.249 | Should be success. |
2. Take corrective action to establish connectivity if a test fails.
Note: If pings to host computers fail, temporarily disable the computer firewall and retest. To disable a Windows firewall, click Start > Control Panel > Windows Firewall, choose Off, and then click OK.
Step 2: Use the tracert command to verify local connectivity.
1. From Host1, issue the tracert command to Host2 and Host3.
2. Record the results:
From Host1 to Host2: Answers should show success
From Host1 to Host3: Answers should show success
Step 3: Verify Layer 2 connectivity.
1. If not already connected, move the console cable from Router1 to Switch1.
2. Press the Enter key until there is a response from Switch1.
3. Issue the command show mac-address-table. This command will display static (CPU) and dynamic, or learned, entries.
4. List the dynamic MAC addresses and corresponding switch ports:
| MAC Address | Switch Port |
|---|---|
| Answers will vary. | Answers will vary. |
| Answers will vary. | Answers will vary. |
| Answers will vary. | Answers will vary. |
5. Verify that there are three dynamically learned MAC addresses, one each from Fa0/1, Fa0/2, and Fa0/3.
Task 5: Reflection
Review any physical or logical configuration problems encountered during this lab. Make sure you have a thorough understanding of the procedures used to verify network connectivity.
Task 6: Challenge
Ask your instructor or another student to introduce one or two problems in your network when you aren’t looking or are out of the lab room. Problems can be either physical (wrong UTP cable) or logical (wrong IP address or gateway). To fix the problems:
1. Perform a good visual inspection. Look for green link lights on Switch1.
2. Use the table provided in Task 3, above, to identify failed connectivity. List the problems:
3. Write down your proposed solution(s):
4. Test your solution. If the solution fixed the problem, document the solution. If the solution did not fix the problem, continue troubleshooting.
Task 7: Clean Up.
Unless directed otherwise by the instructor, restore host computer network connectivity, and then turn off power to the host computers.
Before turning off power to the router and switch, remove the NVRAM configuration file from each device with the privileged exec command erase startup-config.
Carefully remove cables and return them neatly to their storage. Reconnect cables that were disconnected for this lab.
Remove anything that was brought into the lab, and leave the room ready for the next class.
Appendix—List of Cisco IOS commands used in this lab
| Purpose | Command |
|---|---|
| Enter the global configuration mode. | configure terminal Example: Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)# |
| Specify the name for the Cisco device. | hostname name Example: Router(config)#hostname Router1 Router(config)# |
| Specify an encrypted password to prevent unauthorized access to the privileged EXEC mode. | Enable secret password Example: Router(config)#enable secret cisco Router(config)# |
| Specify a password to prevent unauthorized access to the console. | password password login Example: Router(config)#line con 0 Router(config-line)#password class Router(config-line)#login Router(config)# |
| Specify a password to prevent unauthorized Telnet access. Router vty lines: 0 4 Switch vty lines: 0 15 |
password password login Example: Router(config)#line vty 0 4 Router(config-line)#password class Router(config-line)#login Router(config-line)# |
| Configure the MOTD banner. | Banner motd % Example: Router(config)#banner motd % Router(config)# |
| Configure a Router interface. Router interface is OFF by default |
Example: Router(config)#interface Fa0/0 Router(config-if)#description description Router(config-if)#ip address address mask Router(config-if)#no shutdown Router(config-if)# |
| Switch interface is ON by default (VLAN interface is OFF by default) |
Example: Switch(config)#interface Fa0/0 Switch(config-if)#description description Switch(config)#interface vlan1 Switch(config-if)#ip address address mask Switch(config-if)#no shutdown Switch(config-if)# |
| Switch- create a default IP gateway | Switch(config)#ip default-gateway address |
| Save the configuration to NVRAM. | copy running-config startup-config Example: Router#copy running-config startup-config |
