Chapter 4 – Sections & Objectives
- 4.1 Physical Layer Protocols
- Identify device connectivity options.
- Describe the purpose and functions of the physical layer in the network.
- Describe basic principles of the physical layer standards.
- 4.2 Network Media
- Identify the basic characteristics of copper cabling.
- Build a UTP cable used in Ethernet networks (scope – does not include cabling area discussion).
- Describe fiber-optic cabling and its main advantages over other media.
- Connect devices using wired and wireless media.
- 4.3 Data Link Layer Protocols
Describe the purpose and function of the data link layer in preparing communication for transmission on specific media. - 4.4 Media Access Control
- Compare the functions of logical topologies and physical topologies.
- Describe the basic characteristics of media access control methods on WAN topologies.
- Describe the basic characteristics of media access control methods on LAN topologies.
- Describe the characteristics and functions of the data link frame.
4.1 Network Access
Physical Layer Protocols Physical Layer Connection
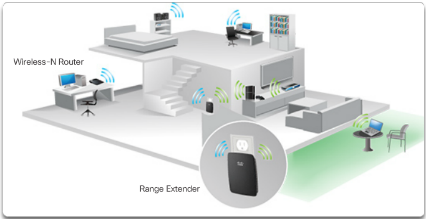
Types of Connections


Network Interface Cards

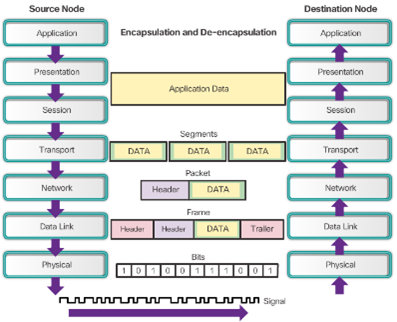
Physical Layer Protocols Purpose of the Physical Layer
- The Physical Layer
- Accepts a complete frame from the data link layer
- Encodes it as a series of signals that are transmitted onto the local media
- Physical Layer Media
Describe the media types - Physical Layer Standards
Physical Layer Protocols Physical Layer Characteristics
- Functions
- Physical components
- Encoding
- Signaling
- Data Transfer
- Bandwidth – capacity to a medium to carry data
- Throughput – measure of the transfer of bits across the media
- Types of Physical Media
4.2 Network Media
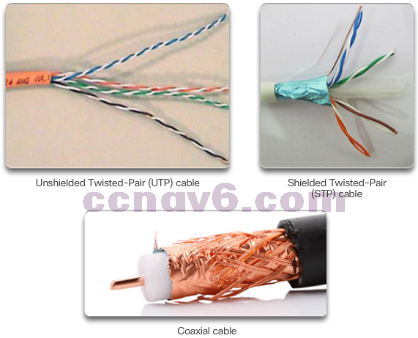
Copper Cabling
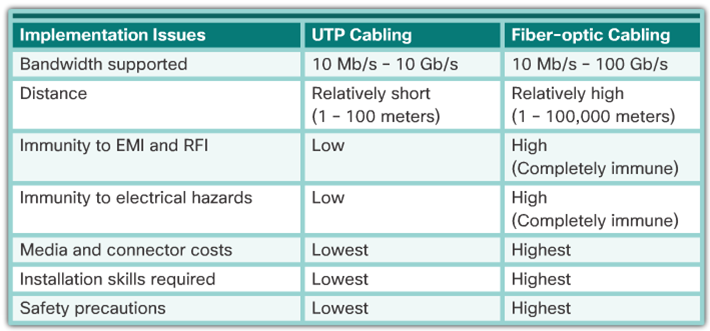
- Characteristics of Copper Cabling
- Inexpensive, easy to install, low resistance to electric current
- Distance and signal interference
- Copper Media
- Unshielded Twisted-Pair Cable
- Shielded Twisted-Pair Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Copper Media Safety
Fire and electrical hazards
UTP Cabling
-
- Properties of UTP Cabling
- Cancellation of EMI and RFI signals with twisted pairs
- Properties of UTP Cabling
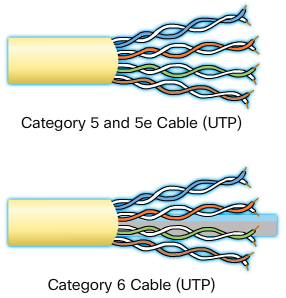
-
- UTP Cabling Standards
- TIA/EIA-568
- IEEE: Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6e
- UTP Cabling Standards

