Chapter 6 – Sections & Objectives
- 6.1 Network Layer Protocols
- Describe the purpose of the network layer in data communication.
- Explain why the IPv4 protocol requires other layers to provide reliability.
- Explain the role of the major header fields in the IPv4 and IPv6 packet.
- 6.2 Routing
- Explain how a host device uses routing tables to direct packets to itself, a local destination, or a default gateway.
- Compare a host routing table to a routing table in a router.
- 6.3 Routers
- Describe the common components and interfaces of a router.
- Describe the boot-up process of a Cisco IOS router.
- 6.4 Configure a Cisco Router
- Configure initial settings on a Cisco IOS router.
- Configure two active interfaces on a Cisco IOS router.
- Configure devices to use the default gateway.
6.1 Network Layer Protocols
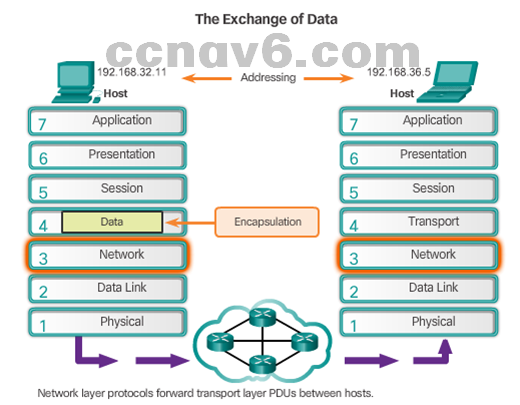
Network Layer in Communications
- The Network Layer
- End to End Transport processes
- Addressing end devices
- Encapsulation
- Routing
- De-encapsulating
- Network Layer Protocols
- IPv4
- IPv6
Characteristics of the IP Protocol
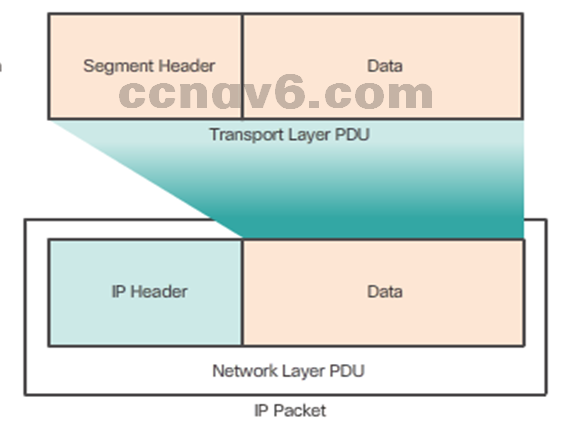
- Encapsulating IP
- Segments are encapsulated into IP packets for transmission.
- The network layer adds a header so packets can be routed to the destination.
- IP – Connectionless
- Sender doesn’t know if the receiver is listening or the message arrived on time.
- Receiver doesn’t know data is coming.
- IP – Best Effort Delivery
No guarantees of delivery are made. - IP – Media Independent
- IP can travel over different types of media.
IPv4 Packet
-
- IPv4 Packet Header
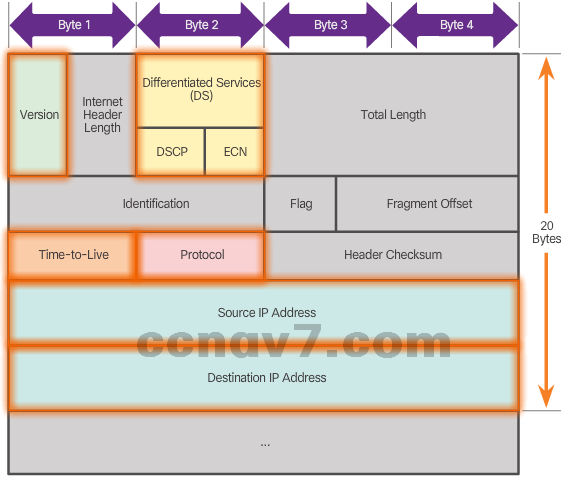
- Version = 0100
- DS = Packet Priority
- TTL = Limits life of Packet
- Protocol = Upper layer protocol such as TCP
- Source IP Address = source of packet
- Destination IP Address = destination of packet
IPv6 Packet
- Limitations of IPv4
- IP address depletion
- Internet routing table expansion
- Lack of end-to-end connectivity
- Introducing IPv6
- Increased address space
- Improved packet handling
- Eliminates the need for NAT
- EncapsulatingIPv6
- Simplified header format
- No checksum process requirement
- More efficient Options Header mechanism
- Flow Label field makes it more efficient.
