13. What are two effects of using multiple OSPF areas? (Choose two.)
- prevention of a flood of queries
- reduction in the size of the LSDB
- reduction in the size of the neighbor table
- limits on the propagation of type 1 and 2 LSAs
- decrease in the number of DR and BDR elections
14. Where can interarea route summarization be performed in an OSPF network?
- ASBR
- DR
- ABR
- any router
15. Refer to the exhibit. What is indicated by the O IA in the router output?
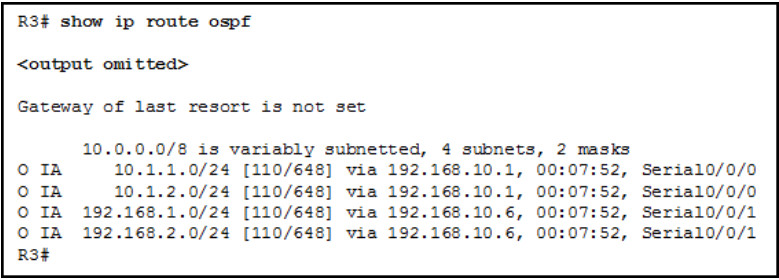
- The route was manually configured.
- The route was learned from within the area.
- The route was learned from outside the internetwork.
- The route was learned from another area.
16. Which statement describes the creation of LSAs by ABRs in the discontinuous network situation?
- Type 3 LSAs received from Area 0 are created for nonbackbone areas.
- Type 1 LSAs received from nonbackbone areas are forwarded into the backbone area.
- Type 3 LSAs received from a nonbackbone area are created in other nonbackbone areas.
- Type 1 LSAs received by the ABR are forwarded into other nonbackbone areas.
17. What is the default maximum number of equal-cost paths supported by OSPF?
- 2
- 4
- 8
- 16
18. When does an OSPF router become an ABR?
- when the router has interfaces in different areas
- when the router is configured as an ABR by the network administrator
- when the router has the highest router ID
- when the router has an OSPF priority of 0
19. Which method can be used to prevent type 3 LSAs on the backbone from being regenerated into a nonbackbone area?
- distribute list
- prefix list
- interarea summarization
- intra-area summarization
20. Which two networks are part of the summary route 192.168.32.0/22? (Choose two.)
- 192.168.31.0/24
- 192.168.33.0/24
- 192.168.37.0/24
- 192.168.35.0/24
- 192.168.36.0/24
- 192.168.38.0/24
21. Which three LSA types build the SPF tree for intra-area and interarea routes? (Choose three).
- type 1
- type 2
- type 3
- type 4
- type 5
- type 7
22. What type of OSPF LSA is originated by ASBR routers to advertise external routes?
- type 1
- type 2
- type 3
- type 5
23. What period of time must elapse before an LSA is purged from the local LSBD if not updated with a new LSA?
- 900 seconds
- 1800 seconds
- 3600 seconds
- 7200 seconds
24. What feature can be configured to filter routes as they are crossing an OSPF ABR?
- prefix list
- summarization
- distribute list
- route map
“Do I Know This Already?” Quiz Answers:
1. True or false: A router with an interface associated with Area 1 and Area 2 will be able to inject routes learned from one area into another area.
- True
- False
2. True or false: A member router contains a complete copy of the LSDBs for every area in the routing domain.
- True
- False
3. How many OSPF link-state announcement (LSA) types are used for routing traditional IPv4 packets?
- Two
- Three
- Five
- Six
- Seven
4. What is the LSA age field in the LSDB used for?
- For version control—to ensure that the most recent LSA is present
- To age out old LSAs by removing an LSA when its age reaches zero
- For troubleshooting—to identify exactly when the LSA was advertised
- To age out old LSAs by removing an LSA when it reaches 3600 seconds
5. Which LSA type exists in all OSPF areas?
- Network
- Summary
- Router
- AS external
6. True or false: When an ABR receives a network LSA, the ABR forwards the network LSA to the other connected areas.
- True
- False
7. When a type 3 LSA is received in a nonbackbone area, what does the ABR do?
- Discards the type 3 LSA and does not process it
- Installs the type 3 LSA for only the area where it was received
- Advertises the type 3 LSA to the backbone area and displays an error
- Advertises the type 3 LSA to the backbone area
8. True or false: OSPF uses the shortest total path metric to identify the best path for every internal OSPF route (intra-area and interarea).
- True
- False
9. True or false: Breaking a large OSPF topology into smaller OSPF areas can be considered a form of summarization.
- True
- False
10. How is the process of summarizing routes on an OSPF router accomplished?
- By using the interface configuration command summary-address network prefix-length
- By using the OSPF process configuration command summary-address network prefix-length
- By using the OSPF process configuration command area area-id range network subnet-mask
- By using the interface configuration command area area-id summary-address network subnet-mask
11. OSPF supports filtering of routes using which of the following techniques? (Choose two.)
- Summarization, using the no-advertise option
- LSA filtering, which prevents type 1 LSAs from being advertised through a member router
- Area filtering, which prevents type 1 LSAs from being generated into a type 3 LSA
- Injection of an OSPF discard route on the router that filtering should apply
