- Which command can you enter to display duplicate IP addresses that the DHCP server assigns?
- A. show ip dhcp conflict 10.0.2.12*
- B. show ip dhcp database 10.0.2.12
- C. show ip dhcp server statistics
- D. show ip dhcp binding 10.0.2.12
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe command “show ip dhcp conflict” is used to display address conflicts found by a Cisco IOS DHCP Server when addresses are offered to the client. An example of the output of this command is shown below:
- What is the default lease time for a DHCP binding?
- A. 24 hours*
- B. 12 hours
- C. 48 hours
- D. 36 hours
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceWe can use the “lease” command to specify the duration of the lease: lease {days [hours][minutes] | infinite}The default is a one-day lease.
- Which statement is correct regarding the operation of DHCP?
- A. A DHCP client uses a ping to detect address conflicts.
- B. A DHCP server uses a gratuitous ARP to detect DHCP clients.
- C. A DHCP client uses a gratuitous ARP to detect a DHCP server.
- D. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool and an administrator must resolve the conflict.*
- E. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool for an amount of time configurable by the administrator.
- F. If an address conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool and will not be reused until the server is rebooted.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceAn address conflict occurs when two hosts use the same IP address. During address assignment, DHCP checks for conflicts using ping and gratuitous ARP. If a conflict is detected, the address is removed from the pool. The address will not be assigned until the administrator resolves the conflict.(Reference: http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/12_1/iproute/configuration/guide/1cddhcp.html)
- Which command is used to build DHCP pool?
- A. ip dhcp pool DHCP*
- B. ip dhcp conflict
- C. ip dhcp-server pool DHCP
- D. ip dhcp-client pool DHCP
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe following example shows how to configure a DHCP Server on a Cisco router:Configuration Description Router(config)#ip dhcp pool CLIENTS Create a DHCP Pool named CLIENTS Router(dhcp-config)#network 10.1.1.0 /24 Specifies the subnet and mask of the DHCP address pool Router(dhcp-config)#default-router 10.1.1.1 Set the default gateway of the DHCP Clients Router(dhcp-config)#dns-server 10.1.1.1 Configure a Domain Name Server (DNS) Router(dhcp-config)#domain-name 9tut.com Configure a domain-name Router(dhcp-config)#lease 0 12 Duration of the lease (the time during which a client computer can use an assigned IP address). The syntax is “lease{days[hours] [minutes] | infinite}”. In this case the lease is 12 hours. The default is a one-day lease.
Before the lease expires, the client typically needs to renew its address lease assignment with the serverRouter(dhcp-config)#exit Router(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.1.1.1 10.1.1.10 The IP range that a DHCP Server should not assign to DHCP Clients. Notice this command is configured under global configuration mode Note: We checked with both Cisco IOS v12.4 and v15.4 but found no “ip dhcp-server pool” command:
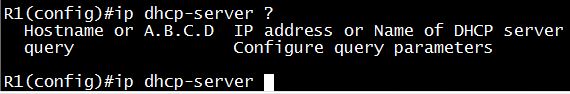
Therefore the answer “ip dhcp-server pool …” is not correct.
- What is the two benefits of DHCP snooping? (Choose two)
- A. static reservation
- B. DHCP reservation
- C. prevent DHCP rouge server*
- D. prevent untrusted host and servers to connect*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceQuick review of DHCP Spoofing and DHCP snooping:
DHCP spoofing is a type of attack in that the attacker listens for DHCP Requests from clients and answers them with fake DHCP Response before the authorized DHCP Response comes to the clients. The fake DHCP Response often gives its IP address as the client default gateway -> all the traffic sent from the client will go through the attacker computer, the attacker becomes a “man-in-the-middle”.
The attacker can have some ways to make sure its fake DHCP Response arrives first. In fact, if the attacker is “closer” than the DHCP Server then he doesn’t need to do anything. Or he can DoS the DHCP Server so that it can’t send the DHCP Response.
DHCP snooping can prevent DHCP spoofing attacks. DHCP snooping is a Cisco Catalyst feature that determines which switch ports can respond to DHCP requests. Ports are identified as trusted and untrusted.