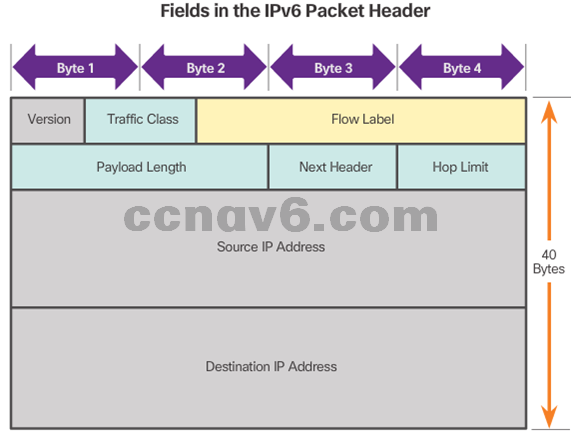
- IPv6 Packet Header
– xx
IPv6 Packet (Cont.)
-
- IPv6 Packet Header
– xx
- IPv6 Packet Header
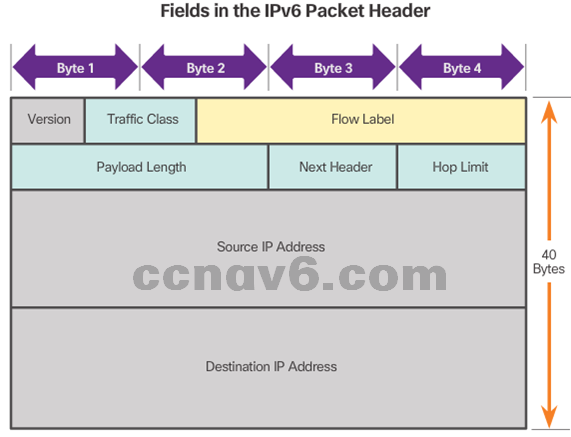
- Version = 0110
- Traffic Class = Priority
- Flow Label = same flow will receive same handling
- Payload Length = same as total length
- Next Header = Layer 4 Protocol
- Hop Limit = Replaces TTL field
6.2 Routing
How a Host Routes
- Host Forwarding Decision
- Three types of destination: itself, local host, remote host.
- Default Gateway
- Routes traffic to other networks
- Has a local IP address in the same address range as other hosts on the network
- Can take data in and forward data out
- Using the Default Gateway
- Hosts will use the default gateway when sending packets to remote networks.
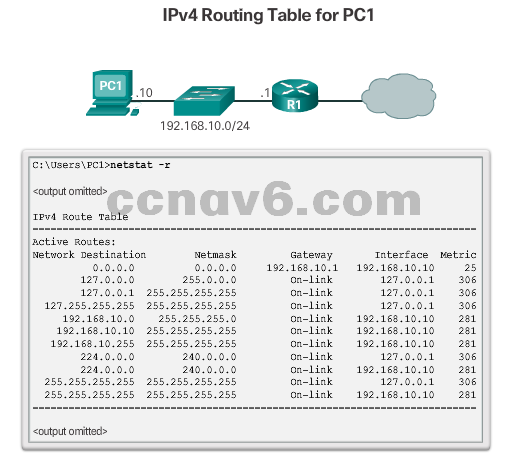
- Host Routing Tables
- Use the netstat –r command to display the
- host routing table on a Windows machine.
How a Host Routes Router Routing Tables
- Router Packet Forwarding Decision
- Routers and hosts forward packets in a similar fashion.
- The main difference is that routers have more interfaces while hosts often have only one.
- Devices on directly connected networks can be reached directly.
- Devices on remote networks are reached through gateway.
