Networking Devices and Initial Configuration Module 7.2.3 Address Resolution Quiz Answers
1. Which protocol is used to discover the destination address needed to be added to an Ethernet frame?
- ARP
- DNS
- DHCP
- HTTP
2. What is one function of the ARP protocol?
- obtaining an IPv4 address automatically
- mapping a domain name to its IP address
- resolving an IPv4 address to a MAC address
- maintaining a table of domain names with their resolved IP addresses
3. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 on VLAN 10 wants to communicate with PC2 on VLAN 20. PC1 sends an ARP request to its default gateway, GW1. How does GW1 respond?
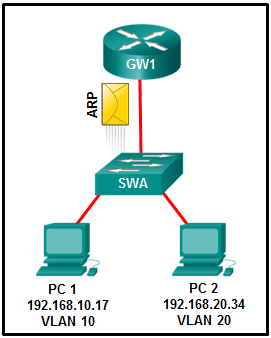
- It sends an ARP reply to PC2.
- It sends an ARP request to PC1.
- It forwards the ARP request from PC1 to PC2.
- It sends an ARP reply to PC1 with its own MAC address.
4. What action does the ARP process take when a host needs to build a frame, but the ARP cache does not contain an address mapping?
- The ARP process sends out an ARP request to the Ethernet broadcast address to discover the IPv4 address of the destination device.
- The ARP process sends out an ARP request to the IPv4 broadcast address to discover the MAC address of the destination device.
- The ARP process sends out an ARP request to the IPv4 broadcast address to discover the IPv4 address of the destination device.
- The ARP process sends out an ARP request to the Ethernet broadcast address to discover the MAC address of the destination device.
5. Which statement describes the treatment of ARP requests on the local link?
- They must be forwarded by all routers on the local network.
- They are received and processed by every device on the local network.
- They are dropped by all switches on the local network.
- They are received and processed only by the target device.
6. What is the aim of an ARP spoofing attack?
- to flood the network with ARP reply broadcasts
- to fill switch MAC address tables with bogus addresses
- to associate IP addresses to the wrong MAC address
- to overwhelm network hosts with ARP requests
7. A cybersecurity analyst believes that an attacker is announcing a forged MAC address to network hosts in an attempt to spoof the default gateway. Which command could the analyst use on the network hosts to see what MAC address the hosts are using to reach the default gateway?
- netsat -r
- route print
- ipconfig /all
- arp -a
8. What will a host do first when preparing a Layer 2 PDU for transmission to a host on the same Ethernet network?
- It will send the PDU to the router directly connected to the network.
- It will query the local DNS server for the name of the destination host.
- It will search the ARP table for the MAC address of the destination host.
- It will initiate an ARP request to find the MAC address of the destination host.
9. Which destination address is used in an ARP request frame?
- 0.0.0.0
- 255.255.255.255
- FFFF.FFFF.FFFF
- 127.0.0.1
- 01-00-5E-00-AA-23
10. Which protocol is used by a computer to find the MAC address of the default gateway on an Ethernet network?
- ARP
- TCP
- UDP
- DHCP
11. Refer to the exhibit. PC1 attempts to connect to File_server1 and sends an ARP request to obtain a destination MAC address. Which MAC address will PC1 receive in the ARP reply?
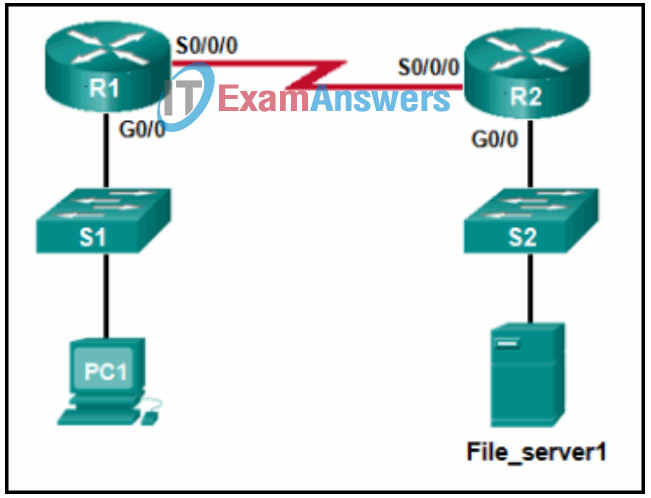
- the MAC address of S1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R1
- the MAC address of the G0/0 interface on R2
- the MAC address of S2
- the MAC address of File_server1
