- Which technology allows a large number of private IP addresses to be represented by a smaller number of public IP addresses?
- A. NAT*
- B. NTP
- C. RFC 1631
- D. RFC 1918
- What is the effect of the overload keyword in a static NAT translation configuration?
- A. It enables port address translation.*
- B. It enables the use of a secondary pool of IP addresses when the first pool is depleted.
- C. It enables the inside interface to receive traffic.
- D. It enables the outside interface to forward traffic.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceBy adding the keyword “overload” at the end of a NAT statement, NAT becomes PAT (Port Address Translation). This is also a kind of dynamic NAT that maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address (many-to-one) by using different ports. Static NAT and Dynamic NAT both require a one-to-one mapping from the inside local to the inside global address. By using PAT, you can have thousands of users connect to the Internet using only one real global IP address. PAT is the technology that helps us not run out of public IP address on the Internet. This is the most popular type of NAT. - Which two types of NAT addresses are used in a Cisco NAT device? (Choose two)
- A. inside local*
- B. inside global*
- C. inside private
- D. outside private
- E. external global
- F. external local
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceNAT use four types of addresses:* Inside local address – The IP address assigned to a host on the inside network. The address is usually not an IP address assigned by the Internet Network Information Center (InterNIC) or service provider. This address is likely to be an RFC 1918 private address.
* Inside global address – A legitimate IP address assigned by the InterNIC or service provider that represents one or more inside local IP addresses to the outside world.
* Outside local address – The IP address of an outside host as it is known to the hosts on the inside network.
* Outside global address – The IP address assigned to a host on the outside network. The owner of the host assigns this address.

- What is the danger of the “permit any” entry in a NAT access list?
- A. It can lead to overloaded resources on the router.*
- B. It can cause too many addresses to be assigned to the same interface.
- C. It can disable the overload command.
- D. It prevents the correct translation of IP addresses on the inside network.
- Which type of address is the public IP address of a NAT device?
- A. outside global
- B. outside local
- C. inside global*
- D. inside local
- E. outside public
- F. inside public
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceNAT use four types of addresses:* Inside local address – The IP address assigned to a host on the inside network. The address is usually not an IP address assigned by the Internet Network Information Center (InterNIC) or service provider. This address is likely to be an RFC 1918 private address.
* Inside global address – A legitimate IP address assigned by the InterNIC or service provider that represents one or more inside local IP addresses to the outside world.
* Outside local address – The IP address of an outside host as it is known to the hosts on the inside network.
* Outside global address – The IP address assigned to a host on the outside network. The owner of the host assigns this address.

- Which command can you enter to display the hits counter for NAT traffic?
- A. show ip nat statistics*
- B. debug ip nat
- C. show ip debug nat
- D. clear ip nat statistics
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceAn example of the output of the “show ip nat statistics” is shown below. As we can see, the “Hits” counter is displayed.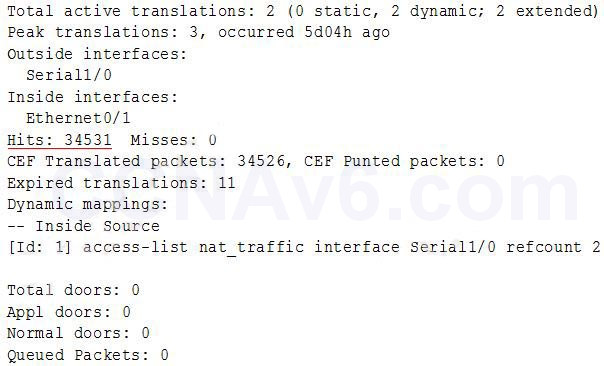
- Which NAT function can map multiple inside addresses to a single outside address?
- A. PAT*
- B. SFTP
- C. RARP
- D. ARP
- E. TFTP
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceBy adding the keyword “overload” at the end of a NAT statement, NAT becomes PAT (Port Address Translation). This is also a kind of dynamic NAT that maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address (many-to-one) by using different ports. - What is the first step in the NAT configuration process?
- A. Define inside and outside interfaces.*
- B. Define public and private IP addresses.
- C. Define IP address pools.
- D. Define global and local interfaces.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceIn NAT configuration we should specify the inside and outside interfaces first with the command “ip nat inside” and “ip nat outside” under interface mode. - Under which circumstance should a network administrator implement one-way NAT?
- A. when the network must route UDP traffic
- B. when traffic that originates outside the network must be routed to internal hosts *
- C. when traffic that originates inside the network must be routed to internal hosts
- D. when the network has few public IP addresses and many private IP addresses require outside access
- Which statement about the inside interface configuration in a NAT deployment is true?
