7.1.3.6 Lab – Configuring Advanced EIGRP for IPv4 Features (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
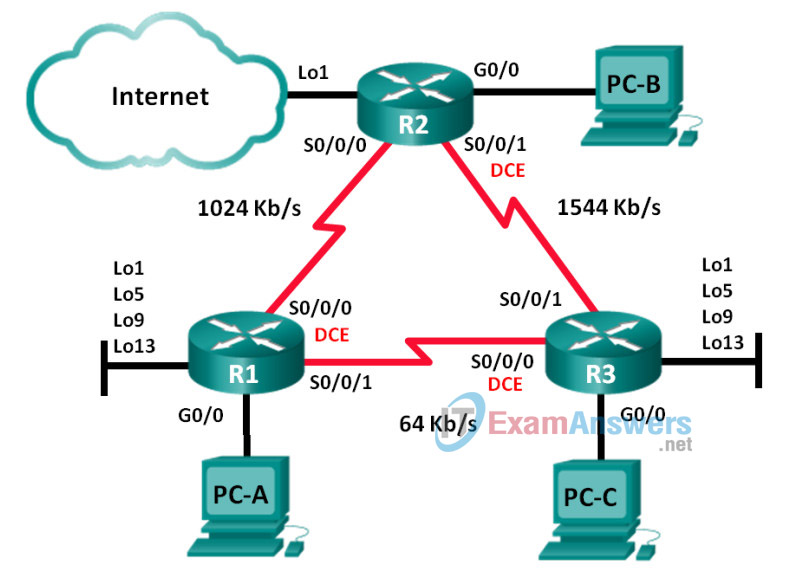
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 (DCE) | 192.168.12.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.13.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo1 | 192.168.11.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo5 | 192.168.11.5 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo9 | 192.168.11.9 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo13 | 192.168.11.13 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R2 | G0/0 | 192.168.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 192.168.12.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 (DCE) | 192.168.23.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo1 | 192.168.22.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| R3 | G0/0 | 192.168.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 (DCE) | 192.168.13.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.23.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo1 | 192.168.33.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo5 | 192.168.33.5 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo9 | 192.168.33.9 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| Lo13 | 192.168.33.13 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A | |
| PC-A | NIC | 192.168.1.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.1.1 |
| PC-B | NIC | 192.168.2.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.2.1 |
| PC-C | NIC | 192.168.3.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.3.1 |
Objectives
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
Part 2: Configure EIGRP and Verify Connectivity
Part 3: Configure EIGRP for Automatic Summarization
Part 4: Configure and Propagate a Default Static Route
Part 5: Fine-Tune EIGRP
- Configure bandwidth utilization for EIGRP.
- Configure the hello interval and hold timer for EIGRP.
Background / Scenario
EIGRP has advanced features to allow changes related to summarization, default route propagation, bandwidth utilization, and metrics.
In this lab, you will configure automatic summarization for EIGRP, configure EIGRP route propagation, and fine-tune EIGRP metrics.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at this end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Ensure that the routers have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 3 Routers (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable)
- 3 PCs (Windows with a terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings on the PC hosts and routers.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Step 2: Configure PC hosts.
Step 3: Initialize and reload the routers as necessary.
Step 4: Configure basic settings for each router.
a. Disable DNS lookup.
b. Configure device name as shown in the topology.
c. Assign cisco as the console and vty passwords.
d. Assign class as the privileged EXEC password.
e. Configure logging synchronous to prevent console messages from interrupting command entry.
f. Configure the IP address listed in the Addressing Table for all interfaces.
Note: Do NOT configure the loopback interfaces at this time.
g. Copy the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Part 2: Configure EIGRP and Verify Connectivity
In Part 2, you will configure basic EIGRP for the topology and set bandwidths for the serial interfaces.
Note: This lab provides minimal assistance with the actual commands necessary to configure EIGRP. However, the required commands are provided in Appendix A. Test your knowledge by trying to configure the devices without referring to the appendix.
Step 1: Configure EIGRP.
a. On R1, configure EIGRP routing with an autonomous system (AS) ID of 1 for all directly connected networks. Write the commands used in the space below.
