Chapter 2 – Sections & Objectives
2.1 IOS Bootcamp
- Explain the purpose of Cisco IOS.
- Explain how to access a Cisco IOS device for configuration purposes.
- Explain how to navigate Cisco IOS to configure network devices.
- Describe the command structure of Cisco IOS software.
2.2 Basic Device Configuration
- Configure hostnames on a Cisco IOS device using the CLI.
- Use Cisco IOS commands to limit access to device configurations.
- Use IOS commands to save the running configuration.
2.3 Address Schemes
- Explain how devices communicate across network media.
- Configure a host device with an IP address.
- Verify connectivity between two end devices.
2.1 IOS Bootcamp
Cisco IOS
-
- Operating Systems
- PC OS allows users to interact with the computer
- User-computer interaction in PC OSs are often done via mouse, keyboard and monitor
- Cisco IOS is also an Operating System
- Cisco IOS allows users to interact with Cisco devices.
- Operating Systems
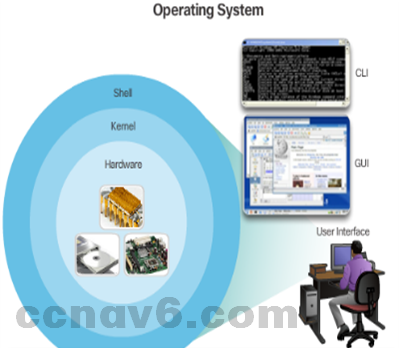
- Cisco IOS enables a technician to:
- Use a keyboard to run CLI-based network programs.
- Use a keyboard to enter text and text-based commands.
- View output on a monitor.
- All Cisco networking devices come with a default IOS.
- It is possible to upgrade the IOS version or feature set.
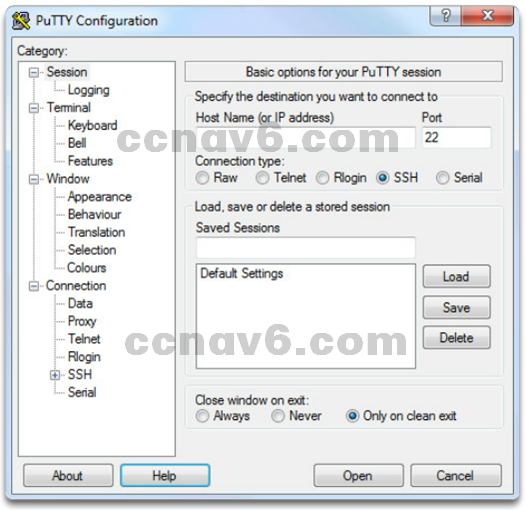
Cisco IOS Access
- Access Methods
- Console
- Auxiliar
- Virtual Terminal (Telnet / SSH)
- Terminal Emulation Programs
- PuTTY
- Tera Term
- SecureCRT
Navigate the IOS
-
- Cisco IOS Modes of Operation
- Initial configuration must be done via console connection.
- Configuration is then done via various CLI command modes.
- Cisco IOS Modes of Operation
- Primary Command Modes
- User EXEC Mode
- Privileged EXEC Mode
- Configuration Command Modes
- The Configure Terminal command enters the Global Configuration Mode.
- Sub-configuration modes are accessible from the Privileged EXEC Mode.
- Examples are: swtich(config-line)# and switch(config-if)#
- Navigate Between IOS Modes
- Navigation between modes is also done via commands.
- The enable command enters the Privileged EXEC Mode.
- The exit commands exits to the parent command mode.
The Command Structure
- Basic IOS Command Structure
- The general syntax for a command is the command followed by any appropriate keywords and arguments.
- Keyword – a specific parameter defined in the operating system
- Argument – not predefined; a value or variable defined by the user
- IOS Command Syntax
- Provides the pattern or format that must be used when entering a command.
- The Cisco IOS Command Reference is the ultimate source of information for a particular IOS command.
- IOS Help Feature
- The IOS has two forms of help available: Context-Sensitive Help and Command Syntax Check.
- Hotkeys and Shortcuts
- Commands and keywords can be shortened to the minimum number of characters that identify a unique selection.
- Line editing keyboard shortcuts such as Ctrl-A are also supported.
2.2 Basic Device Configuration
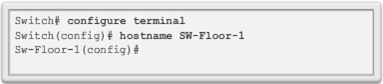
Hostnames
- Device Names
- Hostnames allow devices to be identified by network administrators over a network or the Internet.
- Very important and should also be displayed in the topology.
- Configure Hostnames
- IOS hostnames should:
- Start with a letter
- Contain no spaces
- End with letter or digit
- Use only letters, digits or dashes
- Be less than 64 characters in length
Limit Access to Device Configurations
- Secure Device Access
- Secure privileged EXEC and user EXEC access with a password.
- Secure virtual terminal lines with a password.
- Configure Passwords
- Use strong passwords.
- Avoid re-using passwords
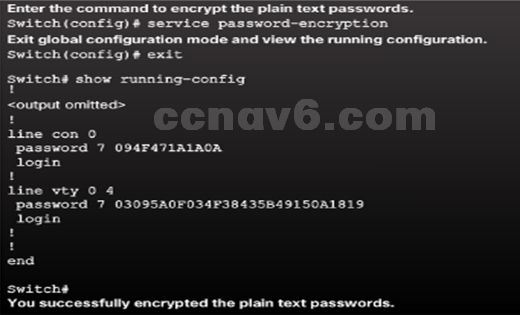
- Encrypt Passwords
- Cisco IOS displays passwords in plain text by default.
- Passwords should be encrypted.
- Banner Messages
- Important part of the legal process in the event that someone is prosecuted for breaking into a device.
- Wording that implies that a login is “welcome” or “invited” is not appropriate.