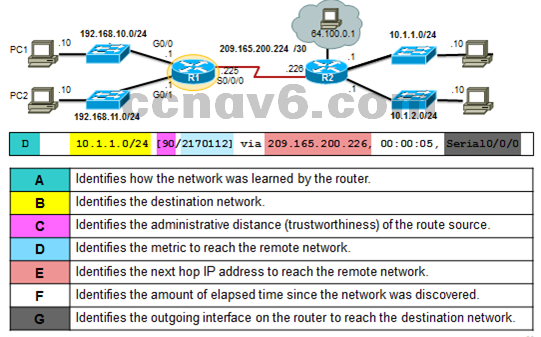
- IPv4 Router Routing Table
- The router routing table stores network routes the router knows about.
- Use the show ip route command to display the routing table on a Cisco router.
- The router routing table also has information on: how the route was learned, its trustworthiness and rating.
- It also contains which interface to use to reach that specifc destination.
- Directly Connected Routing Table Entries
- C – Identifies a directly-connected network, automatically created when an interface is configured with an IP address and activated.
- L – Identifies that this is a local interface. This is the IPv4 address of the interface on the router.
- Remote Network Routing Table Entries
- Remote Network Routing Table Entries
- Remote destinations can’t be reached directly.
- Remote routes contain the address of the intermediate network device to be used to reach the destination.
- Next-Hop Address
Next-Hop address is the address of the intermediate device used to reach a specifc remote destination.
6.3 Routers
Anatomy of a Router
- A Router is a Computer
- Routers have CPU, memory and I/O devices
- Cisco routers use IOS as their operating system.
- Router Memory
- Just as a computer, routers have memory.
- Routers contain RAM, ROM, NVRAM and Flash memory.
- Inside a Router
- Routers have the same general structure.
- Connect to a Router
- Routers have may ports to support connections.
- LAN and WAN Interfaces
- Routers have LAN and WAN ports.
- Different models ship with different ports.
- Ethernet is very common on different router models.

Anatomy of a Router
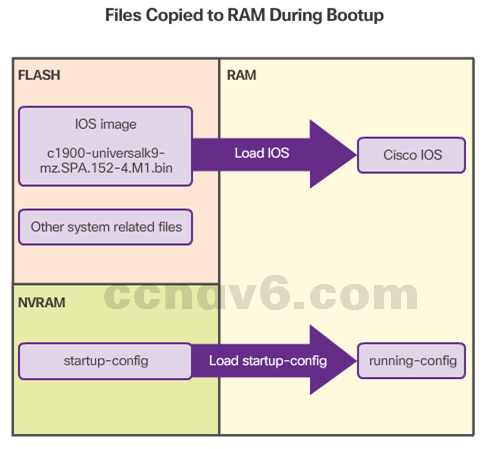
- Bootset Files
- IOS image file, stored in the Flash, contains the IOS.
- The Flash also stores other system files.
- The NVRAM stores configuration parameters.
- Router Bootup Process
- Perform the POST and load the bootstrap program.
- Locate and load the Cisco IOS software.
- Locate and load the startup configuration file or enter setup mode
- Show Version Output
- The show version command is very useful.
- It provides information on the amounts of memory installed, what IOS images was loaded during boot and more.
6.4 Configuring a Cisco Router
Configure Initial Settings
- Basic Switch Configuration Steps
- Configure device name
- Secure EXEC mode
- Secure VTY lines
- Secure privilege EXEC mode
- Secure all passwords
- Provide legal notification
- Configure the management SVI
- Save the configuration
- Basic Router Configuration Steps
- Configure device name
- Secure EXEC mode
- Secure VTY lines
- Secure privilege EXEC mode
- Secure all passwords
- Provide legal notification
- Configure the management SVI
- Save the configuration
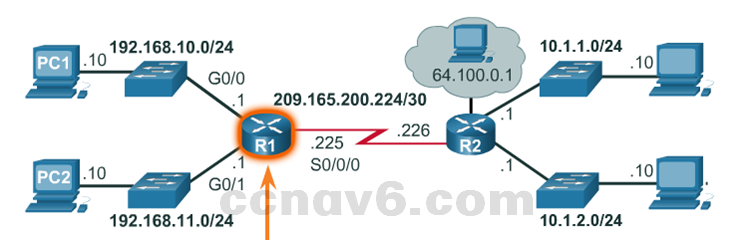
Configure Interfaces
-
- Configure Router Interfaces
- Enter the interface sub-configuration mode.