___________________________________________________
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3
b. For the LAN interface on R1, disable the transmission of EIGRP hello packets. Write the command used in the space below.
___________________________________________________
R1(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0
c. On R1, configure the bandwidth for S0/0/0 to 1024 Kb/s and the bandwidth for S0/0/1 to 64 Kb/s. Write the commands used in the space below. Note: The bandwidth command only affects the EIGRP metric calculation, not the actual bandwidth of the serial link.
___________________________________________________
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 1024
R1(config-if)# interface s0/0/1
R1(config-if)# bandwidth 64
d. On R2, configure EIGRP routing with an AS ID of 1 for all networks, disable the transmission of EIGRP hello packets for the LAN interface, and configure the bandwidth for S0/0/0 to 1024 Kb/s.
e. On R3, configure EIGRP routing with an AS ID of 1 for all networks, disable the transmission of EIGRP hello packets for the LAN interface, and configure the bandwidth for S0/0/0 to 64 Kb/s.
Step 2: Test connectivity.
All PCs should be able to ping one another. Verify and troubleshoot if necessary.
Note: It may be necessary to disable the PC firewall to ping between PCs.
Part 3: Configure EIGRP for Automatic Summarization
In Part 3, you will add loopback interfaces and enable EIGRP automatic summarization on R1 and R3. You will also observe the effects on the routing table of R2.
Step 1: Configure EIGRP for automatic summarization.
a. Issue the show ip protocols command on R1. What is the default status of automatic summarization in EIGRP?
R1# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
<output omitted>
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP-IPv4 Protocol for AS(1)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 192.168.13.1
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.1.0
192.168.12.0/30
192.168.13.0/30
Passive Interface(s):
GigabitEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.12.2 90 00:30:16
192.168.13.2 90 00:30:16
Distance: internal 90 external 170
____________________________________________________
Automatic network summarization is disabled.
b. Configure the loopback addresses on R1.
c. Add the appropriate network statements to the EIGRP process on R1. Record the commands used in the space below.
_____________________________________________________
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.4 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.8 0.0.0.3
R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.12 0.0.0.3
d. On R2, issue the show ip route eigrp command. How are the loopback networks represented in the output?
R2# show ip route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/3014400] via 192.168.12.1, 00:14:58, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/21514560] via 192.168.23.2, 00:11:18, Serial0/0/1
192.168.11.0/30 is subnetted, 4 subnets
D 192.168.11.0 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.11.4 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.11.8 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.11.12 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:00:14, Serial0/0/0
192.168.13.0/30 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.13.0 [90/41024000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:06:11, Serial0/0/1
[90/41024000] via 192.168.12.1, 00:06:11, Serial0/0/0
_____________________________________________________
All subnetworks, including the loopback networks, are listed in the routing table output.
e. On R1, issue the auto-summary command inside the EIGRP process.
R1(config)# router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)# auto-summary R1(config-router)# *Apr 14 01:14:55.463: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.13.2 (Serial0/0/1) is resync: summary configured *Apr 14 01:14:55.463: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.12.2 (Serial0/0/0) is resync: summary configured *Apr 14 01:14:55.463: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.13.2 (Serial0/0/1) is resync: summary up, remove components R1(config-router)#67: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.12.2 (Serial0/0/0) is resync: summary up, remove components *Apr 14 01:14:55.467: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.12.2 (Serial0/0/0) is resync: summary up, remove components *Apr 14 01:14:55.467: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: EIGRP-IPv4 1: Neighbor 192.168.13.2 (Serial0/0/1) is resync: summary up, remove components
How does the routing table on R2 change?
R2# show ip route eigrp
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP
i - IS-IS, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2, ia - IS-IS inter area
* - candidate default, U - per-user static route, o - ODR
P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/3014400] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.3.0/24 [90/20514560] via 192.168.23.2, 00:15:58, Serial0/0/1
192.168.11.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
D 192.168.11.0 [90/3139840] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/0
192.168.12.0/24 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 3 masks
D 192.168.12.0/24 [90/41536000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/1
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
D 192.168.13.0/24 [90/41024000] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/0
D 192.168.13.0/30 [90/41024000] via 192.168.23.2, 00:01:13, Serial0/0/1
____________________________________________________
The 192.168.11.0 networks are summarized at their classful boundary.
f. Repeat substeps b through e by adding loopback interfaces, adding EIGRP process networks and auto-summary on R3.