-
- UTP Connectors

-
- Types of UTP Cable
- Rollover
- Crossover
- Straight-through
- Types of UTP Cable
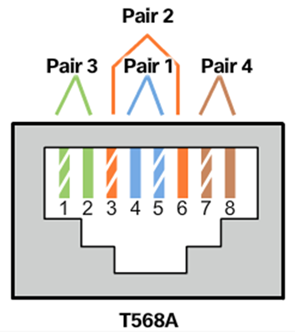
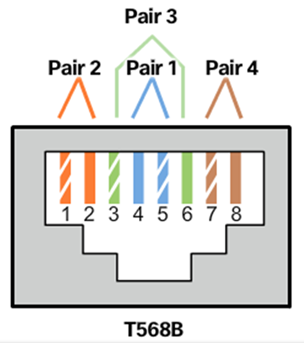
- Testing UTP Cables
- Cable Pinouts
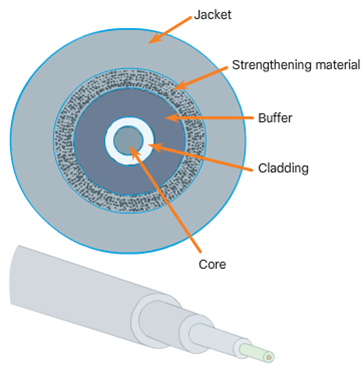
Fiber-Optic Cabling
-
- Properties of Fiber-Optic Cabling
- Transmits data over longer distances
- Flexible, but thin strands of glass
- Transmits with less attenuation
- Immune to EMI and RFI
- Fiber Media Cable Design
- Properties of Fiber-Optic Cabling
- Types of Fiber Media
Single mode and multimode - Fiber-Optic Connectors
- Testing Fiber Cables
- Fiber versus Copper
Wireless Media
- Properties of Wireless Media
– Data communications using radio or microwave frequencies - Types of Wireless Media
– Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, WiMax - Wireless LAN
– Wireless Access Point
– Wireless NIC adapters


4.3 Data Link Layer Protocols
Purpose of the Data Link Layer
- The Data Link Layer
– What is this layer responsible for? - Data Link Sublayers
– LLC communicates with the network layer
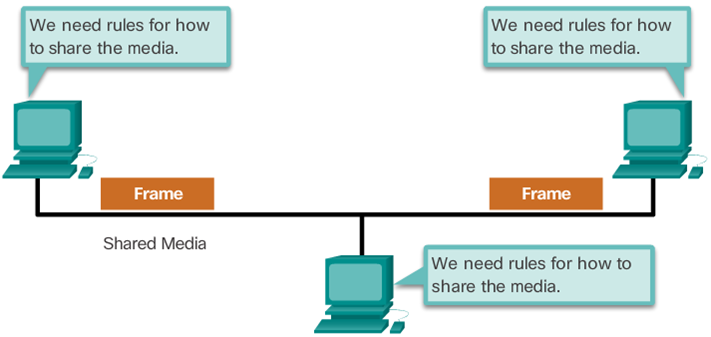
– MAC defines the media access processes - Providing Access to Media
- Data Link Layer Standards
– IEEE
– ITU
– ISO
– ANSI
4.4 Media Access Control
Topologies
- Controlling Access to the Media
- Physical and Logical Topologies
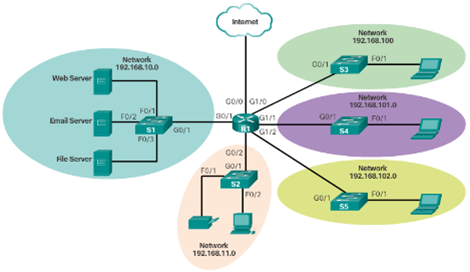
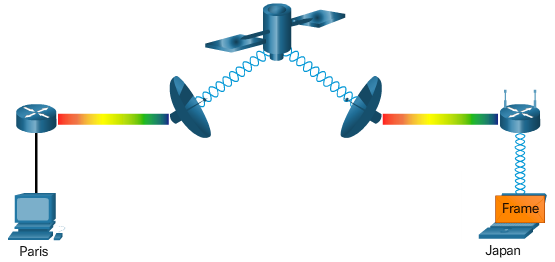
WAN Topologies
- Common Physical WAN Topologies
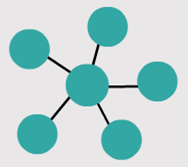
– Point-to-point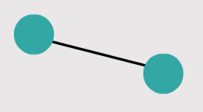 – Hub and spoke
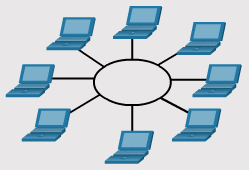
– Hub and spoke
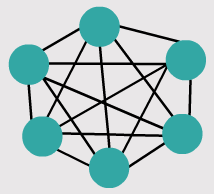
– Mesh
- Physical Point-to-Point Topology
- Logical Point-to-Point Topology

