- Which three statements about link-state routing are true? (Choose three)
- A. It uses split horizon.
- B. Updates are sent to a broadcast address.
- C. RIP is a link-state protocol.
- D. Updates are sent to a multicast address by default.*
- E. Routes are updated when a change in topology occurs.*
- F. OSPF is a link-state protocol.*
- Which three characteristics are representative of a link-state routing protocol? (Choose three)
- A. provides common view of entire topology*
- B. exchanges routing tables with neighbors
- C. calculates shortest path*
- D. utilizes event-triggered updates*
- E. utilizes frequent periodic updates
- What are two drawbacks of implementing a link-state routing protocol? (Choose two)
- A. the sequencing and acknowledgment of link-state packets
- B. the high volume of link-state advertisements in a converged network
- C. the requirement for a hierarchical IP addressing scheme for optimal functionality*
- D. the high demand on router resources to run the link-state routing algorithm*
- E. the large size of the topology table listing all advertised routes in the converged network
- Refer to the exhibit. Router edge-1 is unable to establish OSPF neighbor adjacency with router ISP-1. Which two configuration changes can you make on edge-1 to allow the two routers to establish adjacency? (Choose two)

- A. Set the subnet mask on edge-1 to 255 255.255.252.
- B. Reduce the MTU on edge-1 to 1514.
- C. Set the OSPF cost on edge-1 to 1522.
- D. Reduce the MTU on edge-1 to 1500.*
- E. Configure the ip ospf mtu-ignore command on the edge-1 Gi0/0 interface.*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceIn order to become OSPF neighbor following values must be match on both routers:+ Area ID
+ Authentication
+ Hello and Dead Intervals
+ Stub Flag
+ MTU SizeTherefore we need to adjust the MTU size on one of the router so that they are the same. Or we can tell OSPF to ignore the MTU size check with the command “ip ospf mtu-ignore”.
- A network administrator is troubleshooting the OSPF configuration of routers R1 and R2. The routers cannot establish an adjacency relationship on their common Ethernet link. The graphic shows the output of the show ip ospf interface e0 command for routers R1 and R2. Based on the information in the graphic, what is the cause of this problem?
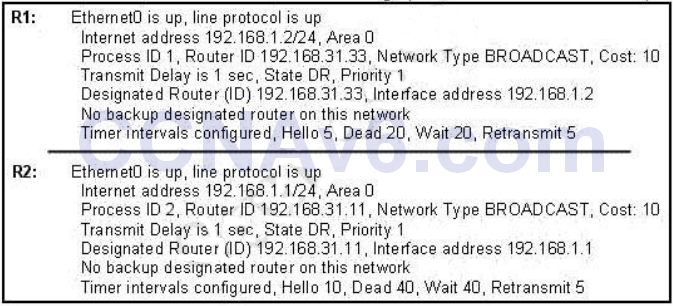
- A. The OSPF area is not configured properly.
- B. The priority on R1 should be set higher.
- C. The cost on R1 should be set higher.
- D. The hello and dead timers are not configured properly.*
- E. A backup designated router needs to be added to the network.
- F. The OSPF process ID numbers must match.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceD is correct because these entries must match on neighboring routers:– Hello and dead intervals
– Area ID (Area 0 in this case)
– Authentication password
– Stub area flagIn this case Ethernet0 of R1 has Hello and Dead Intervals of 5 and 20 while R2 has Hello and Dead Intervals of 10 and 40 -> R1 and R2 cannot form OSPF neighbor relationship.
- What routing protocol use first-hand information?
- A. link-state*
- B. distance-vector
- C. path-vector
- D. other
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe information available to a distance vector router has been compared to the information available from a road sign. Link state routing protocols are like a road map. A link state router cannot be fooled as easily into making bad routing decisions, because it has a complete picture of the network. The reason is that unlike the routing-by-rumor approach of distance vector, link state routers have firsthand information from all their peer routers. Each router originates information about itself, its directly connected links, and the state of those links (hence the name). This information is passed around from router to router, each router making a copy of it, but never changing it. The ultimate objective is that every router has identical information about the internetwork, and each router will independently calculate its own best paths.Reference: http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=24090&seqNum=4
- Refer to the exhibit. If R1 sends traffic to 192.168.10.45 the traffic is sent through which interface?
