Chapter 11 – Sections & Objectives
- 11.1 Network Design
- Identify the devices used in a small network.
- Identify the protocols used in a small network.
- Explain how a small network serves as the basis of larger networks.
- 11.2 Network Security
- Explain why security measures are necessary on network devices.
- Identify security vulnerabilities.
- Identify general mitigation techniques.
- Configure network devices with device hardening features to mitigate security threats.
- Apply the commands to back up and restore an IOS configuration file.
- 11.3 Basic Network Performance
- Use the output of the ping command to establish relative network performance.
- Use the output of the tracert command to establish relative network performance.
- Use show commands to verify the configuration and status of network devices.
- Use host and IOS commands to acquire information about network devices.
- 11.4 Network Troubleshooting
- Apply troubleshooting methodologies to resolve problems
- Troubleshoot interface and cable issues
- Troubleshoot client connectivity issues involving DNS
11.1 Network Design
Network Design Devices in a Small Network
-
- Small Network Topologies
- Comprises one router, a couple of switches, and the user PCs.
- Access to Internet through a single WAN link, cable or DSL.
- Management usually by a third party company.
- Small Network Topologies

-
- Device Selection for a Small Network
- Security, QoS, VoIP, L3 switching, NAT, and DHCP
- Device Selection for a Small Network

-
- IP Addressing for a Small Network
- Address space is a crucial component of a network design.
- All devices connected to the network require an address.
- The address scheme must be planned, documented, and maintained.
- Address space documentation can be very useful for:
- Troubleshooting and control
- Address documentation is also very important when controlling resource access.
- IP Addressing for a Small Network



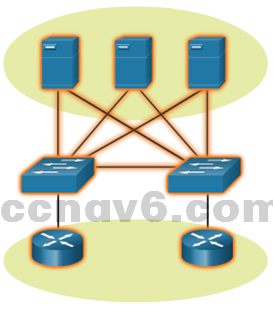
- Redundancy in a Small Network
- A network should reliable by design.
- Network failures are usually very costly.
- Redundancy increases reliability by eliminating single points of failure.
- Network redundancy can be achieved by duplicating network equipment and links.
- A good example is a network’s link to the Internet or to a server farm.
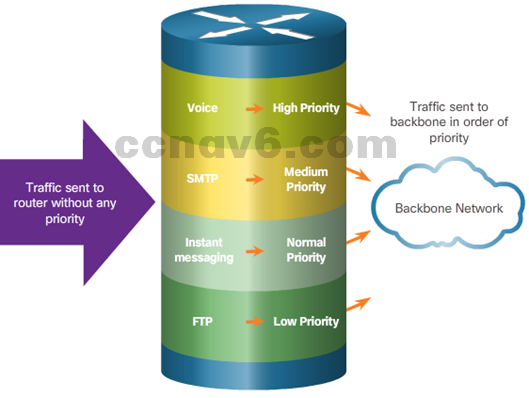
- Traffic Management
- Traffic type and patterns are should also be considered when designing a network.
- A good network design categorizes traffic according to priority.
Small Network Applications and Protocols
-
- Common Applications
- Network Applications
- Used to communicate over the network.
- Email clients and web browsers are examples of this type of application.
- Application Layer Services
- Programs that interface with the network and prepare the data for transfer.
- Each service uses protocols, which define the standards and data formats to be used.
- Network Applications
- Common Protocols
- Processes on either end of a communication session
- How messages are sent and the expected response
- Types and syntax of messages
- Meaning of informational fields
- Interaction with the next lower layer
- Voice and Video Applications
- Infrastructure
- VoIP
- IP Telephony
- Real-time Applications
- Common Applications
Scale to Larger Networks
-
- Small Network Growth
- To scale a network, several elements are required:
- Network documentation
- Device inventory
- Budget
- Traffic analysis
- To scale a network, several elements are required:
- Small Network Growth

-
- Protocol Analysis
- Understand the protocols in use in the network.
- Protocol analyzers are tools designed to help in that task.
- Capture traffic in high-utilization times and in different locations of the network.
- Analysis results allow for more efficient way to manage traffic.
- Protocol Analysis

- Employee Network Utilization
- Be aware of how network use is changing.
- A network administrator can create in-person IT snapshots” of employee application utilization.

