Chapter 7 – Sections & Objectives
- 7.1 IPv4 Network Addresses
- Convert between binary and decimal numbering systems.
- Describe the structure of an IPv4 address including the network portion, the host portion, and the subnet mask.
- Compare the characteristics and uses of the unicast, broadcast, and multicast IPv4 addresses.
- Explain public, private, and reserved IPv4 addresses.
- 7.2 IPv6 Network Addresses
- Explain the need for IPv6 addressing.
- Describe the representation of an IPv6 address.
- Describe types of IPv6 network addresses.
- Configure global unicast addresses.
- Describe multicast addresses.
- 7.3 Connectivity Verification
- Explain how ICMP is used to test network connectivity.
- Use ping and traceroute utilities to test network connectivity.
7.1 IPv4 Network Addresses
Binary and Decimal Conversion
- IPv4 Addresses
-
- consists of a string of 32 bits, divided into four sections called octets.
- Each octet contains 8 bits (or 1 byte) separated with a dot.
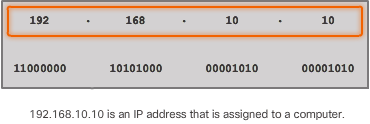
-
- Conversion between Binary to Decimal
-
- Use the chart to help with conversion
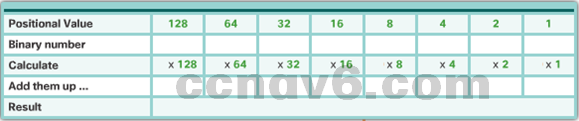
-
IPv4 Address Structure
-
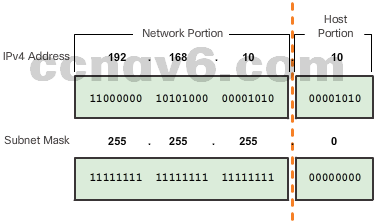
- Network and Host Portions
- The Subnet Mask
- Logical AND
- What is the network address for graphics?
- Prefix Length
- What is the prefix length for the graphics?
- Network, Host, and Broadcast Addresses
- Network Address?
- Range of Valid Hosts?
- Broadcast Address?
IPv4 Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast
- IPv4 Addressing Assignment to a Host
- Static – Type in manually
- Dynamic – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- IPv4 Communication
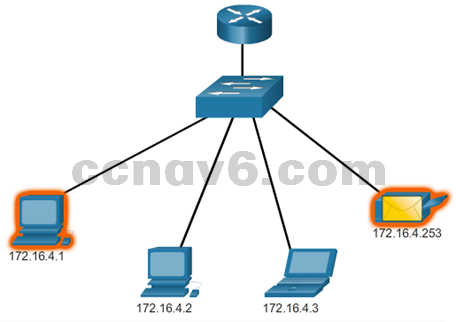
- Unicast – send packets from one host to an individual host
- Broadcast – send packets from one host to all the hosts in the network
- Multicast – send a packet from one host to a selected group of hosts in the same or different network
- Which types of communication are the graphics on the right?
