Section 46 Tasks
- Take the exam below
- Complete the challenge lab
- Review SNMP and syslog, as well as OSPF
- Read the ICND2 cram guide (and the ICND1 cram guide, if taking the CCNA exam)
- Spend 15 minutes on the subnetting.org website
Section 46 Exam
- What is the default STP priority on a switch?
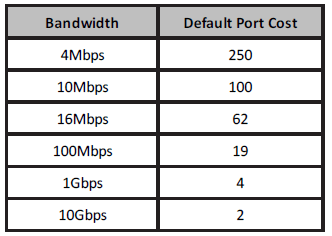
- Write down the port costs for STP connections for all the bandwidths from 4Mbps to 10Gbps.
- Explain the purpose of Port Fast, BPDU Guard, BPDU Filter, Uplink Fast, and Backbone Fast.
- Which command configures the Spanning Tree cost on a port?
Section 46 Answers
1. 32768
2.
3. Port Fast is a feature that is typically enabled only for a port or interface that connects to a host. When the link comes up on this port, the switch skips the first stages of the STA and directly transitions to the Forwarding state. Contrary to popular belief, the Port Fast feature does not disable Spanning Tree on the selected port. This is because even with the Port Fast feature, the port can still send and receive BPDUs.
The BPDU Guard feature is used to protect the Spanning Tree domain from external influence. BPDU Guard is disabled by default but is recommended for all ports on which the Port Fast feature has been enabled. When a port that is configured with the BPDU Guard feature receives a BPDU, it immediately transitions to the errdisable state.
The BPDU Guard and the BPDU Filter features are often confused or even thought to be the same. They are, however, different, and it is important to understand the differences between them. When Port Fast is enabled on a port, the port will send out BPDUs and will accept and process received BPDUs. The BPDU Filter feature prevents the port from receiving any BPDUs but does not prevent it from sending them. If any BPDUs are received, the port will be errdisabled.
The Uplink Fast feature provides faster failover to a redundant link when the primary link fails (direct failure of the Root Port). The primary purpose of this feature is to improve the convergence time of STP in the event of a failure of an uplink. This feature is of most use on Access Layer switches with redundant uplinks to the Distribution Layer; hence, the name.
The Backbone Fast feature provides fast failover when an indirect link failure occurs in the STP domain. Failover occurs when the switch receives an inferior BPDU from its designated bridge (on it’s Root Port). An inferior BPDU indicates that the designated bridge has lost its connection to the Root Bridge, so the switch knows there was an upstream failure and without waiting for timers to expire changes the Root Port.
4. The spanning-tree cost command.
Section 46 Lab – VLANs and STP
Topology
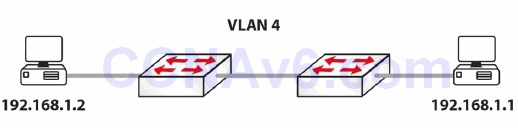
Instructions
Connect to the switch using a console connection. Connect a PC to each switch, or connect the switch to the FastEthernet port on a router:
- Add IP addresses to the PCs or router Ethernet interfaces
- Create VLAN4 on the switches
- Set the ports the PCs connect to as access ports (default, but do it anyway)
- Put the two switch ports into VLAN4
- Configure the link between the switches as trunk ports and no shut them
- Wait about 30 seconds, at most, and then ping from PC to PC
- Check which switch is the Root Bridge with the show spanning-tree vlan 4 command
- Set the other switch as the Root Bridge with the spanning-tree vlan 4 priority 0 command
- Now check to see whether the switch has become the Root Bridge
- Remove the spanning-tree vlan 4 priority 0 command to reset the original switch as the Root Bridge (put no in front of the command)
- Now set the other switch as the Root Bridge with the spanning-tree vlan 4 root primary command
Solution Hints and Commands
vlan 4 to create a VLAN sw mode access sw mode trunk sw access vlan 4