11.2 Network Security
Security Threats and Vulnerabilities
- Types of Threats
- Digital intrusion can be costly.
- Intruders can gain access through software vulnerabilities, hardware attacks, or stolen credentials.
- Common types of digital threats include those listed in this graphic.
- Physical Security
- Hardware
- Environmental
- Electrical
- Maintenance
- Types of Vulnerabilities
- Three primary vulnerabilities: technological, configuration, and security policy
- Endpoints can be under attack ,such as servers and desktop computers.
- Any of these three vulnerabilities can be exploited and used in attacks.
Network Attacks
-
- Types of Malware
- Viruses
- Worms
- Trojan Horses
- Types of Malware

-
- Reconnaissance Attacks
- Discovery and mapping of systems and services
- Acquire enough information on the target system or network to facilitate the search for vulnerabilities.
- Common tools rely mostly on free and public Internet services, such as DNS and Whois.
- Port-scanners and packet sniffers are also commonly used in reconnaissance.
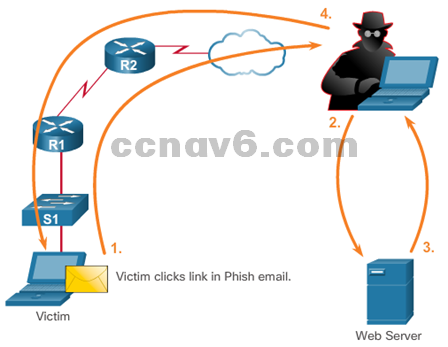
- Access Attacks
- Password Attacks
- Trust Exploitation
- Port Redirection
- Man-in-the-Middle
- Reconnaissance Attacks
-
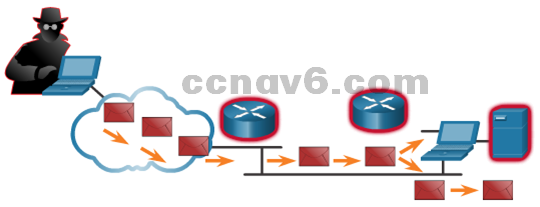
- Denial of Service Attacks
- Although simple, DoS attacks are still dangerous.
- Prevent authorized people from using a service by consuming system resources.
- Prevent DoS attacks by applying the latest security updates.
- Common DoS Attacks:
- Ping of Death
- SYN Flood
- DDoS
- Smurf Attack
- Denial of Service Attacks
Network Attack Mitigation
- Backup, Upgrade, Update, and Patch
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest developments
- Enterprises need to keep current with the latest versions of antivirus software.
- Patches for all known vulnerabilities must be applied.
- A central patch server for managing a large number of servers and systems.
- Patches should be installed without user intervention.
- Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
- AAA services provide access control on a network device.
- Authentication – access a resource
- Authorization – what they can do
- Accounting – actions performed while accessing the resource
- The AAA framework can be very helpful when mitigating network attacks.
- AAA services provide access control on a network device.
- Firewalls
- A firewall controls the traffic and helps prevent unauthorized access
- Techniques for determining what is permitted or denied access to a network include:
- Packet filtering
- Application filtering
- URL filtering
- Stateful packet inspection (SPI)
- Endpoint Security
- Common endpoints are laptops, desktops, servers, smartphones, and tablets.
- Securing endpoint devices is challenging.
- Employees need to be trained on proper use of the network.
- Policies often include the use of antivirus software and host intrusion prevention.
- More comprehensive endpoint security solutions rely on network access control.
Device Security
- Device Security Overview
- Default settings are dangerous because they are well-known.
- Cisco routers have the Cisco AutoSecure feature.
- In addition, the following apply for most systems:
- Change default usernames and passwords immediately
- Restrict access to system resources to authorized individuals only.
- Turn off unnecessary services.
- Update any software and install any security patches prior to production operation.
- Passwords
- Use strong passwords. A strong password has/is:
- At least 8 characters, preferably 10 or more
- A mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, symbols, and spaces.
- No repetition, no common dictionary words, no letter or number sequences, no usernames, relative, or pet names, and no other easily identifiable pieces of information
- Misspelled words
- Changed often
- Cisco routers support the use of a phrase made of many words, which is called a passphrase.
- Use strong passwords. A strong password has/is:
- Basic Security Practices
- Strong passwords are only as useful as they are secret.
- The service password-encryption command encrypts the passwords in the configuration.
- The security passwords min-length command ensures all configured passwords have a minimum specified length.
- Blocking several consecutive login attempts helps minimize password brute-force attacks.
- login block-for 120 attempts 3 within 60 will block login attempts for 120 seconds if there are three failed login attempts within 60 seconds.
- exec timeout automatically disconnect idle users on a line