- Often used for legal notification because it is displayed to all connected terminals.
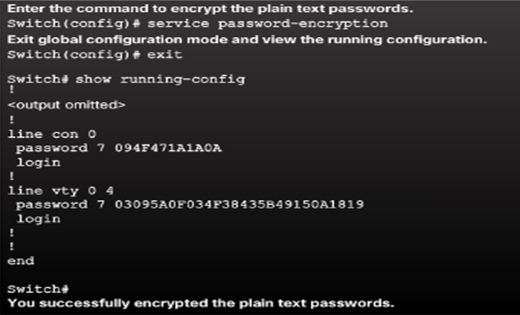
Save Configurations
- Save the Running Configuration File
- File stored in NVRAM that contains all of the commands that will be used upon startup or reboot
- NVRAM does not lose its contents when the device is powered off.
- Alter the Running Configuration
- File stored in RAM that reflects the current configuration, modifying affects the operation of a Cisco device immediately.
- RAM loses all of its content when the device is powered off or restarted.
- Capture Configuration to a Text File
- Configuration files can also be saved and archived to a text document.
- The configuration can then be edited with any text editor and placed back in the device.
2.3 Address Schemes
Ports and Addresses
- IP Addresses
- Each end device on a network must be configured with an IP address.
- Enable devices to establish end-to-end communication on the Internet.
- The structure of an IPv4 address is called dotted decimal notation and is represented by four decimal numbers between 0 and 255.
- IPv6 is the most recent version of IP and the replacement for the more common IPv4.
- Interface and Ports
- Network communications depend on interfaces and the cables that connect them.
- Different types of network media have different features and benefits.
- Ethernet is the most common local area network (LAN) technology.
- SVI provides a means to remotely manage a switch over a network.

Configure IP Addressing
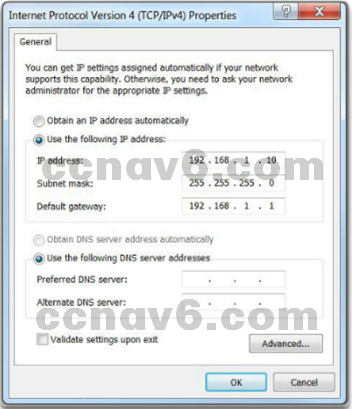
- Manual IP Address Configuration for End Devices
- To manually configure an IPv4 address on a Windows host, open the Control Panel > Network Sharing Center > Change adapter settings and choose the adapter.
- Next right-click and select Properties to display the Local Area Connection Properties shown in Figure 1.
- Automatic IP Address Configuration for End Devices
- DHCP enables automatic IPv4 address configuration for every end device that has DHCP enabled. No extra configuration is needed.
- Switch Virtual Interface Configuration
- To configure an SVI on a switch, use the interface vlan 1 global configuration command. Vlan 1 is not an actual physical interface but a virtual one.
Verifying Connectivity
-
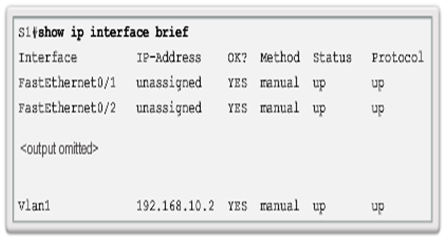
- Interface Addressing Verification
- Cisco IOS supports commands to allow IP configuration verification.
- Interface Addressing Verification
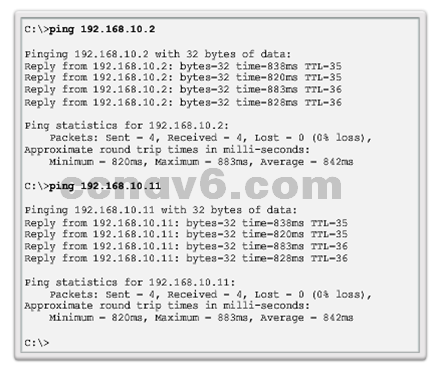
- End-To-End Connectivity Test
- The ping command can be used to test connectivity to another device on the network or a website on the Internet.
2.4 Chapter Summary
Summary
- Explain the features and functions of Cisco IOS Software.
- Configure initial settings on a network device using the Cisco IOS software.
- Given an IP addressing scheme, configure IP address parameters on end devices to provide end-to-end connectivity in a small to medium-sized business network.
Section 2.1 New Terms and Commands
- kernel
- shell
- Command-line interface (CLI)
- Graphical user interface (GUI)
- Cisco IOS
- Firmware
- Console
- Out-of-band
- SSH
- Telnet
- Auxiliary port (AUX)
- PuTTY
- Tera Term
- SecureCRT
- OS X Terminal
- Cisco IOS modes
- User EXEC mode
- Privileged EXEC mode
- Global Configuration Mode
- Line configuration mode
- Interface configuration mode
- enable command
- disable command
- exit command
- end command
- Key combination – Ctrl+Z
- Context-Sensitive Help
- Command Syntax Check
- CLI Hot Keys and Shortcuts
- Hostnames
Section 2.2 New Terms and Commands
- hostname name
- Strong passwords
- enable secret class
- line console 0
- password cisco
- login
- line vty 0 15
- service password-encryption
- banner motd # the message of the day #
- Startup configuration
- Random Access Memory (NVRAM)
- Running configuration
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- show running-config
- copy running-config startup-config
- reload
Section 2.3 New Terms and Commands
- IPv4 address
- Subnet mask
- Default gateway
- Physical ports
- Virtual interface
- Copper
- Fiber Optics
- Wireless
- Ethernet
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Layer 2 switch
- Layer 3 addresses
- Switch virtual interface (SVI)
- Dynamic Host Configuration (DHCP)
- Domain Name System (DNS)
- ipconfig command prompt
- interface vlan 1
