2.2.4.4 Packet Tracer – Configuring IPv6 Static and Default Routes
(Instructor Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
Topology
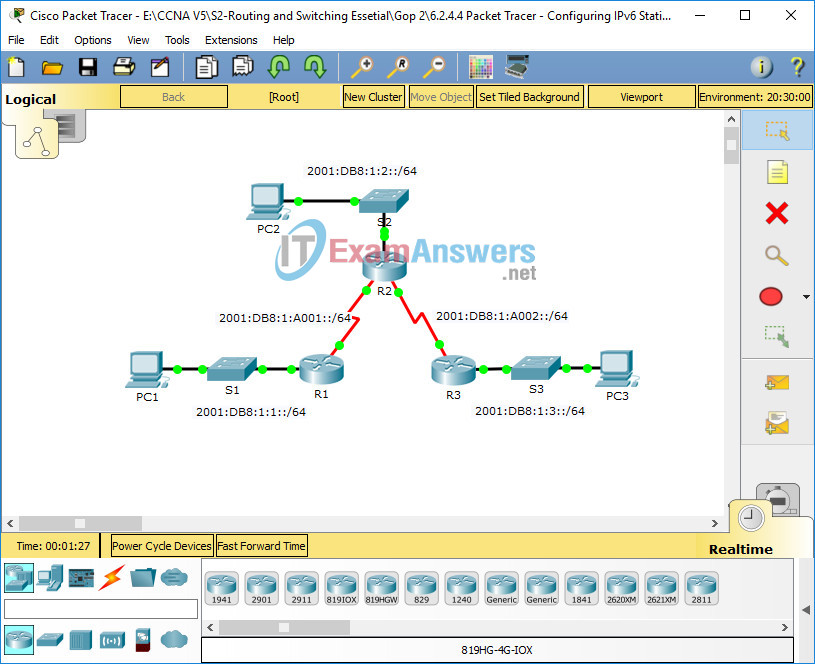
IPv6 Addressing Table
| Device | Interface | IPv6 Address/Prefix | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | G0/0 | 2001:DB8:1:1::1/64 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 2001:DB8:1:A001::1/64 | N/A | |
| R2 | G0/0 | 2001:DB8:1:2::1/64 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 2001:DB8:1:A001::2/64 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 2001:DB8:1:A002::1/64 | N/A | |
| R3 | G0/0 | 2001:DB8:1:3::1/64 | N/A |
| S0/0/1 | 2001:DB8:1:A002::2/64 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | 2001:DB8:1:1::F/64 | FE80::1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 2001:DB8:1:2::F/64 | FE80::2 |
| PC3 | NIC | 2001:DB8:1:3::F/64 | FE80::3 |
Objectives
- Part 1: Examine the Network and Evaluate the Need for Static Routing
- Part 2: Configure IPv6 Static and Default Routes
- Part 3: Verify Connectivity
Background
In this activity, you will configure IPv6 static and default routes. A static route is a route that is entered manually by the network administrator in order to create a route that is reliable and safe. There are four different static routes used in this activity: a recursive static route; a directly attached static route; a fully specified static route; and a default route.
Part 1: Examine the Network and Evaluate the Need for Static Routing
a. Looking at the topology diagram, how many networks are there in total?
5
b. How many networks are directly connected to R1, R2, and R3?
R1 has 2, R2 has 3, and R3 has 2.
c. How many static routes are required by each router to reach networks that are not directly connected?
R1 needs to configure 3 static routes, R2 needs to configure 2 static routes, and R3 needs to configure 3 static routes.
d. Which command is used to configure IPv6 static routes?
ipv6 route [network/prefix] [exit interface/next hop address]
Part 2: Configure IPv6 Static and Default Routes
Step 1: Enable IPv6 routing on all routers.
Before configuring static routes, we must configure the router to forward IPv6 packets
Which command accomplishes this?
ipv6 unicast-routing
Enter this command on each router.
Step 2: Configure recursive static routes on R1.
Configure an IPv6 recursive static route to every network not directly connected to R1.
ipv6 route 2001:DB8:1:2::/64 2001:DB8:1:A001::2 ipv6 route 2001:DB8:1:A002::/64 2001:DB8:1:A001::2 ipv6 route 2001:DB8:1:3::/64 2001:DB8:1:A001::2
Step 3: Configure a directly attached and a fully specified static route on R2.
a. Configure a directly attached static route from R2 to the R1 LAN.
ipv6 route 2001:DB8:1:1::/64 Serial0/0/0
b. Configure a fully specific route from R2 to the R3 LAN.
Note: Packet Tracer v6.0.1 only checks for directly attached and recursive static routes. Your instructor may ask to review your configuration of a fully specified IPv6 static route.
ipv6 route 2001:DB8:1:3::/64 Serial0/0/1 2001:DB8:1:A002::2
Step 4: Configure a default route on R3.
Configure a recursive default route on R3 to reach all networks not directly connected.
ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:1:A002::1
Step 5: Verify static route configurations.
a. Which command is used in Packet Tracer to verify the IPv6 configuration of a PC from the command prompt?
ipv6config
b. Which command displays the IPv6 addresses configured on a router’s interface?
show ipv6 interface brief
c. Which command displays the contents of the IPv6 routing table?
show ipv6 route
Part 3: Verify Network Connectivity
Every device should now be able to ping every other device. If not, review your static and default route configurations.
Suggested Scoring Rubric
| Activity Section | Question Location | Possible Points | Earned Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part 1: Exam the Network and Evaluate the Need for Static Routing | a – d | 20 | |
| Part 1 Total | 20 | ||
| Part 2: Configure IPv6 Static and Default Routes | Step 1 | 5 | |
| Step 5 | 15 | ||
| Part 2 Total | 20 | ||
| Packet Tracer Score | 60 | ||
| Total Score | 100 | ||