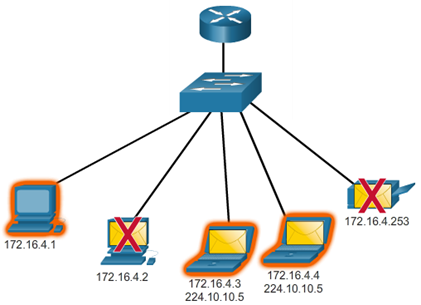
Types of IPv4 Addresses
-
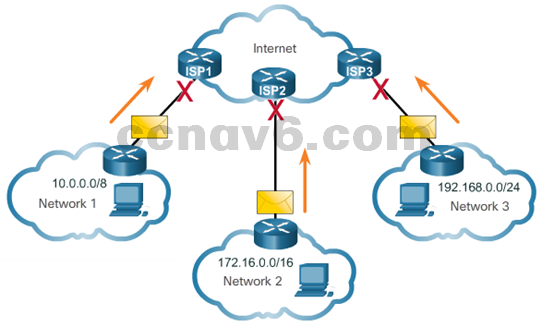
- Public and Private IPv4 Addresses
- Private addresses are not routed over the Internet
- Private Addresses:
- 10.0.0.0/8 or 10.0.0.0 to10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 /12 or 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 /16 or 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
- Public and Private IPv4 Addresses
-
- Special User IPv4 Addresses
- Loopback addresses
– 127.0.0.0 /8 or 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.254 - Link-Local addresses or Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA) addresses
– 169.254.0.0 /16 or 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254 - TEST-NET addresses
– 192.0.2.0/24 or 192.0.2.0 to 192.0.2.255
- Loopback addresses
- Classless Addressing
- CIDR
- Allocated IPv4 addresses based on prefix length
- Assignment of IP Addresses
- Special User IPv4 Addresses
7.2 IPv6 Network Addresses
IPv4 Issues
- The Need for IPv6
- Depletion of IPv4 address space
- Internet of Everything
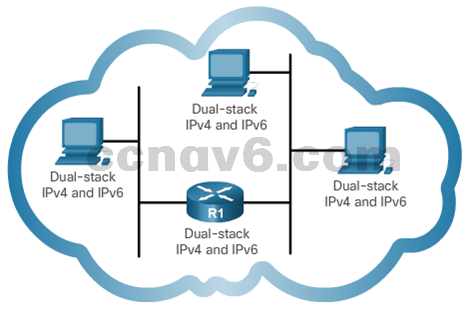
- IPv4 and IPv6 Coexistence
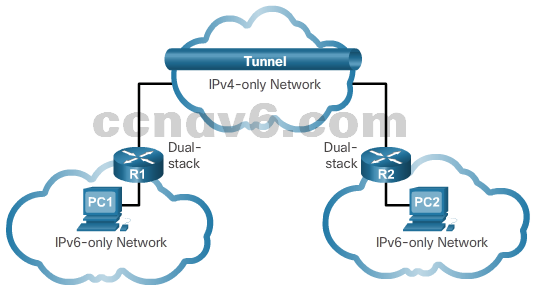
- Dual Stack – IPv4 and IPv6 on the same network
- Tunneling – IPv6 packets inside IPv4 packets
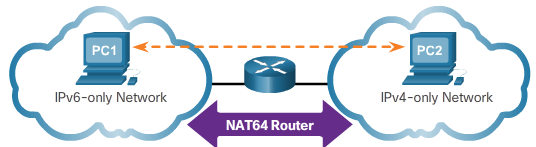
- Translation – IPv6 packet is translated to an IPv4 packet, and vice versa.
IPv6 Addressing
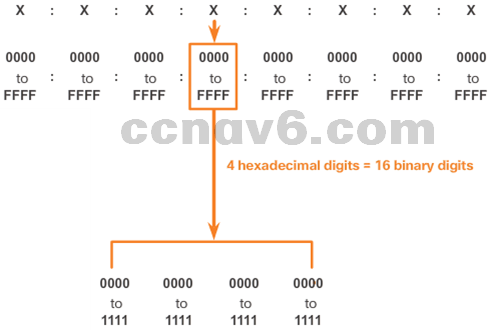
- IPv6 Address Representation
x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x, where x represents 4 hexadecimal values - Apply the rules to simply these IPv6 Addresses
- Rule 1: Omit Leading 0s
- Rule 2: Omit All 0 Segments
- 2001:0DB8:0000:1133:0000:0000:0000:0200
- 2001:0DB8:CAFE:0000:1111:0000:0000:0200
- 2001:0DB8:000A:0000:0000:0000:0000:1000
- 2001:0DB8:ACAD:1234:0000:0000:0000:0000
- 2001:0DB8:0000:1111:0020:0000:ACAD:0000
- FF02:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001
- FE80:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0003
- 0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000
Types of IPv6 Addresses
-
- IPv6 Address Types
- Unicast
- Multicast