- Enable SSH
- Telnet is not secure.
- It is highly recommended to use SSH for remote shell protocol.
- To configure a Cisco device to support SSH takes four steps:
- Step 1. Ensure that the router has a unique hostname and a IP domain name.
- Step 2. Generate the SSH keys.
- Step 3. Create a local username.
- Step 4. Enable vty inbound SSH sessions.
- The router can now be remotely accessed only by using SSH.
11.3 Basic Network Performance
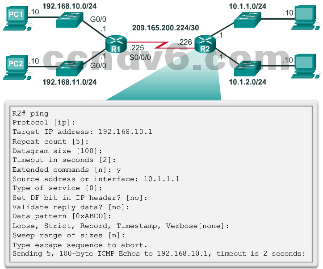
The ping Command
- Interpreting Ping Results
- Using the ping command is an effective way to test connectivity.
- Use the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) to verify Layer 3 connectivity.
- Help to identify the source of the problem.
- What do these common ping indicators tell you?
– ! . U - Extended Ping
– Allows for more options
- Network Baseline
- Built over a period of time.
- Saved results from commands, such as ping or trace, along with error messages an response times
- Time stamped for later comparison.
- Increased response time could indicate latency issue.
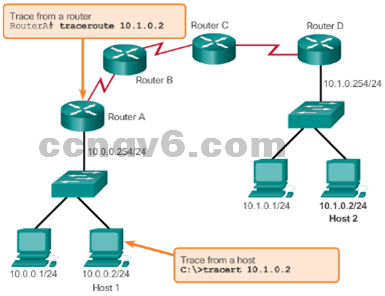
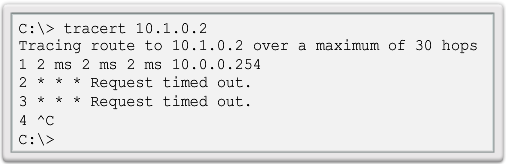
The traceroute and tracert Command
- Interpreting Trace Message
- Returns a list of hops as a packet is routed through a network.
- Use tracert for Windows-based systems.
- Use traceroute for Cisco IOS and UNIX-based systems.
- Extended Traceroute
- Allows adjustment of parameters
- Command terminates when:
- Destination responds with an ICMP echo reply
- User interrupts the trace with the escape sequence
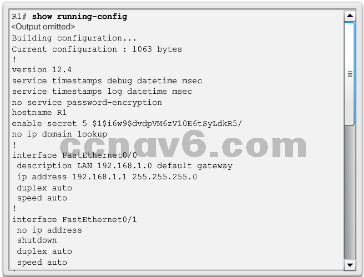
Show Commands
-
- The Cisco IOS CLI show commands are powerful troubleshoot tools.
- The show commands display configuration files, checking the status of device interfaces and processes, and verifying the device operational status.
- The status of nearly every process or function of the router can be displayed using a show command.
- Some of the more popular show commands are:
- show running-config
- show interfaces
- show arp
- show ip route
- show protocols
- show version
Host and IOS Commands
-
- The ipconfig Command
- Display IP and default gateway information on a Windows-based computer.
- What do these commands display?
- ipconfig /all
- ipconfig /displaydns
- The arp Command
- The arp –a command lists all devices currently in the ARP cache of the host.
- The cache can be cleared by using the arp -d command.
- The ipconfig Command
-
- The show cdp neighbors Command
- CDP is a Cisco-proprietary protocol that runs at the data link layer.
- Two or more Cisco network devices can learn about each other even if Layer 3 connectivity does not exist.
- CDP can be a security risk.
- To disable CDP globally, use the global configuration command no cdp run.
- To disable CDP on an interface, use the interface command no cdp enable.
- What information does the cdp neighbors details command provide?
- The show ip interface brief Command
- Displays a summary of the key information for all the network interfaces on a router.
- Verify the status of the switch interfaces.
- The show cdp neighbors Command
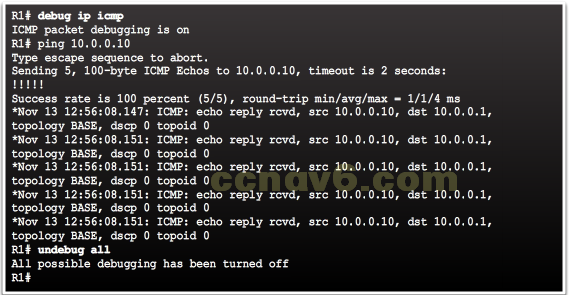
Debugging
- The debug Command
- Allows the administrator to display
messages generated by the following
processes in real-time for analysis:- IOS processes
- Protocols
- Mechanisms
- Events
- undebug all turns off all debug commands
- What are the available debug commands?
- What can you do to limit the amount of displayed messages?
- Allows the administrator to display
- The terminal monitor Command
- Displays the log messages while connected remotely, such as SSH
- Stop displaying the log message: terminal no monitor
11.4 Network Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Methodologies
- Basic Troubleshooting Approaches
- Identify the Problem
- Establish a Theory of Probable Causes
- Test the Theory to Determine Cause
- Establish a Plan of Action to Resolve the Problem and Implement the Solution
- Verify Full System Functionality and Implement Preventative Measures
- Document Findings, Actions, and Outcomes
- Resolve or Escalate?
- Verify and Monitor Solution
- What IOS commands can you use to verify and monitor the solution?
Troubleshoot Cables and Interfaces
- Duplex Operation
- Direction of data transmission between two devices
- Two connected Ethernet network interfaces should operate in the same duplex mode for best performance
- Duplex Mismatch
- Log messages can indicate duplex mismatches.
- What IOS commands can you use to determine duplex mismatch?

