5.5.3 Packet Tracer – Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol Answers
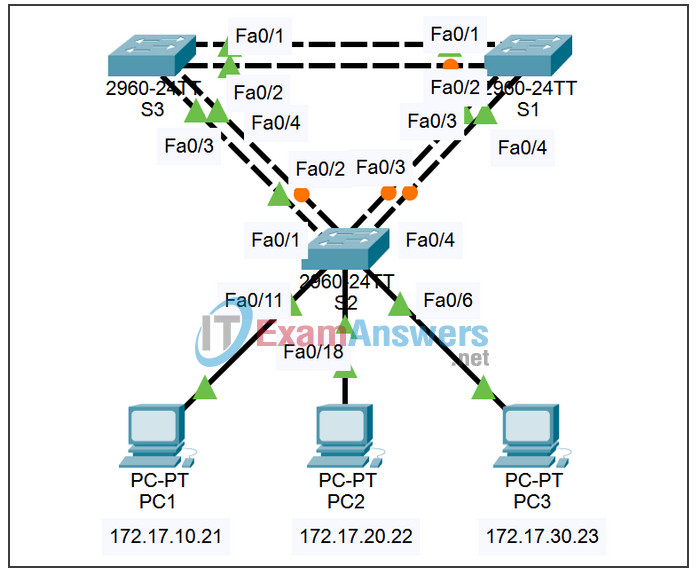
Topology
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | VLAN 99 | 172.17.99.11 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S2 | VLAN 99 | 172.17.99.12 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S3 | VLAN 99 | 172.17.99.13 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.17.10.21 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.17.10.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.17.20.22 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.17.20.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 172.17.30.23 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.17.30.1 |
Port Assignments – S2
| Ports | Assignment | Network |
|---|---|---|
| Fa0/1 – 0/5 | 802.1q Trunks (Native VLAN 99) | 172.17.99.0 /24 |
| Fa0/6 – 0/10 | VLAN 30 – Guest (Default) | 172.17.30.0 /24 |
| Fa0/11 – 0/17 | VLAN 10 – Faculty/Staff | 172.17.10.0 /24 |
| Fa0/18 – 0/24 | VLAN 20 – Students | 172.17.20.0 /24 |
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
- Analyze a congestion problem in a redundant, switched LAN network.
- Recognize the capabilities for per-VLAN load balancing with PVST.
- Modify the default STP configuration to optimize available bandwidth.
- Verify that modifications have had the intended effect.
Scenario
You are responsible for the operation of the redundant switched LAN shown in the topology diagram. You and your users have been observing increased latency during peak usage times, and your analysis points to congested trunks. You recognize that of the six trunks configured, only three are forwarding packets in the default STP configuration currently running. The solution to this problem requires more effective use of the available trunks. The PVST+ feature of Cisco switches provides the required flexibility to distribute the inter-switch traffic using all six trunks.
This lab is complete when all wired trunks are carrying traffic, and all three switches are participating in per-VLAN load balancing for the three user VLANs.
Task 1: Prepare the Network
Step 1: Cable a network that is similar to the one in the topology diagram.
You can use any current switch in your lab as long as it has the required interfaces shown in the topology diagram. The output shown in this lab is based on Cisco 2960 switches. Other switch models may produce different output.
Set up console connections to all three switches.
Step 2: Clear any existing configurations on the switches.
Clear NVRAM, delete the vlan.dat file, and reload the switches.
Step 3: Load the switches with the following script:
S1 Configuration
hostname S1 enable secret class no ip domain-lookup ! vtp mode server vtp domain Lab5 vtp password cisco ! vlan 99 name Management exit ! vlan 10 name Faculty/Staff exit ! vlan 20 name Students exit ! vlan 30 name Guest exit ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface range FastEthernet0/5-24 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/2 shutdown ! interface Vlan99 ip address 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! line con 0 logging synchronous password cisco login line vty 0 no login line vty 1 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login ! end
S2 Configuration
hostname S2 ! enable secret class no ip domain-lookup ! vtp mode client vtp domain Lab5 vtp password cisco ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface range FastEthernet0/5 - 10 switchport access vlan 30 switchport mode access ! interface range FastEthernet0/11 - 17 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access ! interface range FastEthernet0/18 - 24 switchport access vlan 20 switchport mode access ! interface fa0/6 no shutdown interface fa0/11 no shutdown interface fa0/18 no shutdown ! interface Vlan99 ip address 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! line con 0 password cisco logging synchronous login line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco
S3 Configuration
hostname S3 ! enable secret class no ip domain-lookup ! vtp mode client vtp domain Lab5 vtp password cisco ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/3 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport trunk native vlan 99 switchport mode trunk no shutdown ! interface range FastEthernet0/5 - 10 switchport access vlan 30 switchport mode access ! interface range FastEthernet0/11 - 17 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access ! interface range FastEthernet0/18 - 24 switchport access vlan 20 switchport mode access ! interface Vlan99 ip address 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! line con 0 password cisco login line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login end
Task 2: Configure Host PCs
Configure the Ethernet interfaces of PC1, PC2, and PC3 with the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway indicated in the addressing table.
Task 3: Identify the Initial State of All Trunks
On each of the switches, display the spanning tree table with the show spanning-tree command. Note which ports are forwarding on each switch, and identify which trunks are not being used in the default configuration. You can use your network topology drawing to document the initial state of all trunk ports.
Task 4: Modify Spanning Tree to Achieve Load Balancing
Modify the spanning tree configuration so that all six trunks are in use. Assume that the three user LANs (10, 20, and 30) carry an equal amount of traffic. Aim for a solution that will have a different set of ports forwarding for each of the three user VLANs. At a minimum, each of the three user VLANs should have a different switch as the root of the spanning tree.
Task 5: Document the Switch Configuration
When you have completed your solution, capture the output of the show run command and save it to a text file for each switch.
Task 6: Clean Up
Erase the configurations and reload the switches. Disconnect and store the cabling. For PC hosts that are normally connected to other networks (such as the school LAN or to the Internet), reconnect the appropriate cabling and restore the TCP/IP settings.
Solution
There are a number of different ways that load balancing can be accomplished. One of the most direct is the following:
S1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 4096 S1(config)#spanning-tree vlan 20 priority 16384 S2(config)#spanning-tree vlan 20 priority 4096 S2(config)#spanning-tree vlan 30 priority 16384 S3(config)#spanning-tree vlan 30 priority 4096 S3(config)#spanning-tree vlan 10 priority 16384