- A. It is defined globally
- B. It identifies the location of source addresses for outgoing packets to be translated using access or route maps.*
- C. It must be configured if static NAT is used
- D. It identifies the public IP address that traffic will use to reach the internet.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceWhen we specify a NAT “inside” interface (via the “ip nat inside” command under interface mode), we are specifying the source IP addresses. Later in the “ip nat” command under global configuration mode, we will specify the access or route map for these source addresses.For example the command:
Router(config)# ip nat inside source list 1 pool PoolforNAT
after the keyword “source” we need to specify one of the three keywords:
+ list: specify access list describing local addresses (but this command does not require an “inside” interface to be configured)
+ route-map: specify route-map
+ static: specify static local -> global mapping - Which NAT type is used to translate a single inside address to a single outside address?
- A. dynamic NAT
- B. NAT overload
- C. PAT
- D. static NAT*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThere are two types of NAT translation: dynamic and static.Static NAT: Designed to allow one-to-one mapping between local and global addresses. This flavor requires you to have one real Internet IP address for every host on your network
Dynamic NAT: Designed to map an unregistered IP address to a registered IP address from a pool of registered IP addresses. You don’t have to statically configure your router to map an inside to an outside address as in static NAT, but you do have to have enough real IP addresses for everyone who wants to send packets through the Internet. With dynamic NAT, you can configure the NAT router with more IP addresses in the inside local address list than in the inside global address pool. When being defined in the inside global address pool, the router allocates registered public IP addresses from the pool until all are allocated. If all the public IP addresses are already allocated, the router discards the packet that requires a public IP address.
In this question we only want to translate a single inside address to a single outside address so static NAT should be used.
- What are two benefits of using NAT? (choose two)
- A. NAT protects network security because private networks are not advertised.*
- B. NAT accelerates the routing process because no modifications are made on the packets.
- C. Dynamic NAT facilitates connections from the outside of the network.
- D. NAT facilitates end-to-end communication when IPsec is enable.
- E. NAT eliminates the need to re-address all host that require external access.*
- F. NAT conserves addresses through host MAC-level multiplexing.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceBy not reveal the internal IP addresses, NAT adds some security to the inside network -> A is correct.NAT has to modify the source IP addresses in the packets -> B is not correct.
Connection from the outside to a network through “NAT” is more difficult than a normal network because IP addresses of inside hosts are hidden -> C is not correct.
In order for IPsec to work with NAT we need to allow additional protocols, including Internet Key Exchange (IKE), Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Authentication Header (AH) -> more complex -> D is not correct.
By allocating specific public IP addresses to inside hosts, NAT eliminates the need to re-address the inside hosts -> E is correct.
NAT does conserve addresses but not through host MAC-level multiplexing. It conserves addresses by allowing many private IP addresses to use the same public IP address to go to the Internet -> F is not correct.
- Which command can you enter to create a NAT pool of 6 addresses?
- A. Router(config)#ip nat pool test 175.17.12.69 175.17.12.74 prefix-length 24*
- B. Router(config)#ip nat pool test 175.17.12.69 175.17.13.74 prefix-length 16
- C. Router(config)#ip nat pool test 175.17.12.66 175.17.12.72 prefix-length 8
- D. Router(config)#ip nat pool test 175.17.12.69 175.17.12.76 prefix-length 8
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe syntax to create a NAT pool is:Router(config)#ip nat pool pool_name start_ip end_ip { netmask netmask | prefix-length prefix-length }
Therefore answer A is surely correct. Answer B is not correct as it creates many addresses (from 12.69 to 12.255 then to 13.74).
Answer C and D are not correct as we cannot use prefix-length of 8 (/8) for a class B subnet.
- How does NAT overloading provide one-to-many address translation?
- A. It uses a pool of addresses
- B. It converts IPV4 addresses to unused IPv6 Addresses
- C. It assigns a unique TCP/UDP port to each session*
- D. It uses virtual MAC Address and Virtual IP Addresses
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceBy adding the keyword “overload” at the end of a NAT statement, NAT becomes PAT (Port Address Translation). This is also a kind of dynamic NAT that maps multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address (many-to-one) by using different ports. - What is the danger of the permit any entry in a NAT access list?
- A. It can lead to overloaded resources on the router.*
- B. It can cause too many addresses to be assigned to the same interface.
- C. It can disable the overload command.
- D. It prevents the correct translation of IP addresses on the inside network.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceUsing permit any can result in NAT consuming too many router resources, which can cause network problems. You should only limit the NAT access list to a specific range of IP addresses. - Which configuration can be used with PAT to allow multiple inside address to be translated to a single outside address?
- A. Dynamic Routing
- B. DNS
- C. Preempt
- D. Overload*