Part 4: Configure and Propagate a Default Static Route
In Part 4, you will configure a default static route on R2 and propagate the route to all other routers.
a. Configure the loopback address on R2.
b. Configure a default static route with an exit interface of Lo1.
R2(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Lo1
c. Use the redistribute static command within the EIGRP process to propagate the default static route to other participating routers.
R2(config)# router eigrp 1 R2(config-router)# redistribute static
d. Use the show ip protocols command on R2 to verify the static route is being distributed.
R2# show ip protocols
*** IP Routing is NSF aware ***
<output omitted>
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
Redistributing: static
EIGRP-IPv4 Protocol for AS(1)
Metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
NSF-aware route hold timer is 240
Router-ID: 192.168.23.1
Topology : 0 (base)
Active Timer: 3 min
Distance: internal 90 external 170
Maximum path: 4
Maximum hopcount 100
Maximum metric variance 1
Automatic Summarization: disabled
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
192.168.2.0
192.168.12.0/30
192.168.23.0/30
Passive Interface(s):
GigabitEthernet0/0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
192.168.12.1 90 00:13:20
192.168.23.2 90 00:13:20
Distance: internal 90 external 170
e. On R1, issue the show ip route eigrp | include 0.0.0.0 command to view statements specific to the default route. How is the static default route represented in the output? What is the administrative distance (AD) for the propagated route?
R1# show ip route eigrp | include 0.0.0.0 Gateway of last resort is 192.168.12.2 to network 0.0.0.0 D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/3139840] via 192.168.12.2, 00:06:27, Serial0/0/0
___________________________________________________
As an externally learned EIGRP route:
D*EX 0.0.0.0/0 [170/3139840] via 192.168.12.2, 00:06:27, Serial0/0/0
The administrative distance is 170 as it is an external EIGRP route.
Part 5: Fine-Tune EIGRP
In Part 5, you will configure the percentage of bandwidth that can be used for EIGRP traffic on an interface and change the hello interval and hold timers for EIGRP interfaces.
Step 1: Configure bandwidth utilization for EIGRP.
a. Configure the serial link between R1 and R2 to allow only 75 percent of the link bandwidth for EIGRP traffic.
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75 R2(config)# interface s0/0/0 R2(config-if)# ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75
b. Configure the serial link between R1 and R3 to allow 40 percent of the links bandwidth for EIGRP traffic.
Step 2: Configure the hello interval and hold timer for EIGRP.
a. On R2, use the show ip eigrp interfaces detail command to view the hello interval and hold timer for EIGRP.
R2# show ip eigrp interfaces detail
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(1)
Xmit Queue PeerQ Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Se0/0/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/15 50 0
Hello-interval is 5, Hold-time is 15
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 29/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 390/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 35/39
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Interface BW percentage is 75
Authentication mode is not set
Se0/0/1 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/16 50 0
Hello-interval is 5, Hold-time is 15
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 34/5
Hello's sent/expedited: 382/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 31/42
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 2
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
What is the default value for hello time? ____________5 seconds
What is the default value for hold time? ____________15 seconds
b. Configure S0/0/0 and S0/0/1 interfaces on R1 to use a hello interval of 60 seconds and a hold time of 180 seconds in that specific order.
R1(config)# interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 R1(config)# interface s0/0/1 R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180
c. Configure the serial interfaces on R2 and R3 to use a hello interval of 60 seconds and a hold time of 180 seconds.
d. Use the show ip eigrp interfaces detail command on R2 to verify configuration.