- Anycast
- IPv6 Prefix Length
- Indicates the network portion
- Format: IPv6 address /prefix length
- Prefix length range from 0 to 128
- Typical length is /64
- IPv6 Address Types
- Common Types of IPv6 Addresses
-
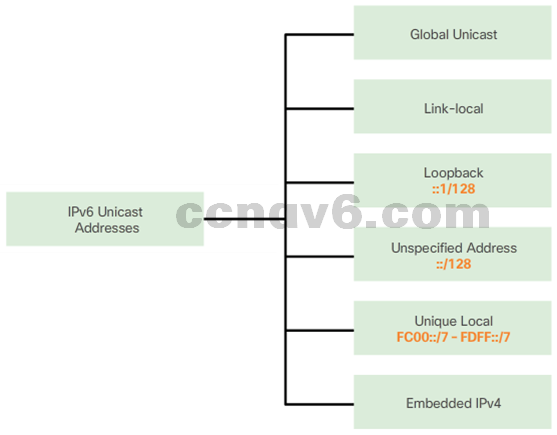
- Unicast Addresses
– Unique, Internet routable addresses
– Configured statically or assigned dynamically - Link-Local Unicast Addresses
– Communicate with other IPv6 enabled devices on the same link
– Device creates its own link local address without DHCP server - Unique Local Addresses
– Unique local unicast
– Used for local addresses within a site or between a limited number of sites
- Unicast Addresses
-
IPv6 Unicast Addresses
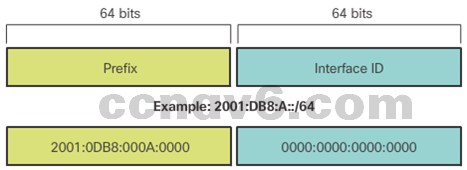
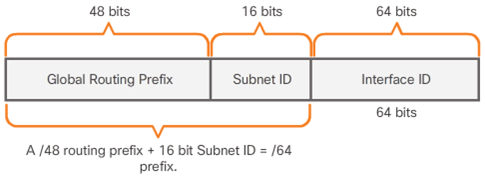
- Structure of an IPv6 Global Unicast Address
- Global Routing Prefix
- Subnet ID
- Interface ID
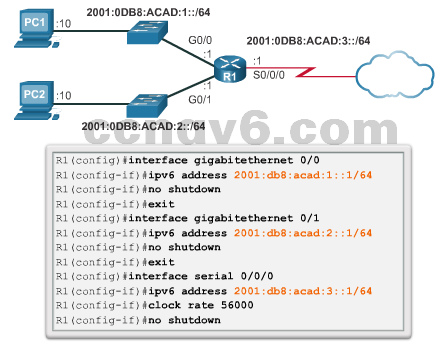
- Static Configuration of a Global Unicast Address
- ipv6 address ipv6-address/prefix-length
- Dynamic Configuration
- SLAAC
- DHCPv6
- Link-Local Addresses
- Dynamic or Static
- Verifying IPv6 Address Configuration
- show ipv6 interface brief
IPv6 Multicast Addresses
- Assigned IPv6 Multicast Addresses
- IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8
– FF02::1 All-nodes multicast group
– FF02::2 All-routers multicast group
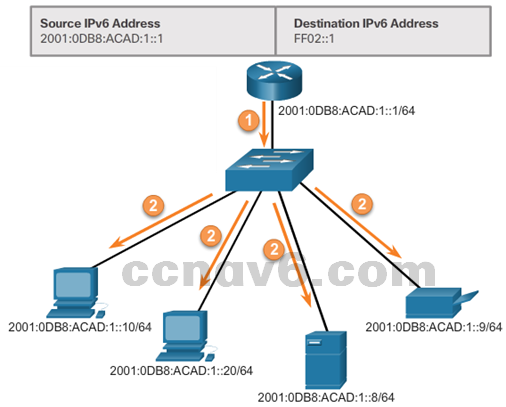
- IPv6 multicast addresses have the prefix FF00::/8
- Solicited-Node IPv6 Multicast Addresses
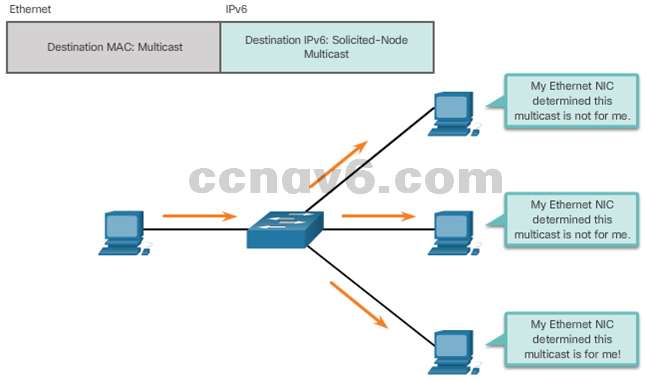
7.3 Connectivity Verification
ICMP
- ICMPv4 and ICMPv6
- Host Confirmation
- Destination or Service Unreachable
- Time Exceeded
- Router Redirection
- ICMPv6 Router Solicitation and Router Advertisement Messages
- Messaging between an IPv6 router and an IPv6 device:
- Router Solicitation (RS) message
- Router Advertisement (RA) message
- Messaging between IPv6 devices:
- Neighbor Solicitation (NS) message
- Neighbor Advertisement (NA) message
- Duplicate Address Detection (DAD)
- Messaging between an IPv6 router and an IPv6 device:

Testing and Verification
- Ping
- Testing the Local Stack
– 127.0.0.1 (IPv4) or ::1 (IPv6) - Testing Connectivity to the Local LAN
