Networking Devices and Initial Configuration Module 8.3.3 IP Addressing Services Quiz Answers
1. Which network service automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on the network?
- DHCP
- Telnet
- DNS
- traceroute
Explanation: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) can be used to allow end devices to automatically configure IP information, such as their IP address, subnet mask, DNS server, and default gateway. The DNS service is used to provide domain name resolution, mapping hostnames to IP addresses. Telnet is a method for remotely accessing a CLI session of a switch or router. Traceroute is a command used to determine the path a packet takes as it traverses the network.
2. A host PC has just booted and is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. Which two messages will the client typically broadcast on the network? (Choose two.)
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
Explanation: When a host uses DHCP to automatically configure an IP address, the typically sends two messages: the DHCPDISCOVER message and the DHCPREQUEST message. These two messages are usually sent as broadcasts to ensure that all DHCP servers receive them. The servers respond to these messages using DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK, and DHCPNACK messages, depending on the circumstance.
3. Refer to the exhibit. Host A is trying to resolve the name www.internal.cisco.com to an IP address. When the name resolution request is received by a root DNS server, which server will be included in the response for further resolution?
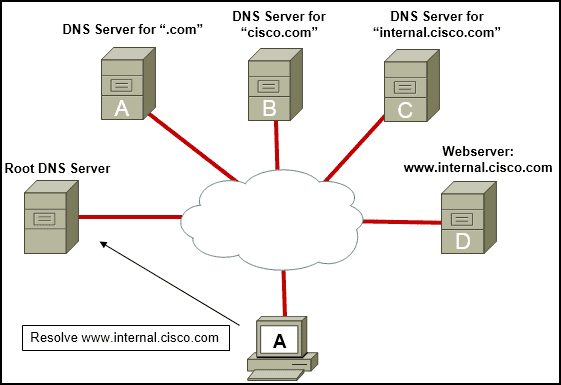
- DNS server A
- DNS server B
- DNS server C
- web server D
Explanation: Root DNS servers only carry records for top-level domains (like .com or .org). If a host requests resolution from a root DNS server for the domain www.cisco.com, for example, the root DNS server would refer the client to the DNS server responsible for the .com domain. This DNS server would then refer the client to the DNS server for cisco.com. Finally, the DNS server for cisco.com is authoritative for that domain and would return the IP address of the host record “www”, completing the resolution of www.cisco.com.
4. Which statement is true about DHCP operation?
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREQUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREQUEST message.
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
Explanation: The client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network. A DHCP server replies with a DHCPOFFER message. This message offers to the client a lease that contains such information as the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway. After the client receives the lease, the received information must be renewed through another DHCPREQUEST message prior to the lease expiration.
5. Which DHCPv4 message will a client send to accept an IPv4 address that is offered by a DHCP server?
- unicast DHCPACK
- broadcast DHCPACK
- unicast DHCPREQUEST
- broadcast DHCPREQUEST
Explanation: When a DHCP client receives DHCPOFFER messages, it will send a broadcast DHCPREQUEST message for two purposes. First, it indicates to the offering DHCP server that it would like to accept the offer and bind the IP address. Second, it notifies any other responding DHCP servers that their offers are declined.
6. Which protocol translates a website name such as www.cisco.com into a network address?
Explanation: Domain Name Service translates names into numerical addresses, and associates the two. DHCP provides IP addresses dynamically to pools of devices. HTTP delivers web pages to users. FTP manages file transfers.
7. What type of information is contained in a DNS MX record?
- the FQDN of the alias used to identify a service
- the IP address for an FQDN entry
- the domain name mapped to mail exchange servers
- the IP address of an authoritative name server
Explanation: MX, or mail exchange messages, are used to map a domain name to several mail exchange servers that all belong to the same domain.
8. A technician is adding a new PC to a LAN. After unpacking the components and making all the connections, the technician starts the PC. After the OS loads, the technician opens a browser, and verifies that the PC can reach the Internet. Why was the PC able to connect to the network with no additional configuration?
- The PC does not require any additional information to function on the network
- The PC came preconfigured with IP addressing information from the factory.
- The PC was preconfigured to use DHCP.
- The PC used DNS to automatically receive IP addressing information from a server.
- The PC virtual interface is compatible with any network.
Explanation: The new PC was preconfigured to use DHCP. When the PC is connected to a network that uses DHCP, it gets the IP address settings from the DHCP server that will allow it to function on the network. All devices require at least an IP address and subnet mask to function on a LAN. DNS does not automatically configure addresses on hosts. PC virtual interfaces are not universally compatible with LANs and do not necessarily provide a host with an IP address. At this place in the course, virtual interfaces are used on network switches.
9. Which network server is malfunctioning if a user can ping the IP address of a web server but cannot ping the web server host name?
- the DNS server
- the DHCP server
- the FTP server
- the HTTP server
Explanation: If pings are successful to an IP address but not to a host name, then the problem may be that a DNS server cannot be accessed.
10. Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol allows a user to type www.cisco.com instead of an IP address to access the web server?
Explanation: Web servers are assigned static IP addresses. They are also registered with domain names so people can remember them easily. However, web servers are connected through their IP addresses. DNS provides the service to map the domain name to its IP address.
11. What action does a DNS server take if it does not have an entry for a requested URL?
- The server drops the request.
- The server returns a “page not found” response to the client.
- The server checks with another DNS server to see if it has an entry.
- The server assigns a temporary IP address to the name and sends this IP address to the client.
Explanation: When a client types a URL to visit a web server, the browser sends a request to the DNS server with the IP address configured on the computer. When the DNS server receives the request, it checks its table to determine the IP address associated with that web server. If the local DNS server does not have an entry for the requested name, it queries another upstream DNS server. When the DNS server learns the IP address, that information is sent back to the client.


