10.2.3.6 Lab – Configuring Syslog and NTP (Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology

Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | S0/0/0 (DCE) | 10.1.1.1 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| R2 | S0/0/0 | 10.1.1.2 | 255.255.255.252 | N/A |
| G0/0 | 172.16.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| PC-B | NIC | 172.16.2.3 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.2.1 |
Objectives
Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings
Part 2: Configure NTP
Part 3: Configure Syslog
Background / Scenario
Syslog messages that are generated by the network devices can be collected and archived on a syslog server. The information can be used for monitoring, debugging, and troubleshooting purposes. The administrator can control where the messages are stored and displayed. Syslog messages can be time-stamped for analysis of the sequence of network events; therefore, it is important to synchronize the clock across the network devices with a Network Time Protocol (NTP) server.
In this lab, you will configure R1 as the NTP server and R2 as a Syslog and NTP client. The syslog server application, such as Tftp32d or other similar program, will be running on PC-B. Furthermore, you will control the severity level of log messages that are collected and archived on the syslog server.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 1941 Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 (universalk9 image). Other routers and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of this lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Make sure that the routers have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure, contact your instructor.
Instructor Note: Refer to the Instructor Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices.
Required Resources
- 2 Routers (Cisco 1941 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(4)M3 universal image or comparable)
- 1 PC (Windows 7, Vista, or XP with terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term, and Syslog software, such as Tftpd32)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet and serial cables as shown in the topology
Part 1: Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings, such as the interface IP addresses, routing, device access, and passwords.
Step 1: Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Step 2: Initialize and reload the routers as necessary.
Step 3: Configure basic settings for each router.
a. Console into the router and enter global configuration mode.
b. Copy the following basic configuration and paste it to the running-configuration on the router.
no ip domain-lookup service password-encryption enable secret class banner motd # Unauthorized access is strictly prohibited. # line con 0 password cisco login logging synchronous line vty 0 4 password cisco login
c. Configure the host name as shown in the topology.
d. Apply the IP addresses to Serial and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces according to the Addressing Table and activate the physical interfaces.
e. Set the clock rate to 128000 for the DCE serial interface.
Step 4: Configure routing.
Enable RIPv2 on the routers. Add all the networks into the RIPv2 process.
Step 5: Configure PC-B.
Configure the IP address and default gateway for PC-B according to the Addressing Table.
Step 6: Verify end-to-end connectivity.
Verify that each device is able to ping every other device in the network successfully. If not, troubleshoot until there is end-to-end connectivity.
Step 7: Save the running configuration to the startup configuration.
Part 2: Configure NTP
In Part 2, you will configure R1 as the NTP server and R2 as the NTP client of R1. Synchronized time is important for syslog and debug functions. If the time is not synchronized, it is difficult to determine what network event caused the message.
Step 1: Display the current time.
Issue the show clock command to display the current time on R1.
R1# show clock *12:30:06.147 UTC Tue May 14 2013
Record the information regarding the current time displayed in the following table.
| Date | Answer will vary. In this example: May 14, 2013 |
| Time | Answer will vary. In this example: 12:30:06.147 |
| Time Zone | Answer will vary. In this example: UTC |
Step 2: Set the time.
Use the clock set command to set the time on R1. The following is an example of setting the date and time.
R1# clock set 9:39:00 05 july 2013 R1# *Jul 5 09:39:00.000: %SYS-6-CLOCKUPDATE: System clock has been updated from 12:30:54 UTC Tue May 14 2013 to 09:39:00 UTC Fri Jul 5 2013, configured from console by console.
Note: The time can also be set using the clock timezone command in the global configuration mode. For more information regarding this command, research the clock timezone command at www.cisco.com to determine the zone for your region.
Step 3: Configure the NTP master.
Configure R1 as the NTP master by using the ntp master stratum-number command in global configuration mode. The stratum number indicates the number of NTP hops away from an authoritative time source. In this lab, the number 5 is the stratum level of this NTP server.
R1(config)# ntp master 5
Step 4: Configure the NTP client.
a. Issue show clock command on R2. Record the current time displayed on R2 in the following table.
| Date | Answer will vary. |
| Time | Answer will vary. |
| Time Zone | Answer will vary. |
b. Configure R2 as the NTP client. Use the ntp server command to point to the IP address or hostname of the NTP server. The ntp update-calendar command periodically updates the calendar with NTP time.
R2(config)# ntp server 10.1.1.1 R2(config)# ntp update-calendar
Step 5: Verify NTP configuration.
a. Use the show ntp associations command to verify that R2 has an NTP association with R1.
R2# show ntp associations address ref clock st when poll reach delay offset disp *~10.1.1.1 127.127.1.1 5 11 64 177 11.312 -0.018 4.298 * sys.peer, # selected, + candidate, - outlyer, x falseticker, ~ configured
b. Issue show clock on R1 and R2 to compare the timestamp.