- Add a description to the Interface (optional)
- Configure an IPv4 or IPv6 address.
- Activate the interface with a no shutdown command
- Verify Interface Configuration
- show ip route – Displays the contents of the IPv4 routing table stored in RAM.
- show interfaces – Displays statistics for all interfaces on the device.
- show ip interface – Displays the IPv4 statistics for all interfaces on a router.
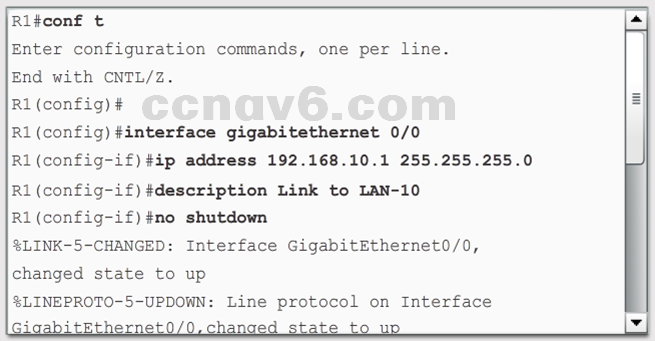
Configure the Default Gateway
-
- Default Gateway for a Host
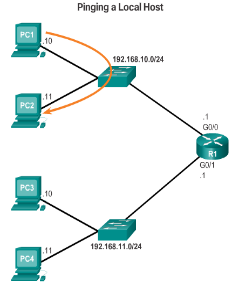
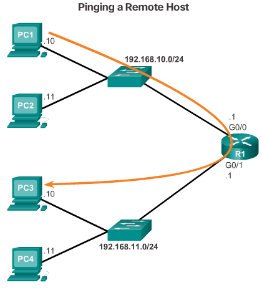
- Default Gateway for a Switch
- A default gateway is required for remote network communication.
- If a switch is to be managed via its VTY lines, it needs a default gateway.
- Use the ip default-gateway command to configure the default gateway for a switch.
6.5 Chapter Summary
Summary
- Explain how network layer protocols and services support communications across data networks.
- Explain how routers enable end-to-end connectivity in a small to medium-sized business network.
- Explain how devices route traffic in a small to medium-sized business network.
- Configure a router with basic configurations.
Section 6.1 New Terms and Commands
- encapsulation
- routing
- de-encapsulation
- data
- packet
- frame
- Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4)
- Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6)
- Network Layer PDU = IP Packet
- Transport Layer PDu
- Segment Header
- IP Header
- Auxiliary port (AUX)
- connectionless
- best effort delivery
- media independent
- Connectionless
- unreliable
- maximum transmission unit (MTU)
- Version
- Differentiated Services (DS)
- Time-to-Live (TTL)
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- data payload
- Identification, Flags, Fragment Offset fields
- keyword
- Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Traffic Class
- Flow Label
- Payload Length
- Next Header
- Hop Limit
- local host
- remote host
- default gateway
Section 6.2 New Terms and Commands
- netstat –r
- route print
- interface list
- IPv4 Route Table
- IPv6 Route Table
- directly-connected routes
- remote routes
- default route
- show ip route
- route source
- destination network
- outgoing interface
- administrative distance
- metric
- next-hop
- route timestamp
- branch routers
- WAN routers
- service provider routers
Section 6.3 New Terms and Commands
- Power-on-self-test POST
- RAM
- ROM
- NVRAM
- Flash
- Synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM)
- WIC
- high-speed WIC (HWIC)
- ROMMON
- Advanced Integration Module (AIM)
- Enhanced high-speed WAN interface card (eHWIC)
- Serial module
- Ethernet interfaces
- Auxiliary (AUX) RJ-45 port
- In-band router interfaces
- Console
- Out-of-band
- Secure Shell (SSH)
- Telnet
- startup-config
- running-config
- bootstrap program
- Trivial File Transport Protocol (TFTP)
- setup mode
- show version
Section 6.4 New Terms and Commands
- interface type-and-number
- ip address ipv4-address subnet-mask
- description description-text
- no shutdown
- show ip interface brief
- ping ip address
- show ip route
- show interfaces
- show ip interface brief
- ip default-gateway ip-address