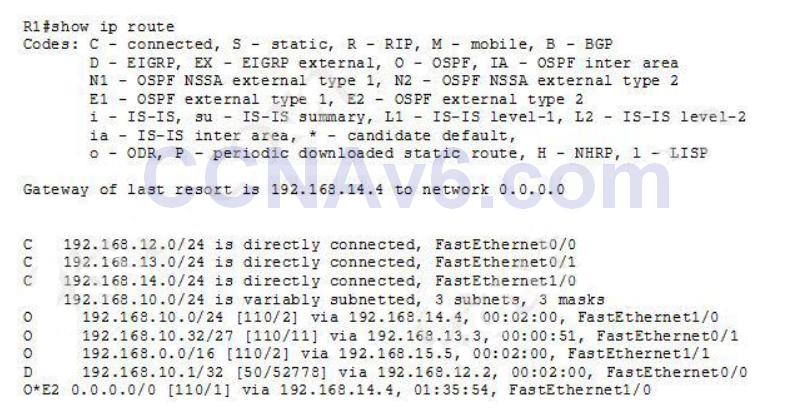
- A. FastEthernet0/1*
- B. FastEthernet0/0
- C. FastEthernet1/0
- D. FastEthernet1/1
Show (Hide) Explanation/Reference192.168.10.45 belongs to 192.168.10.32/27 subnet (range from 192.168.10.32 to 192.168.10.63) so the router will use FastEthernet0/1 as the exit interface. - R1 is unable to establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with R3. What are possible reasons for this problem? (Choose two)
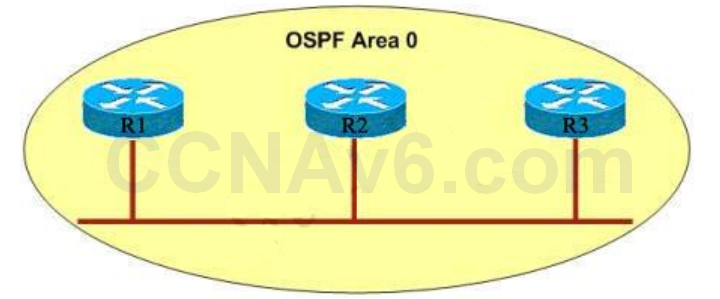
- A. All of the routers need to be configured for backbone Area 1.
- B. R1 and R2 are the DR and BDR, so OSPF will not establish neighbor adjacency with R3.
- C. A static route has been configured from R1 to R3 and prevents the neighbor adjacency from being established.
- D. The hello and dead interval timers are not set to the same values on R1 and R3. *
- E. EIGRP is also configured on these routers with a lower administrative distance.
- F. R1 and R3 are configured in different areas.*
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceA is not correct because the backbone area of OSPF is always Area 0.
B is not correct because R1 or R3 must be the DR or BDR -> it has to establish neighbor adjacency with the other.
C is not correct because OSPF neighbor relationship is not established based on static routing. It uses multicast address 224.0.0.5 to establish OSPF neighbor relationship.
E is not correct because configure EIGRP on these routers (with a lower administrative distance) will force these routers to run EIGRP, not OSPF.D and F are correct because these entries must match on neighboring routers:
– Hello and dead intervals
– Area ID (Area 0 in this case)
– Authentication password
– Stub area flag - Refer to the exhibit. You have discovered that computers on the 192.168.10.0/24 network can ping their default gateway, but they cannot connect to any resources on a remote network. Which reason for the problem is most likely true?
R1 interface Loopback0 ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.255 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 1 router-id 172.16.1.1 network 172.16.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
- A. The 192.168.12.0/24 network is missing from OSPF.*
- B. The OSPF process ID is incorrect.
- C. The OSPF area number is incorrect.
- D. An ARP table entry is missing for 192.168.10.0.
- E. A VLAN number is incorrect for 192.168.10.0.
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe most obvious thing in this configuration is R1 forgot to run OSPF on interface Fa0/0 (with the “network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 area …”) command so the computers behind 192.168.10.0/24 network does not know how to reach resources on a remote network. - Which parameter or parameters are used to calculate OSPF cost in Cisco routers?
- A. Bandwidth, Delay and MTU
- B. Bandwidth*
- C. Bandwidth and MTU
- D. Bandwidth, MTU, Reliability, Delay and Load
Show (Hide) Explanation/ReferenceThe well-known formula to calculate OSPF cost isCost = 108 / Bandwidth
so B is the correct answer.
CCNA 200-125 Exam: OSPF Questions With Answers
Subscribe
0 Comments