Only ports that connect to an authorized DHCP server are trusted, and allowed to send all types of DHCP messages. All other ports on the switch are untrusted and can send only DHCP requests. If a DHCP response is seen on an untrusted port, the port is shut down -> Answer D is correct.
The fundamental use case for DHCP snooping is to prevent unauthorized (rogue) DHCP servers offering IP addresses to DHCP clients. Rogue DHCP servers are often used in man in the middle or denial of service attacks for malicious purposes -> C is correct.
- What command can you enter in config mode to create DHCP pool?
- A. ip dhcp pool DHCP_pool*
- B. ip dhcp exclude -add
- C. ip dhcp conflict logging
- D. service dhcp
- Where information about untrusted hosts are stored?
- A. CAM table
- B. Trunk table
- C. MAC table
- D. binding database*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe DHCP snooping binding database is also referred to as the DHCP snooping binding table. The DHCP snooping feature dynamically builds and maintains the database using information extracted from intercepted DHCP messages. The database contains an entry for each untrusted host with a leased IP address if the host is associated with a VLAN that has DHCP snooping enabled. The database does not contain entries for hosts connected through trusted interfaces. - Which command can you enter to determine the addresses that have been assigned on a DHCP Server?
- A. show ip dhcp database
- B. show ip dhcp pool
- C. show ip dhcp binding*
- D. show ip dhcp server statistic
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe “show ip dhcp binding” command displays the IP address bindings and their associated leases. Below is an example of the output of this command.R1#show ip dhcp binding IP address Hardware address Lease expiration Type 172.15.1.5 0100.0103.85e9.87 Apr 03 2017 08:55 PM Automatic 172.15.1.6 0100.50da.2a5e.a2 Apr 03 2017 09:00 PM Automatic 172.15.1.7 0100.0103.ea1b.ed Apr 03 2017 08:58 PM Automatic
- Which command can you enter to troubleshoot the failure of address assignment?
- A. show ip dhcp database
- B. show ip dhcp pool*
- C. show ip dhcp import
- D. show ip dhcp server statistics
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe command “show ip dhcp pool” is used to display information about the DHCP address pools. There are some information we can use to check the failure of address assignment. For example we can see how many IP addresses have been leased for a specific pool. If some IP addresses have been assigned from a pool but a client of that pool has not received the assignment then maybe the issue belongs to the client itself.R1#show ip dhcp pool Pool SERVER : Utilization mark (high/low) : 100 / 0 Subnet size (first/next) : 0 / 0 Total addresses : 1 Leased addresses : 1 Pending event : none 0 subnet is currently in the pool : Current index IP address range Leased addresses 172.16.200.100 172.16.200.100 - 172.16.200.100 1
- Requirement to configure DHCP binding (Choose two)
- A. DHCP pool
- B. IP address*
- C. Hardware address*
- D. other option
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceAn address binding is a mapping between the IP address and MAC address of a client. The IP address of a client can be assigned manually by an administrator or assigned automatically from a pool by a DHCP server. Manual bindings are IP addresses that have been manually mapped to the MAC addresses of hoststhat are found in the DHCP database.All DHCP clients send a client identifier (DHCP option 61) in the DHCP packet. To configure manual bindings, you must enter the client-identifier DHCP pool configuration command with the appropriate hexadecimal values identifying the DHCP client. For example:
ip dhcp pool SERVER host 172.16.200.100 255.255.255.0 client-identifier 01aa.bbcc.0003.00 default-router 172.16.200.1 !
Therefore two requirements for DHCP binding is the IP address and the hardware address (MAC address) of the client. Notice that in the above example “aabb.cc00.0300” is the MAC address of the client while prefix “01” represents the Ethernet media type.
Reference: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/12_2/ip/configuration/guide/fipr_c/1cfdhcp.html
In fact the “DHCP pool” option is also correct but two above choices are better.
CCNA 200-125 Exam: DHCP Questions With Answers
Subscribe
0 Comments
