Chapter 3 – Sections & Objectives
- 3.1 Rules of Communication
- Describe the types of rules that are necessary to successfully communicate.
- 3.2 Network Protocols and Standards
- Explain why protocols are necessary in communication.
- Explain the purpose of adhering to a protocol suite.
- Explain the role of standards organizations in establishing protocols for network interoperability.
- Explain how the TCP/IP model and the OSI model are used to facilitate standardization in the communication process.
- 3.3 Data Transfer in the Network
- Explain how data encapsulation allows data to be transported across the network.
- Explain how local hosts access local resources on a network.
3.1 Rules of Communication
The Rules
- Rule Establishment
- Identified sender and receiver
- Common language and grammar
- Speed and timing of delivery
- Confirmation or acknowledgment requirements
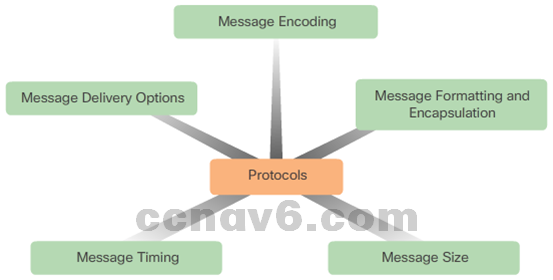
- Message Encoding
Process of converting information into another acceptable form - Message Formatting and Encapsulation
- Message Size
- Message Timing
- Access method
- Flow control
- Response timeout
- Message Delivery Options
- Unicast
- Multicast
- Broadcast
3.2 Network Protocols and Standards
Protocols
- Rules that Govern Communications
- Network Protocols
- The role of protocols
- How the message is formatted or structured
- The process by which networking devices share information about pathways with other networks
- How and when error and system messages are passed between devices
- The setup and termination of data transfer sessions
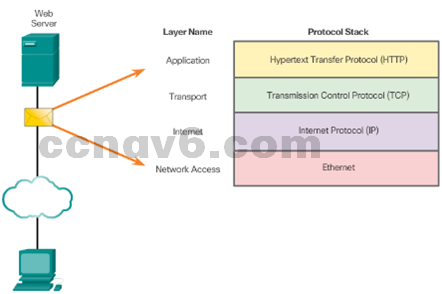
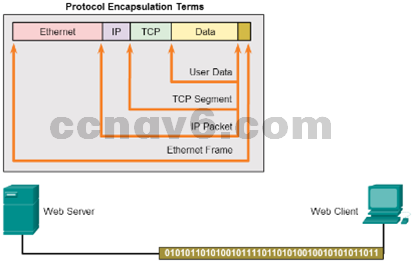
- Protocol Interaction
Example: web server and client
Protocol Suites
- Protocol Suites and Industry Standards
- TCP/IP is an open standard
- Can you name other protocol suites?
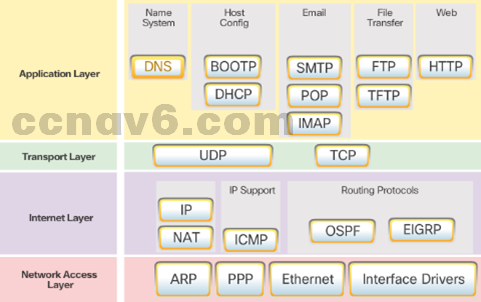
- TCP/IP Protocol Suites
Can you name some of the protocols from the TCP/IP protocol suite. - TCP/IP Communication Process
Can you describe the process?
Standard Organizations
- Open Standards
Name some advantages of open standards - Internet Standards
Name a few standard organizations - Electronics and Communications Standards Organizations
Name a few organizations

Reference Models
- The Benefits of Using a Layered Model
Name some benefits - The OSI Reference Model
- Provides list of functions
- Describes interactions between layers
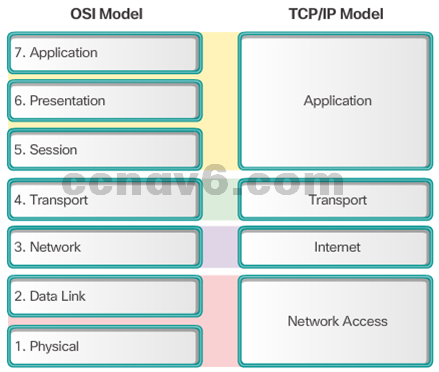
- OSI Model and TCP/IP Model Comparison
- Similar: transport and network layers
- Contrast: relationship between layers
3.3 Data Transfer in the Network
Data Encapsulation
- Message Segmentation
- Segmentation – Break communication into pieces
- Multiplexing – interleaving the pieces
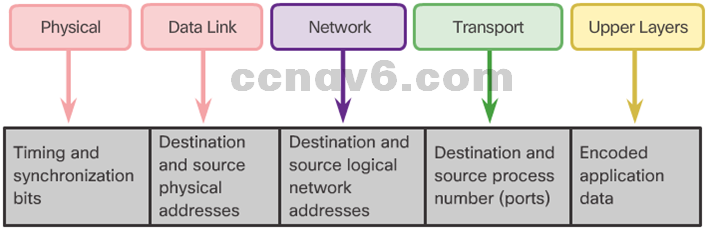
- Protocol Data Units
What are PDUs called at each layer? - Encapsulation and de-encapsulation process
Data Access
- Network Addresses
- Source IP address
- Destination IP address
- Deliver the IP packet from the original source to the final destination, either on the same network or to a remote network.
- Data Link Addresses
- Source data link address
- Destination data link address
- Deliver the data link frame from one network interface card (NIC) to another NIC on the same network
- Devices on the Same Network
- Devices on a Remote Network
3.4 Chapter Summary
Summary
- Explain how rules are used to facilitate communication.
- Explain the role of protocols and standards organizations in facilitating interoperability in network communications.
- Explain how devices on a LAN access resources in a small to medium-sized business network.
Section 3.1 New Terms and Commands
- access method
- acknowledgement
- broadcast
- decoder
- encapsulation
- encoder
- flow control
- message
- message delivery options
- message encoding
- message formatting
- message formatting and encapsulation
- message size
- message timing
- multicast
- protocols
- receiver
- response timeout
- segmenting
- transmission medium
- transmitter
- unacknowledged
- unicast
Section 3.2 New Terms and Commands
- Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET)
- AppleTalk
- application protocol
- Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA)
- Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
- IEEE 802.3
- IEEE 802.11
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
- International Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
- International Telecommunications Union-Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T)
- Internet Architecture Board (IAB)
- Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- internet protocol
- Internet Society (ISOC)
- Internetwork Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange (IPX/SPX)
- Media Access Control (MAC)
- network access protocols
- network protocol suite
- protocol model
- protocol stack
- proprietary protocol
- reference model
- Request for Comments (RFC)
- standards organization
- standards-based protocol
- Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
- Transmission Control Protocol/IP (TCP/IP)
- transport protocol
Section 3.3 New Terms and Commands
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
- bits
- data
- data encapsulation
- data link address
- de-encapsulation
- default gateway
- destination data link address
- destination IP address
- frame
- Multiplexing
- network address
- packet
- protocol data unit (PDU)
- source IP address
- source data link address
- Segment
- segmentation
