Lab Objective:
The objective of this lab exercise is for you to learn and understand how to configure Cisco IOS DHCP clients.
Lab Purpose:
Configuring the Cisco IOS DHCP client feature is a fundamental skill. DHCP provides dynamic addressing information to hosts on a network. Typically, physical DHCP servers (such as Microsoft Windows servers) are used to provide addressing information to DHCP clients (which are devices that request configuration via DHCP). In most cases, DHCP clients are typically computers and other such devices; however, it is also possible to configure Cisco IOS devices to act as DHCP clients and automatically receive configuration information from a DHCP server. As a Cisco engineer, as well as in the Cisco CCNA exam, you will be expected to know how to configure the Cisco IOS DHCP client feature.
Certification Level:
This lab is suitable for CCNA certification exam preparation.
Lab Difficulty:
This lab has a difficulty rating of 5/10.
Readiness Assessment:
When you are ready for your certification exam, you should complete this lab in no more than 10 minutes.
IMPORTANT NOTE: In order to test DHCP functionality, you will need a DHCP server configured and be ready to provide IP addressing information. However, this may not be possible unless you have access to live equipment or Packet Tracer, so the purpose of this lab exercise is to be able to configure the IOS DHCP client feature. The solution will provide information on what you would look for if this was a real network with a functioning DHCP server.
Lab Topology:
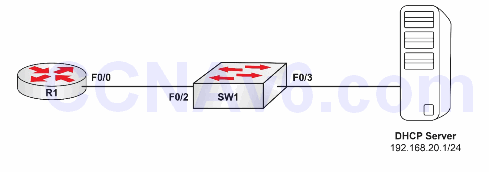
Please use the following topology to complete this lab exercise:
Task 1:
Configure hostnames on R1 and Sw1 as illustrated in the topology.
Task 2:
Configure VLAN100 on Sw1 and name it DHCP_VLAN. Assign port Fa0/2 and Fa0/3 to this VLAN. To prevent DHCP request timeouts, enable the ports to automatically transition to the Spanning Tree Forwarding state.
Task 3:
Assuming that the DHCP server is correctly configured, configure R1 F0/0 to receive IP addressing via DHCP. Verify that R1 has received automatic configuration information via DHCP. You can easily configure DHCP settings on a router or Packet Tracer server, which we covered earlier.
Configuration and Verification
Task 1:
For reference information on configuring hostnames, please refer to earlier labs.
Task 2:
Sw1#config t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z. Sw1(config)#vlan100 Sw1(config-vlan)#name DHCP_VLAN Sw1(config-vlan)#exit Sw1(config)#interface range fastethernet0/2 – 3 Sw1(config-if-range)#switchport mode access Sw1(config-if-range)switchport access vlan100 Sw1(config-if-range)#spanning-tree portfast %Warning: portfast should only be enabled on ports connected to a single host. Connecting hubs, concentrators, switches, bridges, etc... to this interface when portfast is enabled, can cause temporary bridging loops. Use with CAUTION %Portfast will be configured in 2 interfaces due to the range command but will only have effect when the interfaces are in a non-trunking mode. Sw1(config-if-range)#no shutdown Sw1(config-if-range)#end Sw1#
Task 3:
R1#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CTRL/Z. R1(config)#int fa0/0 R1(config-if)#ip address dhcp R1(config-if)#no shutdown R1(config-if)#end *Mar 1 02:25:29.029: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up *Mar 1 02:25:30.030: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up *Mar 1 02:25:33.164: %DHCP-6-ADDRESS_ASSIGN: Interface FastEthernet0/0 assigned DHCP address 192.168.20.3, mask 255.255.255.0, hostname R1 R1#
NOTE: When you see the log message %DHCP-6-ADDRESS_ASSIGN: you know that your device has been assigned an IP address via DHCP. Verify that the interface specified is the one you configured for DHCP.
R1#show ip interface fastethernet0/0 FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet address is 192.168.20.3/24 Broadcast address is 255.255.255.255 Address determined by DHCP R1#show dhcp server DHCP server: ANY (255.255.255.255) Leases: 2 Offers: 2 Requests: 2 Acks: 2 Naks: 0 Declines: 0 Releases: 3 Bad: 0 DNS0: 172.16.1.254, DNS1: 172.16.2.254 NBNS0: 10.1.1.254, NBNS1: 10.2.2.254 Subnet: 255.255.255.0 DNS Domain: howtonetwork.com
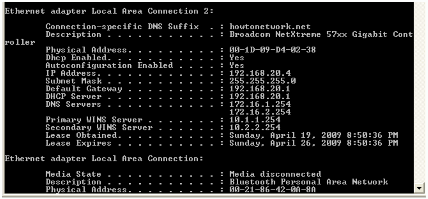
NOTE: From the output above, you can see that the DHCP server provided two DNS servers as specified by the line DNS0: 172.16.1.254, DNS1: 172.16.2.254, as well as two WINS servers, as specified by the line NBNS0: 10.1.1.254, NBNS1: 10.2.2.254. The subnet mask is /24 and the DNS domain provided is howtonetwork.com. howtonetwork.com. If a workstation, such as a Windows-based computer, were provided IP addressing information from the same DHCP server and you issued ipconfig /all at the command prompt, you would see: