- Which step in the router boot process searches for an IOS image to load into the router?
- A. bootstrap*
- B. POST
- C. mini-IOS
- D. ROMMON mode
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe following details the router boot process:1. The router is powered on.
2. The router first runs Power-On Self Test (POST)
3. The bootstrap checks the Configuration Register value to specify where to load the IOS. By default (the default value of Configuration Register is 2102, in hexadecimal), the router first looks for “boot system” commands in startup-config file. If it finds these commands, it will run boot system commands in order they appear in startup-config to locate the IOS. If not, the IOS image is loaded from Flash . If the IOS is not found in Flash, the bootstrap can try to load the IOS from TFTP server or from ROM (mini-IOS).
4. After the IOS is found, it is loaded into RAM.
5. The IOS attempts to load the configuration file (startup-config) from NVRAM to RAM. If the startup-config is not found in NVRAM, the IOS attempts to load a configuration file from TFTP. If no TFTP server responds, the router enters Setup Mode (Initial Configuration Mode).
For more information about booting process please read our Cisco Router Boot Sequence tutorial.
- If a router has four interfaces and each interface is connected to four switches, how many broadcast domains are present on the router?
- A. 1
- B. 2
- C. 4 *
- D. 8
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceRemember that only route interface can separate broadcast domain (while switch interface separate collision domain) so the broadcast domains are equal to the number of router interfaces, which is four in this case. - What is the purpose of the POST operation on a router?
- A. determine whether additional hardware has been added*
- B. locate an IOS image for booting
- C. enable a TFTP server
- D. set the configuration register
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceIn short, when powered on the router needs to do:1. Run POST to check hardware
2. Search for a valid IOS (the Operating System of the router)
3. Search for a configuration file (all the configurations applied to this router) - Which command can you execute to set the user inactivity timer to 10 seconds?
- A. SW1(config-line)#exec-timeout 0 10*
- B. SW1(config-line)#exec-timeout 10
- C. SW1(config-line)#absolute-timeout 0 10
- D. SW1(config-line)#absolute-timeout 10
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe “exec-timeout” command is used to configure the inactive session timeout on the console port or the virtual terminal. The syntax of this command is:exec-timeout minutes [seconds]
Therefore we need to use the “exec-timeout 0 10” command to set the user inactivity timer to 10 seconds.
- After you configure the Loopback0 interface, which command can you enter to verify the status of the interface and determine whether fast switching is enabled?
- A. Router#show ip interface loopback 0*
- B. Router#show run
- C. Router#show interface loopback 0
- D. Router#show ip interface brief
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceAn example of the output of the “show ip interface loopback 0” is shown below.
- A Cisco router is booting and has just completed the POST process. It is now ready to find and load an IOS image. What function does the router perform next?
- A. It checks the configuration register*
- B. It attempts to boot from a TFTP server
- C. It loads the first image file in flash memory
- D. It inspects the configuration file in NVRAM for boot instructions
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceWhen you turn the router on, it runs through the following boot process.The Power-On Self Test (POST) checks the router’s hardware. When the POST completes successfully, the System OK LED indicator comes on.
The router checks the configuration register to identify where to load the IOS image from. A setting of 0×2102 means that the router will use information in the startup-config file to locate the IOS image. If the startup-config file is missing or does not specify a location, it will check the following locations for the IOS image:1. Flash (the default location)
2. TFTP server
3. ROM (used if no other source is found)The router loads the configuration file into RAM (which configures the router). The router can load a configuration file from:
+ NVRAM (startup-configuration file)
+ TFTP server
If a configuration file is not found, the router starts in setup mode. - Which command is used to show the interface status of a router?
- A. show interface status
- B. show ip interface brief*
- C. show ip route
- D. show interface
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe “show ip interface brief” command can be used to view a summary of the router interfaces. This command displays the IP address, interface status, and additional information. An example of the “show ip interface brief” command is shown below. We can see the interface status of E0/0 is “up/up”.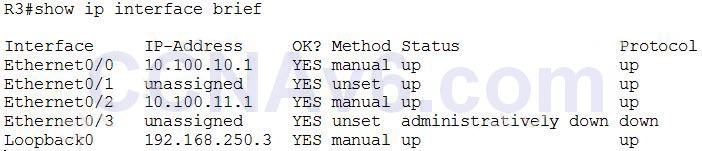
- Which of the following privilege level is the most secured?
- A. Level 0
- B. Level 1
- C. Level 15*
- D. Level 16
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceBy default, the Cisco IOS CLI has two privilege levels enabled, level 1 and level 15.+ User EXEC mode (privilege level 1): provides the lowest EXEC mode user privileges and allows only user-level commands available at the Router> prompt.
+ Privileged EXEC mode (privilege level 15): includes all enable-level commands at the Router# prompt. Level 15 users can execute all commands and this is the most secured and powerful privilege level.However, there are actually 16 privilege levels available on the CLI, from 0 to 15 and you can assign users to any of those levels. Zero-level access allows only five commands -logout, enable, disable, help, and exit. User level (level 1) provides very limited read-only access to the router, and privileged level (level 15) provides complete control over the router.
- What to do when the router password was forgotten?
