6.2.2.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring Traditional Inter-VLAN Routing Answers
Topology
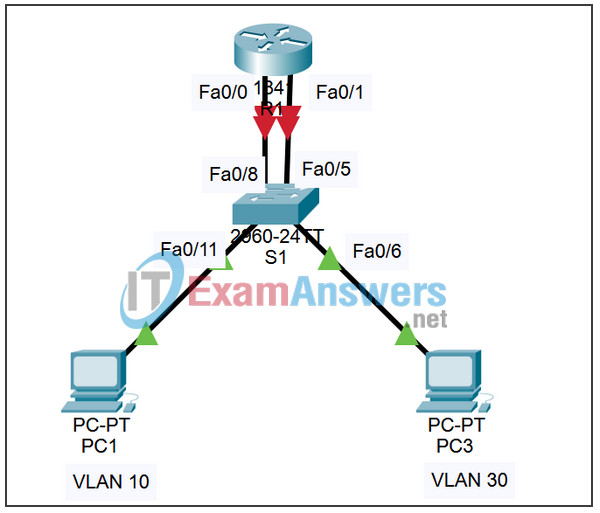
Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Fa0/0 | 172.17.10.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| Fa0/1 | 172.17.30.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.17.10.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.17.10.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.17.30.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.17.30.1 |
Learning Objectives
- Test connectivity without inter-VLAN routing
- Add VLANs to a switch
- Configure IP addressing on a router
- Test connectivity with inter-VLAN routing
Introduction
In this activity, you will configure traditional inter-VLAN routing simply by configuring two Fast Ethernet interfaces on a router. R1 has two connections to S1, one for each of the two VLANs. S1 and R1 already have basic configurations. The user EXEC password is cisco, and the privileged EXEC password is class. You will complete the configuration by adding VLANs to S1 and assigning VLANs to the correct ports. Then you will configure R1 with IP addressing. In traditional inter-VLAN routing, there are no additional, VLAN-related configurations needed on R1.
Task 1: Test Connectivity Without Inter-VLAN Routing
Step 1. Ping between PC1 and PC3.
Wait for switch convergence. The link lights on the switch connecting to PC1 and PC3 change from amber to green. When the link lights are green, ping between PC1 and PC3. Because the two PCs are on separate networks and the router is not configured, they cannot communicate with one another, so the ping fails.
Step 2. Switch to simulation mode to monitor pings.
- Switch to simulation mode by clicking the Simulation tab or pressing Shift+S.
- Click Capture/Forward to see the steps the ping takes between PC1 and PC3.
- Notice how the ping cannot even cross the switch.
Your completion percentage should be 0%.
Task 2: Add VLANs
Step 1. Create VLANs on S1.
Create two VLANs on S1, one for PC1 and one for PC3. PC1 belongs to VLAN 10, and PC3 belongs to VLAN 30. To create the VLANs, issue the vlan 10 and vlan 30 commands in global configuration mode.
S1#configure terminal S1(config)#vlan 10 S1(config-vlan)#vlan 30
To check whether the VLANs were created, issue the show vlan brief command from the privileged EXEC prompt.
S1#show vlan brief
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4
Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8
Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12
Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16
Fa0/17, Fa0/18, Fa0/19, Fa0/20
Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
Gig1/1, Gig1/2
10 VLAN0010 active
30 VLAN0030 active
1002 fddi-default active
1003 token-ring-default active
1004 fddinet-default active
1005 trnet-default active
Step 2. Assign the VLANs to ports.
Each port on the switch is assigned to a VLAN to allow for inter-VLAN communication.
Assign the switch ports as follows:
- Assign the Fa0/8 and Fa0/11 interfaces to VLAN 10.
- Assign the Fa0/5 and Fa0/6 interfaces to VLAN 30.
To assign a VLAN to a port, enter the interface configuration. For Fa0/8, the command is interface fa0/8. The switchport mode access command sets the port to access mode.The switchport access vlan 10 command assigns VLAN 10 to that port.
S1(config)#interface fa0/8 S1(config-if)#switchport mode access S1(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10
Repeat the above steps for Fa0/5, Fa0/6, and Fa0/11, assigning the correct VLANs to each interface.
Step 3. Test connectivity between PC1 and PC3.
Now issue a ping between PC1 and PC3. The ping should still fail.
Step 4. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 45%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 3: Configure IP Addressing
Step 1. Configure IP addressing on R1.
Configure the Fa0/0 interface of R1 with the IP address 172.17.10.1 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
Configure the Fa0/1 interface with the IP address 172.17.30.1 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0.
Issue the no shutdown command on both interfaces to bring them up.
R1(config)#interface fa0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address 172.17.10.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#interface fa0/1 R1(config-if)#ip address 172.17.30.1 255.255.255.0 R1(config-if)#no shutdown
Step 2. Check results.
Your completion percentage should be 100%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
Task 4: Test Connectivity Again
Step 1. Ping between PC1 and PC3.
Wait for STP to converge. Then ping from PC1 to PC3. The ping should succeed.
Step 2. Switch to simulation mode to monitor pings.
- Switch to simulation mode by clicking the Simulation tab or pressing Shift+S.
- Click Capture/Forward to see the steps the ping takes between PC1 and PC3.
- Watch as the ping goes from PC1 through S1, then to R1, then back to S1, and finally to the PC3.