Note: It could take a few minutes before the timestamp on R2 is synchronized with R1.
R1# show clock 09:43:32.799 UTC Fri Jul 5 2013 R2# show clock 09:43:37.122 UTC Fri Jul 5 2013
Part 3: Configure Syslog
Syslog messages from network devices can be collected and archived on a syslog server. In this lab, Tftpd32 will be used as the syslog server software. The network administrator can control the types of messages that can be sent to the syslog server.
Step 1: (Optional) Install syslog server.
If a syslog server is not already installed on the PC, download and install the latest version of a syslog server, such as Tftpd32, on the PC. The latest version of Tftpd32 can be found at the following link: http://tftpd32.jounin.net/
Step 2: Start the syslog server on PC-B.
After starting the Tftpd32 application, click the syslog server tab.
Step 3: Verify that the timestamp service is enabled on R2.
Use the show run command to verify that the timestamp service is enabled for logging on R2.
R2# show run | include timestamp service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec
If the timestamp service is not enabled, use the following command to enable it.
R2(config)# service timestamps log datetime msec
Step 4: Configure R2 to log messages to the syslog server.
Configure R2 to send Syslog messages to the syslog server, PC-B. The IP address of the PC-B syslog server is 172.16.2.3.
R2(config)# logging host 172.16.2.3
Step 5: Display the default logging settings.
Use the show logging command to display the default logging settings.
R2# show logging
Syslog logging: enabled (0 messages dropped, 2 messages rate-limited, 0 flushes, 0
overruns, xml disabled, filtering disabled)
No Active Message Discriminator.
No Inactive Message Discriminator.
Console logging: level debugging, 47 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Monitor logging: level debugging, 0 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Buffer logging: level debugging, 47 messages logged, xml disabled,
filtering disabled
Exception Logging: size (4096 bytes)
Count and timestamp logging messages: disabled
Persistent logging: disabled
No active filter modules.
Trap logging: level informational, 49 message lines logged
Logging to 172.16.2.3 (udp port 514, audit disabled,
link up),
6 message lines logged,
0 message lines rate-limited,
0 message lines dropped-by-MD,
xml disabled, sequence number disabled
filtering disabled
Logging Source-Interface: VRF Name:
What is the IP address of the syslog server? ____________172.16.2.3
What protocol and port is syslog using? ___________UDP port 514
At what level is trap logging enabled? ____________informational
Step 6: Configure and observe the effect of logging severity levels on R2.
a. Use the logging trap ? command to determine the various trap levels availability. When configuring a level, the messages sent to the syslog server are the trap level configured and any lower levels.
R2(config)# logging trap ? <0-7> Logging severity level alerts Immediate action needed (severity=1) critical Critical conditions (severity=2) debugging Debugging messages (severity=7) emergencies System is unusable (severity=0) errors Error conditions (severity=3) informational Informational messages (severity=6) notifications Normal but significant conditions (severity=5) warnings Warning conditions (severity=4) <cr>
If the logging trap warnings command was issued, which severity levels of messages are logged?
____________________________________________________warnings (level 4) errors (level 3), critical (level 2), alerts (level 1), and emergency (level 0)
b. Change the logging severity level to 4.
R2(config)# logging trap warnings
or
R2(config)# logging trap 4
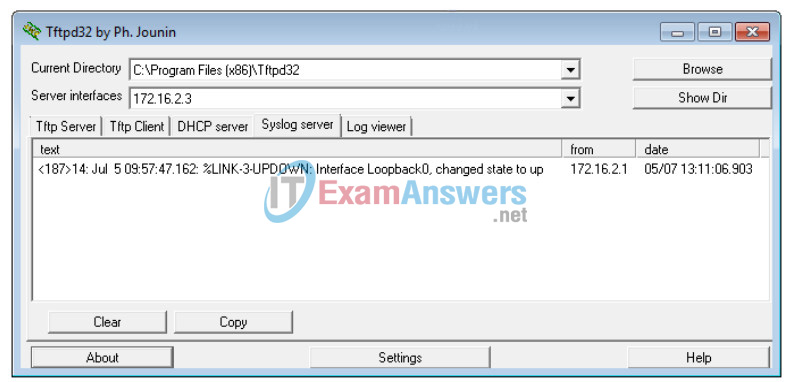
c. Create interface Loopback0 on R2 and observe the log messages on both the terminal window and the syslog server window on PC-B.
R2(config)# interface lo 0 R2(config-if)# Jul 5 09:57:47.162: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Loopback0, changed state to up Jul 5 09:57:48.162: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up
d. Remove the Loopback 0 interface on R2 and observe the log messages.
