2.3.2 Packet Tracer – Verify Connectivity of Directly Connected Devices Answers
Topology
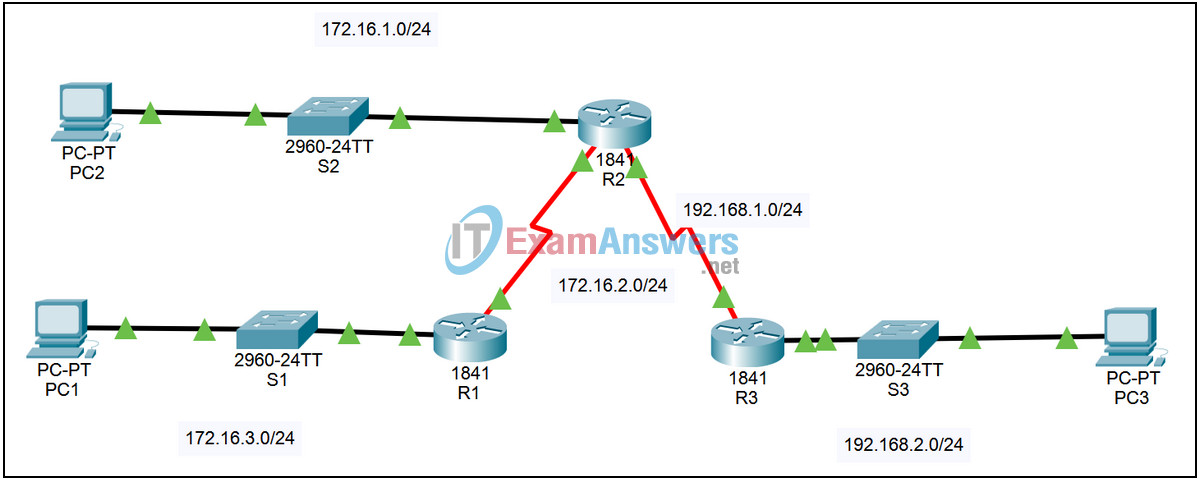
| Device | Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Default Gateway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | Fa0/0 | 172.16.3.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.16.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| R2 | Fa0/0 | 172.16.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/0 | 172.16.2.2 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.1.2 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| R3 | Fa0/0 | 192.168.2.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A |
| S0/0/1 | 192.168.1.1 | 255.255.255.0 | N/A | |
| PC1 | NIC | 172.16.3.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.3.1 |
| PC2 | NIC | 172.16.1.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 172.16.1.1 |
| PC3 | NIC | 192.168.2.10 | 255.255.255.0 | 192.168.2.1 |
Introduction:
Directly connected devices configured for IP can communicate with each other. Without routing, these devices cannot communicate with other devices on networks that are not directly connected.
Learning Objectives:
- Check connectivity between devices.
- Check connectivity between hosts and routers.
- Check connectivity between routers.
Task 1: Check connectivity between devices.
Step 1 – Check connectivity between hosts and routers.
From the command prompt on PC1, issue the command ping 172.16.3.1 to ping the FastEthernet0/0 interface on router R1. From the command prompt on PC1 issue the command ping 172.16.2.1 to ping the Serial0/0/0 interface on router R1. Both pings will succeed because router R1 is directly connected to PC1. From the command prompt on PC1, issue the command ping 172.16.2.2 to ping the Serial0/0/0 interface on router R2. This ping will fail because router R2 is not directly connected to PC1. From PC2 and PC3 ping, the IP addresses of all the router interfaces and note the results.
Step 2 – Check connectivity between routers.
From the CLI on router R1 issue the command ping 172.16.3.10 to ping the FastEthernet interface on PC1. From the CLI on router R1 issue the command ping 172.16.2.2 to ping the Serial0/0/0 interface on router R2. Both pings will succeed because router R1 is directly connected to PC1 and interface Serial0/0 on R2 is in the same subnet as Serial0/0/0 on router R1. From the CLI on router R1 issue the command ping 172.16.1.1 to ping the FastEathernet0/0 interface on router R2. This ping will fail because even though router R2 is directly connected to router R1 the FastEathernet0/0 interface on router R2 is in a different subnet and the IP routing table on router R1 does not have a route to that destination. This can be confirmed by issuing the show ip route command on router R1. From router R2 and router R3 ping the IP addresses of all the router and PC interfaces and note the results.
