- What routing protocol use first-hand information from peers?
- A. link state*
- B. distance-vector
- C. path-vector
- D. other
- Which prefix does OSPFv3 use when multiple IPv6 address are configured on a single interface?
- A. all prefix on the interface*
- B. the prefix that the administrator configure for OSPFv3 use
- C. the lowest prefix on the interface
- D. the highest prefix on the interface
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceIn IPv6, you can configure many address prefixes on an interface. In OSPFv3, all address prefixes on an interface are included by default. You cannot select some address prefixes to be imported into OSPFv3; either all address prefixes on an interface are imported, or no address prefixes on an interface are imported. - After you apply the given configuration to R1, you notice that it failed to enable OSPF. Which action can you take to correct the problem?
R1 ipv6 cef interface FastEthernet0/0 no ip address ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::1/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.1
- A. Configure a loopback interface on R1
- B. Enable IPv6 unicast routing on R1*
- C. Configure an IPv4 address on interface Fa0/0
- D. Configure an autonomous system number on OSPF
- Refer to the exhibit. If R1 receives a packet destined to 172.16.1.1, to which IP address does it send the packet?
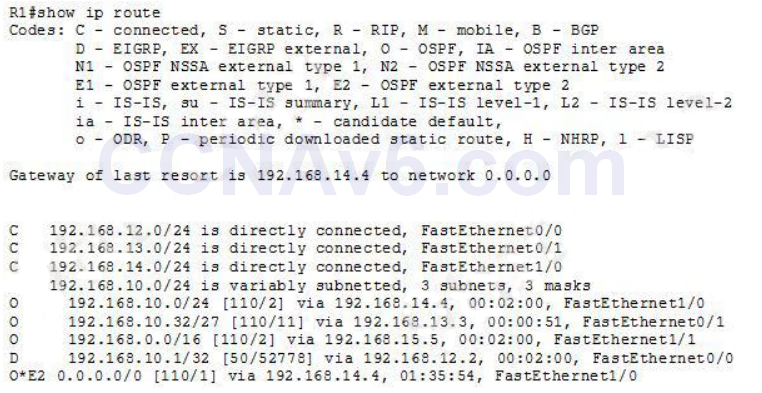
- A. 192.168.14.4*
- B. 192.168.12.2
- C. 192.168.13.3
- D. 192.168.15.5
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceBecause the destination of 172.16.1.1 is not present in the routing table so this router would use the default route (O*E2) to forward this packet. Usually the O*E2 is the result of the “default-information originate” command on the upstream router. - If two OSPF neighbors have formed complete adjacency and are exchanging link -state advertisements, which state have they reached?
- A. Exstart
- B. 2-Way
- C. FULL*
- D. Exchange
- Which two steps must you perform on each device that is configured for IPv4 routing before you implement OSPFv3? (Choose two)
- A. Configure an autonomous system number
- B. Configure a loopback interface
- C. Configure a router ID
- D. Enable IPv6 on an interface*
- E. Enable IPv6 unicast routing*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceBefore you enable OSPF for IPv6 on an interface, you must perform the following:+ Complete the OSPF network strategy and planning for your IPv6 network. For example, you must decide whether multiple areas are required.
+ Enable IPv6 unicast routing.
+ Enable IPv6 on the interface.Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/ip-version-6-ipv6/112100-ospfv3-config-guide.html
Note: If we have already had an active interface, we don’t need to configure the router ID for OSPFv3 anymore because the device will automatically choose that IPv4 address for its router ID).
- Which command must you enter to enable OSPFv2 in an IPv4 network?
- A. ip ospf hello-interval seconds
- B. router ospfv2 process-id
- C. router ospf value
- D. router ospf process-id*
- Why do large OSPF networks use a hierarchical design? (Choose three)
- A. to confine network instability to single areas of the network*
- B. to reduce the complexity of router configuration
- C. to speed up convergence*
- D. to lower costs by replacing routers with distribution layer switches
- E. to decrease latency by increasing bandwidth
- F. to reduce routing overhead*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceHierarchical design of OSPF (basically means that you can separate the larger internetwork into smaller internetworks called areas) helps us create a network with all features listed above (decrease routing overhead, speed up convergence, confine network instability to single areas of the network). - Refer to the exhibit.
R1
ipv6 unicast-routing interface FastEthernet0/0 no ip address ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:12::1/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 0 ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.1
R2
ipv6 unicast-routing interface FastEthernet0/0 no ip address ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:12::2/64 ipv6 ospf 1 area 1 ipv6 router ospf 1 router-id 172.16.2.2
After you apply the give configurations to R1 and R2 you notice that OSPFv3 fails to start. Which reason for the problem is most likely true?
- A. The area numbers on R1 and R2 are mismatched*
- B. The IPv6 network addresses on R1 and R2 are mismatched
- C. The autonomous system numbers on R1 and R2 are mismatched
- D. The router ids on R1 and R2 are mismatched
- When running OSPF, what would cause router A not to form an adjacency with router B?
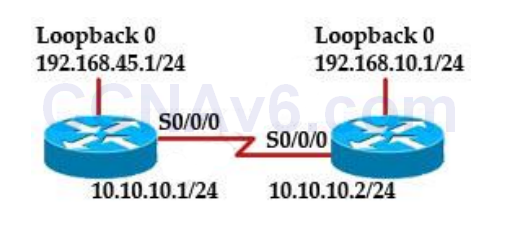
- A. The loopback addresses are on different subnets.
- B. The values of the dead timers on the routers are different.*
- C. Route summarization is enabled on both routers.
- D. The process identifier on router A is different than the process identifier on router
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceTo form an adjacency (become neighbor), router A & B must have the same Hello interval, Dead interval and AREA number.
CCNA 200-125 Exam: OSPF Questions 2 With Answers
Subscribe
0 Comments