R2(config-if)# no interface lo 0 R2(config)# Jul 5 10:02:58.910: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Loopback0, changed state to administratively down Jul 5 10:02:59.910: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to down
At severity level 4, are there any log messages on the syslog server? If any log messages appeared, explain what appeared and why.
___________________________________________________
There was a summary warning log message indicating a change in the interface state. The addition of the interface was not enough to trigger and send more detailed informational messages to the syslog server at level 4.
e. Change the logging severity level to 6.
R2(config)# logging trap informational
or
R2(config)# logging trap 6
f. Clear the syslog entries on PC-B. Click Clear in the Tftpd32 dialog box.
g. Create the Loopback 1 interface on R2.
R2(config)# interface lo 1 Jul 5 10:05:46.650: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Loopback1, changed state to up Jul 5 10:05:47.650: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback1, changed state to up
h. Remove the Loopback 1 interface from R2.
R2(config-if)# no interface lo 1 R2(config-if)# Jul 5 10:08:29.742: %LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Loopback1, changed state to administratively down Jul 5 10:08:30.742: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback1, changed state to down
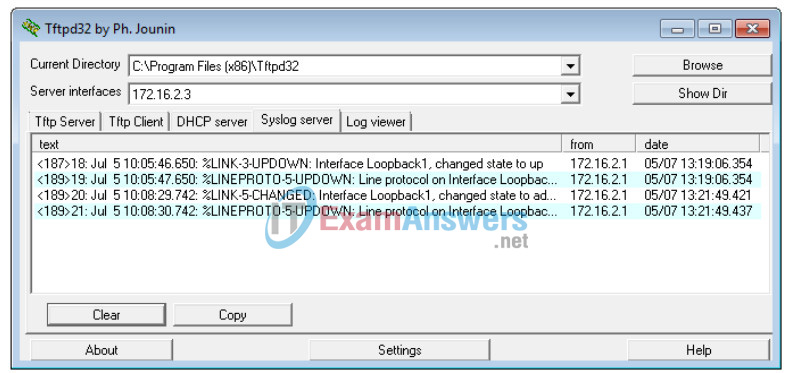
i. Observe the syslog server output. Compare this result with the results at trapping level 4. What is your observation?
_________________________________________________
More log messages were trapped when the severity was set to 6 (informational) than when it was set at 4 (warnings).
Reflection
What is the problem with setting the level of severity too high (lowest level number) or too low (highest level
number) for syslog?
___________________________________________________
When the severity level is set too high (lowest level number), the generated log could be missing important, but not critical messages. However, setting it too low (highest level number), it can generate too many entries and fill the logs with unnecessary information.
Router Interface Summary Table
| Router Interface Summary | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Router Model | Ethernet Interface #1 | Ethernet Interface #2 | Serial Interface #1 | Serial Interface #2 |
| 1800 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 1900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2801 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) | Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
| 2811 | Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) | Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| 2900 | Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) | Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) | Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) | Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
| Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface. | ||||
Device Configs
Router R1
R1#show run Building configuration... Current configuration : 1572 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname R1 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! ip cef ! no ip domain lookup no ipv6 cef ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! redundancy ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 clock rate 128000 ! interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown ! router rip version 2 network 10.1.1.0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! control-plane ! banner motd ^CUnauthorized access is prohibited.^C ! line con 0 password 7 110A1016141D logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password 7 01100F175804 login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ntp master 5 ! end
Router R2
Building configuration... Current configuration : 1742 bytes ! version 15.2 service timestamps debug datetime msec service timestamps log datetime msec service password-encryption ! hostname R2 ! boot-start-marker boot-end-marker ! enable secret 4 06YFDUHH61wAE/kLkDq9BGho1QM5EnRtoyr8cHAUg.2 ! no aaa new-model memory-size iomem 15 ! ip cef ! no ip domain lookup no ipv6 cef ! multilink bundle-name authenticated ! redundancy ! interface Embedded-Service-Engine0/0 no ip address shutdown ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 duplex auto speed auto ! interface GigabitEthernet0/1 no ip address shutdown duplex auto speed auto ! interface Serial0/0/0 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 ! interface Serial0/0/1 no ip address shutdown clock rate 2000000 ! router rip version 2 network 10.1.1.0 network 172.16.2.0 ! ip forward-protocol nd ! no ip http server no ip http secure-server ! logging host 172.16.2.3 ! control-plane ! banner motd ^CUnauthorized access is prohibited.^C ! line con 0 password 7 121A0C041104 logging synchronous login line aux 0 line 2 no activation-character no exec transport preferred none transport input all transport output pad telnet rlogin lapb-ta mop udptn v120 ssh stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password 7 01100F175804 login transport input all ! scheduler allocate 20000 1000 ntp update-calendar ntp server 10.1.1.1 ! end
