- Which value is indicated by the next hop in a routing table?
- A. preference of the route source
- B. IP address of the remote router for forwarding the packets*
- C. how the route was learned
- D. exit interface IP address for forwarding the packets
- Which component of the routing table ranks routing protocols according to their preferences?
- A. administrative distance*
- B. next hop
- C. metric
- D. routing protocol code
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe administrative distance of each protocol is compared to see if that route is better or not. - Which route source code represents the routing protocol with a default administrative distance of 90 in the routing table?
- A. S
- B. E
- C. D *
- D. R
- E. O
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceLetter “D” is used to symbolize for EIGRP (with a default AD of 90). Letter “E” is not used for EIGRP because it has been used for Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP). It is a obsolete routing protocol now. - When enabled, which feature prevents routing protocols from sending hello messages on an interface?
- A. virtual links
- B. passive-interface*
- C. directed neighbors
- D. OSPF areas
- How does a router handle an incoming packet whose destination network is missing from the routing table?
- A. It broadcast the packet to each interface on the router
- B. It discards the packet*
- C. It broadcasts the packet to each network on the router
- D. It routes the packet to the default route
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceIf there is a default route then surely the router will forward all unknown traffic to there. But if there is no default route in the routing table then the router will discard the packet. In this question we suppose there is no default route in the routing table. Otherwise the question should state it (this question is unclear). - Which path does a router choose when it receives a packet with multiple possible paths to the destination over different routing protocols?
- A. the path with both the lowest administrative distance and the highest metric
- B. the path with the lowest administrative distance*
- C. the path with the lowest metric
- D. the path with both the lowest administrative distance and lowest metric
- If a route is not present in the routing table for a particular destination, what would the router do?
- A. Default route
- B. Flood
- C. Drop*
- When a device learns multiple routes to a specific network, it installs the route with?
- A. longest bit match (highest subnet mask)
- B. lowest AD*
- C. lowest metric
- D. equal load balancing
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceMaking a forwarding decision actually consists of three sets of processes: the routing protocols, the routing table, and the actual process which makes a forwarding decision and switches packets. The longest prefix match always wins among the routes actually installed in the routing table, while the routing protocol with the lowest administrative distance always wins when installing routes into the routing table.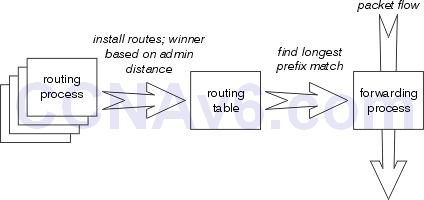
- When a router is unable to find a known route in the routing table, how does it handle the packet?
- A. It discards the packet*
- B. It sends the packet over the route with the best metric
- C. It sends the packet to the next hop address
- D. It sends the packet to the gateway of last resort
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceIn fact this question is not clear. If we understand that “router is unable to find a known route in the routing table” and there is no default route in the routing table then the router will surely discard the packet -> A is correct. But we are not sure if there is a default route or not so let learn more about gateway of last resort.A Gateway of Last Resort is a route used by the router when no other known route exists to send the IP packet. For CCNA level, when ip routing feature is enabled, a gateway of last resort is usually created by:
+ The “ip default-network” command (but dynamic routing protocols have different behaviors). But in general, the “ip default-network” cannot set the gateway of last resort without a known route in the routing table.
+ Creating a static route to network 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 is another way to set the gateway of last resort on a router. This is the reason why this question is not clear as it does not tell us if a default route exists or not.Maybe in this question a default route does not exist. Otherwise the author would notice and indicate it in the question.
For more information about Gateway of Last Resort, please read: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/routing-information-protocol-rip/16448-default.html
- If router R1 knows a static route to a destination network and then learns about the same destination network through a dynamic routing protocol, how does R1 respond?
- A. It refuses to advertise the dynamic route to other neighbors
- B. It sends a withdrawal signal to the neighboring router
- C. It disables the routing protocol
- D. It prefers the static route*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe default administrative distance value of static route is 1 which is always smaller than any dynamic routing protocol so it is always preferred to dynamic routing protocols.
CCNA 200-125 Exam: IP Routing 2 With Answers
Subscribe
0 Comments