- Testing Connectivity to Remote
- Testing the Local Stack
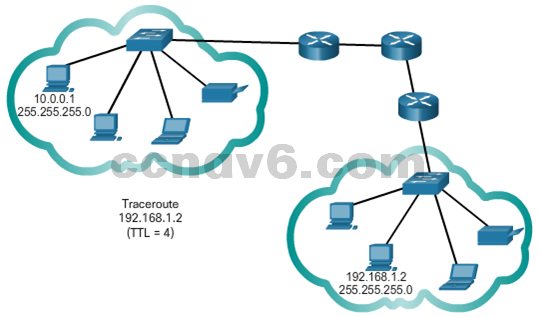
- Traceroute
- Testing the Path
– Round Trip Time (RTT)
– IPv4 TTL and IPv6 Hop Limit
- Testing the Path
7.4 Chapter Summary
Summary
- Explain the use of IPv4 addresses to provide connectivity in a small to medium-sized business network.
- Configure IPv6 addresses to provide connectivity in small to medium-sized business networks.
- Use common testing utilities to verify network connectivity.
Section 7.1 New Terms and Commands
-
- ANDing
- Binary Numbering System
- Broadcast
- Broadcast Address
- Broadcast Domain
- Class A
- Class B
- Class C
- Class D
- Class E
- Classless Inter-domain Routing (CIDR)
- DHCP Server
- DHCP Client Dynamic Assignment
- Directed Broadcast
-
-
- Dotted Decimal Format
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- Host Address
- Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
- IPv4 Loopback Address
- Limited Broadcast
- Link-local Addresses
- Multicast Transmission
- Multicast
- Multicast Addresses
- Network Address
-
-
-
- Octet
- Positional Notation
- Prefix Length
- Private Address
- Public Address
- radix
- Regional Internet Registries (RIRs)
- RFC 1918
- Slash Notation
- Static IP Addressing
- Subnet Mask
- TEST-NET Addresses
- Unicast
-
Section 7.2 New Terms and Commands
-
-
- Address Resolution
- Assigned multicast
- Destination or Service Unreachable
- Dual-stack
- Duplicate Address Detection
- EUI-64 Process
- FF02::1 All-nodes multicast group
- FF02::2 All-routers multicast group
- Global Unicast Address
- Hextet
- Host confirmation
-
-
-
- ICMPv6
- IPv4 Time-to-Live (TTL)
- IPv6
- IPv6 Anycast
- IPv6 Hop Limit
- IPv6 link-local address
- IPv6 Loopback Address
- IPv6 Multicast
- IPv6 Prefix Length
- IPv6 Unicast
- Leading Zeros
- Link-local Address
- Network Address Translation (NAT64)
-
-
-
- Round Trip Time (RTT)
- Route redirection
- Router Advertisement
- Router Solicitation
- show ipv6 interface brief
- show ipv6 route
- Solicited node multicast
- Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC)
- Time exceeded
- Tunneling
- Unique Local Address
- Unspecified Address
-