- A. use default password cisco to reset
- B. access router physically
- C. use ssl/vpn
- D. Type confreg 0x2142 at the rommon 1*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceTo reset the password we can type “confreg 0x2142” under rommon mode to set the configuration register to 2142 in hexadecimal (the prefix 0x means hexadecimal (base 16)). With this setting when that router reboots, it bypasses the startup-config. - How do you configure a hostname?
- A. Router(config)#hostname R1*
- B. Router#hostname R1
- C. Router(config)#host name R1
- D. Router>hostname R1
- Which two Cisco IOS commands, used in troubleshooting, can enable debug output to a remote location? (Choose two)
- A. no logging console
- B. logging host ip-address*
- C. terminal monitor*
- D. show logging | redirect flashioutput.txt
- E. snmp-server enable traps syslog
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe “no logging console” turns off logging to the console connection (it is turned on by default) and it is often used if the console received large amount of logging output. But this command is not recommended in normal configuration -> A is not correct.The command “logging host ip-address” instructs the device to send syslog messages to an external syslog server -> B is correct.
The “show logging | redirect flashioutput.txt” command will put the text file in the router flash memory because we did not specify a remote location (like tftp) -> D is not correct.
The command “snmp-server enable traps syslog” instructs the device to send syslog messages to your network management server as SNMP traps instead of syslog packets. This command itself does not enable debug output to a remote location -> E is not correct.
By default, Cisco IOS does not send log messages to a terminal session over IP, that is, telnet or SSH connections don’t get log messages. But notice that console connections on a serial cable do have logging enabled by default. The command “terminal monitor” helps logging messages appear on the your terminal. First we don’t think this is a correct answer but after reading the question again, we believe it is a suitable one as a Telnet/SSH session may be considered a “remote location” -> C is correct.
- Which statement about recovering a password on a Cisco router is true?
- A. The default reset password is cisco
- B. It requires a secure SSL/VPN connection
- C. A factory reset is required if you forget the password
- D. It requires physical access to the router*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceOther choices are surely incorrect so only “physical access” answer is the correct one. In order to recover a password on a Cisco router, the first thing you have to do is either switch off or shut down the router. For more information about this process, please read http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/routers/2800-series-integrated-services-routers/112033-c2900-password-recovery-00.html - Refer to the exhibit. Why is flash memory erased prior to upgrading the IOS image from the TFTP server?
Router# copy tftp flash Address or name of remote host []? 192.168.2.167 Source filename []? c1600-k8sy-mz.123-16a.bin Destination filename [c1600-k8sy-mz.123-16a.bin]? Accessing tftp://192.168.2.167/ c1600-k8sy-mz.l23-16a.bin… Erasing flash before copying? [confirm] Erasing the flash filesystem will remove all files! continue? [confirm] Erasing device Eeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee Eeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeeee …erased Erase of flash: complete Loading c1600-k8sy-mz.l23-16a.bin from 192.168.2.167 (via Ethernet0): !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! [OK – 6888962/13777920 bytes] verifying checksum… OK (0x7BF3) 6888962 bytes copied in 209.920 secs (32961 bytes/sec) Router#
- A. The router cannot verify that the Cisco IOS image currently in flash is valid
- B. Flash memory on Cisco routers can contain only a single IOS image.
- C. Erasing current flash content is requested during the copy dialog.*
- D. In order for the router to use the new image as the default, it must be the only IOS image in flash.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceDuring the copy process, the router asked “Erasing flash before copying? [confirm]” and the administrator confirmed (by pressing Enter) so the flash was deleted.Note: In this case, the flash has enough space to copy a new IOS without deleting the current one. The current IOS is deleted just because the administrator wants to do so. If the flash does not have enough space you will see an error message like this:
%Error copying tftp://192.168.2.167/ c1600-k8sy-mz.l23-16a.bin (Not enough space on device) - In which CLI configuration mode can you configure the hostname of a device?
- A. line mode
- B. interface mode
- C. global mode*
- D. router mode
- Which three commands can you use to set a router boot image? (Choose three)
- A. Router(config)# boot system flash c4500-p-mz.121-20.bin*
- B. Router(config)# boot system tftp c7300-js-mz.122-33.SB8a.bin*
- C. Router(config)#boot system rom c7301-advipservicesk9-mz.124-24.T4.bin*
- D. Router> boot flash:c180x-adventerprisek9-mz-124-6T.bin
- E. Router(config)#boot flash:c180x-adventerprisek9-mz-124-6T.bin
- F. Router(config)#boot bootldr bootflash:c4500-jk9s-mz.122-23f.bin
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe correct syntax of the “boot” command is “boot system” path. In which the popular for path can be:
+ flash
+ rom
+ tftp
+ ftp
+ IP address (IP address of the server containing the system image file)Therefore answers A, B, C are correct.
- Which configuration register value can you set on a Cisco device so that it ignores the NVRAM when it boots?
- A. 0x2124
- B. 0x2120
- C. 0x2142*
- D. 0x2102
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceTo reset the password we can type “confreg 0x2142” under rommon mode to set the configuration register to 2142 in hexadecimal (the prefix 0x means hexadecimal (base 16)). With this setting when that router reboots, it bypasses the startup-config.
CCNA 200-125 Exam: Router Questions With Answers
Subscribe
0 Comments