Troubleshooting Scenarios
- IP Addressing Issues on IOS Devices
- Manual assignment mistakes
- DHCP-related issues
- Which show commands?
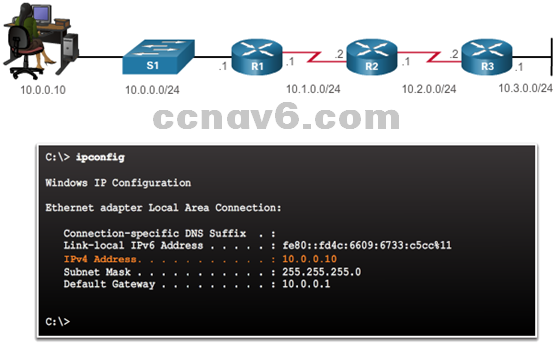
- IP Addressing Issues on End Devices
- 169.254.0.0/16 on Windows-based system
- ipconfig to verify IP addresses assigned to a Windows-based system
- Default Gateway Issues
- Unable to communicate outside the network
- ipconfig to verify default gateway assigned to a Windows-based system
- Troubleshooting DNS Issues
- ipconfig /all to determine DNS server used
- nslookup to manually place DNS queries and analyze DNS response
11.5 Chapter Summary
Summary
- Explain how a small network can scale into a larger network.
- Configure switches and routers with device hardening features to enhance security.
- Use common show commands and utilities to establish a relative performance baseline for the network.
- Apply troubleshooting methodologies and command host and IOS commands to resolve problems.
- Explain how a small network of directly connected segments is created, configured, and verifies.
Section 11.2 New Terms and Commands
- Application Filtering
- Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA)
- auto secure (command)
- exec timeout (command)
- crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus modulus-size (command)
- endpoint security
- ip domain-name domain-name (command)
- login block-for 120 attempts 3 within 60 (command)
- Packet Filtering
- passphrase
- Personal firewalls
- security passwords min-length (command)
- Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI)
- service password-encryption (command)
- transport input ssh
- URL Filtering
Section 11.3 New Terms and Commands
- ! . U
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- exec timeout (command)
- crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus modulus-size (command)
- ip domain-name domain-name (command)
- ipconfig (host command)
- login block-for 120 attempts 3 within 60 (command)
- loopback address 127.0.0.1
- ping (command)
- security passwords min-length (command)
- service password-encryption (command)
- show cdp neighbors (IOS command)
- show ip interface brief (IOS command)
- tracert (host command)
- traceroute (IOS command)
- transport input ssh