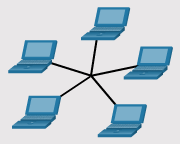
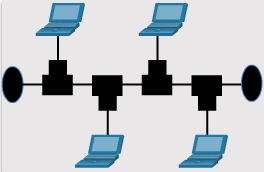
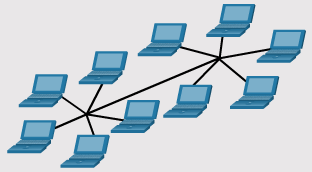
LAN Topologies
- Physical LAN Topologies
- Half and Full Duplex
- Media Access Control Methods
- Contention-Based Access
– CSMA/CD vs. CSMA/CA
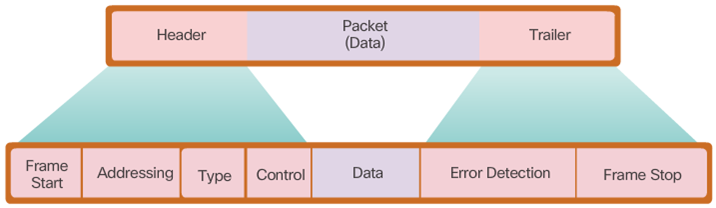
Data Link Frame
- The Frame
– Header
– Data
– Trailer - Frame Fields
- Layer 2 Address
- LAN and WAN Frames
– 802.11 Wireless Frame
– PPP Frame
– HDLC
– Frame Relay
– Ethernet Frame
4.5 Chapter Summary
Summary
- Explain how physical layer protocols and services support communications across data networks.
- Build a simple network using the appropriate media.
- Explain how the Data Link layer supports communications across data networks.
- Compare media access control techniques and logical topologies used in networks.
Section 4.1 New Terms and Commands
- Access Point (AP)
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Bandwidth
- CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization)
- CSA (Canadian Standards Association)
- Copper cable
- European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) Encoding
- Federal Communication Commission (FCC) in the USA
- Fiber-optic cable
- Gigabits per second (Gb/s)
- Goodput
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
- Integrated Service Router (ISR)
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- JSA/JIS (Japanese Standards Association)
- Kilobits per second (kb/s)
- Latency
- Manchester encoding
- Megabits per second (Mb/s)
- Modulation
- Network Interface Cards (NICs)
- OSI Physical Layer
- Signaling
- Telecommunications Industry Association/Electronic Industries Association (TIA/EIA)
- Throughput
- Wireless
- Wireless Local Network (WLAN)
Section 4.2 New Terms and Commands
- Cancelation
- Category 5 cable (Cat 5)
- Enhanced Category 5 cable (Cat5e)
- Category 6 cable (Cat6)
- Category 6a cable (Cat6a)
- Category 7 cable (Cat7)
- Cladding
- Coaxial
- Coaxial cabling
- Core
- Coverage area
- Crosstalk
- Dispersion
- Duplex Multimode LC Connector
- Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
- End gap
- End finish
- Enterprise networks
- Fiber-to-the-home (FTTH)
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
- Interference
- Jacket
- Lasers
- Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
- Long-haul networks
- Misalignment
- Multi-mode fiber (MMF)
- Optical fiber cable
- Radio frequency interference (RFI)
- RJ45 connector
- Rollover
- Shared medium
- Shielded twisted pair cabling (STP)
- Signal attenuation
- Single-mode fiber (SMF)
- ST, SC, and LC fiber-optic connectors
- Submarine networks
- TIA 568A
- TIA 568B
- TIA/EIA 568 standard
- Unshielded twisted pair (UTP)
- Wireless Access Point (AP)
- Wireless NIC adapters
Section 4.3 New Terms and Commands
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
- Data link layer (layer 2)
- Ethernet interface
- Frames
- Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Logical Link Control (LLC)
- Media Access Control (MAC)
- Serial interface
Section 4.4 New Terms and Commands
- 802.11 frame
- 802.11 Wireless
- Bus
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA)
- Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
- Collision
- Contention-based access
- Control
- Controlled access
- Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) value
- Data
- Error Detection
- Ethernet
- Extended Star
- Frame Check Sequence (FCS) Frame Relay
- Frame Relay
- Frame start and stop indicator flags
- Full-Duplex Communications
- Half-Duplex Communications
- HDLC
- Header
- Hub and Spoke
- Logical Point-to-Point Topology
- Logical Topology
- Media Access Control
- Media Sharing
- Mesh
- Physical Point-to-Point Topology
- Physical Topology
- Point-to-Point
- Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
- Quality of Service (QOS)
- Ring
- Star
- Topology
- Trailer
- Type
- Virtual circuit

Thank-you for all your uploads,
This slide download link is broken.
Hello, there is just download-not-available.txt instead of PPTX file.
Thanks for solve.
Jojo