- Which command can you enter to verify that a BGP connection to a remote device is established?
- A. show ip bgp summary*
- B. show ip community-list
- C. show ip bgp paths
- D. show ip route
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThis command can be used to verify if a BGP connection to a BGP neighbor is good or not. Let’s see an example: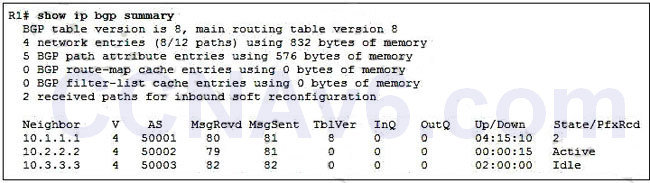
Please pay attention to the “State/PfxRcd” column of the output. It indicates the number of prefixes that have been received from a neighbor. If this value is a number (including “0”, which means BGP neighbor does not advertise any route) then the BGP neighbor relationship is good. If this value is a word (including “Idle”, “Connect”, “Active”, “OpenSent”, “OpenConfirm”) then the BGP neighbor relationship is not good.
In the outputs above we see the BGP neighbor relationship between R1 & 10.1.1.1 is good with 2 Prefix Received (PfxRcd) while the BGP neighbor relationships between R1 & 10.2.2.2; R1 & 10.3.3.3 are not good (they are in “Active” and “Idle” state).
- Which two components are used to identify a neighbor in a BGP configuration? (Choose two)
- A. autonomous system number*
- B. version number
- C. router ID
- D. subnet mask
- E. IP address*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThis is an example of how to configure BGP neighbor between two routers (suppose all interfaces are configured correctly)
R1(config)#router bgp 1 R1(config-router)#neighbor 11.0.0.2 remote-as 2
R2(config)#router bgp 2 R2(config-router)#neighbor 11.0.0.1 remote-as 1
So as you see, we need the neighbor’s IP address and neighbor’s AS number for the BGP neighbor relationship.
-
interface fa0/0 ip address 172.16.1.33 255.255.255.224 router bgp XXX neighbor 10.1.5.2 remote as 65001
You need to advertise the network of int fa0/0. Which of the following would you type in the “network” command?
- A. 172.16.1.32 mask 255.255.255.224*
- B. 172.16.1.32 255.255.255.224
- C. 172.16.1.32 mask 0.0.0.31
- D. 172.16.1.33 mask 255.255.255.224
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceFirst please notice that unlike other routing protocols like OSPF or EIGRP, we have to use subnet mask, not wildcard mask, to advertise the routes in the “network” command -> C is not correct.Secondly, with BGP, you must advertise the correct network and subnet mask in the “network” command ( in this case network 172.16.1.32/27). BGP is very strict in the routing advertisements. In other words, BGP only advertises the network which exists exactly in the routing table (in this case network x.x.x.32/27 exists in the routing table as the Fa0/0 interface). If you put the command “network x.x.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0” or “network x.0.0.0 mask 255.0.0.0” or “network x.x.x.33 mask 255.255.255.255” then BGP will not advertise anything.
Therefore the full command in this question is “network 172.16.1.32 mask 255.255.255.224”.
For more information about BGP configuration, please read our Basic BGP Configuration tutorial.
- Which two statements about eBGP neighbor relationships are true? (Choose two)
- A. The two devices must reside in different autonomous systems*
- B. Neighbors must be specifically declared in the configuration of each device*
- C. They can be created dynamically after the network statement is con-figured.
- D. The two devices must reside in the same autonomous system
- E. The two devices must have matching timer settings
- What does it take for BGP to establish connection? (Choose two)
- A. Enable CDP
- B. AS number on local router*
- C. AS number on remote router*
- D. IGP
- E. EGP
CCNA 200-125 Exam: BGP Questions With Answers
Subscribe
0 Comments