R2# show ip eigrp interfaces detail
EIGRP-IPv4 Interfaces for AS(1)
Xmit Queue PeerQ Mean Pacing Time Multicast Pending
Interface Peers Un/Reliable Un/Reliable SRTT Un/Reliable Flow Timer Routes
Se0/0/0 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/15 50 0
Hello-interval is 60, Hold-time is 180
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 38/1
Hello's sent/expedited: 489/4
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 40/48
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 0
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Interface BW percentage is 75
Authentication mode is not set
Se0/0/1 1 0/0 0/0 1 0/16 50 0
Hello-interval is 60, Hold-time is 180
Split-horizon is enabled
Next xmit serial <none>
Packetized sent/expedited: 45/5
Hello's sent/expedited: 481/2
Un/reliable mcasts: 0/0 Un/reliable ucasts: 46/55
Mcast exceptions: 0 CR packets: 0 ACKs suppressed: 2
Retransmissions sent: 0 Out-of-sequence rcvd: 0
Topology-ids on interface - 0
Authentication mode is not set
Reflection
1. What are the benefits of summarizing routes?
_______________________________________________________
Summarization can be used to limit the number of routing advertisements and the size of routing tables.
2. When setting EIGRP timers, why is it important to make the hold time value equal to or greater than the hello interval?
_______________________________________________________
If the hold time is less than the hello interval, the neighbor adjacency will go down.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Interface Summary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. | ||||
Appendix A: Configuration Commands
Router R1
R1(config)# router eigrp 1 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.4 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.8 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# network 192.168.11.12 0.0.0.3 R1(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0 R1(config-router)# auto-summary R1(config)# int s0/0/0 R1(config-if)# bandwidth 1024 R1(config-if)# ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75 R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 R1(config-if)# int s0/0/1 R1(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R1(config-if)# ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 40 R1(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R1(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180
Router R2
R2(config)# router eigrp 1 R2(config-router)# network 192.168.2.0 R2(config-router)# network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 R2(config-router)# network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 R2(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0 R2(config-router)# redistribute static R2(config)# int s0/0/0 R2(config-if)# bandwidth 1024 R2(config-if)# ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75 R2(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R2(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 R2(config-if)# int s0/0/1 R2(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R2(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180
Router R3
R3(config)# router eigrp 1 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.3.0 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.33.0 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.33.4 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.33.8 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# network 192.168.33.12 0.0.0.3 R3(config-router)# passive-interface g0/0 R3(config-router)# auto-summary R3(config)# int s0/0/0 R3(config-if)# bandwidth 64 R3(config-if)# ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 40 R3(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R3(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 R3(config-if)# int s0/0/1 R3(config-if)# ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 R3(config-if)# ip hold-time eigrp 1 180
Device Configs – R1, R2, and R3
Router R1
R1# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2378 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ip cef no ipv6 cef ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! redundancy ! interface Loopback1 ip address 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback5 ip address 192.168.11.5 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback9 ip address 192.168.11.9 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback13 ip address 192.168.11.13 255.255.255.252 ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 bandwidth 1024 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.252 ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 clock rate 2000000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 bandwidth 64 ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.252 ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 40 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.1.0 network 192.168.11.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.11.4 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.11.8 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.11.12 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 auto-summary passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input none ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
Router R2
R2# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2223 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname R2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 no aaa new-model ! no ip domain lookup ip cef no ipv6 cef ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! ! redundancy ! interface Loopback1 ip address 192.168.22.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 bandwidth 1024 ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.252 ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 75 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.252 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 clock rate 2000000 ! ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.2.0 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 redistribute static passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Loopback1 ! ! ! ! control-plane ! ! ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input none ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
Router R3
R3# show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 2456 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec no service password-encryption ! hostname R3 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! no ip domain lookup ip cef no ipv6 cef ! interface Loopback1 ip address 192.168.33.1 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback5 ip address 192.168.33.5 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback9 ip address 192.168.33.9 255.255.255.252 ! interface Loopback13 ip address 192.168.33.13 255.255.255.252 ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 bandwidth 64 ip address 192.168.13.2 255.255.255.252 ip bandwidth-percent eigrp 1 40 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 clock rate 2000000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.252 ip hello-interval eigrp 1 60 ip hold-time eigrp 1 180 ! ! router eigrp 1 network 192.168.3.0 network 192.168.13.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.33.0 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.33.4 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.33.8 0.0.0.3 network 192.168.33.12 0.0.0.3 auto-summary passive-interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login transport input none ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ! end
