Section 55 Tasks
- Take the exam below
- Complete the challenge lab
- Review the subject of your choice
- Write out the ICND2 cram guide (and the ICND1 cram guide, if taking the CCNA exam) from memory
- Spend 15 minutes on the subnetting.org website
Section 55 Exam
- Name at least three reasons for EIGRP neighbour relationships not forming.
- Which command can you use to verify EIGRP K values?
- Which command can you use to verify EIGRP packets statistics?
- Name at least two common reasons for EIGRP route installation failures.
- The administrative distance concept is used to determine how reliable the route source is. True or false?
- By default, EIGRP automatically summarises at classful boundaries and creates a summary route pointing to the Null0 interface. True or false?
- Name the command you can use to debug FSM events.
- Which command can you use to see the originating router ID of a specific prefix?
- Which command can you use to show the EIGRP event log?
- What is the best command to use when debugging various routing issues?
Section 55 Answers
- The neighbour routers are not on a common subnet; mismatched primary and secondary
subnets; mismatched K values; mismatched ASN; ACLs are filtering EIGRP packets; Physical
Layer issues; Data Link Layer issues; and mismatched authentication parameters. - The show ip protocols command.
- The show ip eigrp traffic command.
- The same route is received via another protocol with a lower administrative distance;
EIGRP summarisation; duplicate router IDs are present within the EIGRP domain; and the
routes do not meet the Feasibility Condition. - True.
- True.
- The debug eigrp fsm command.
- The show ip eigrp topology x.x.x.x y.y.y.y command.
- The show ip eigrp events command.
- The debug ip routing command.
Section 55 Lab – OSPF and NAT
Topology
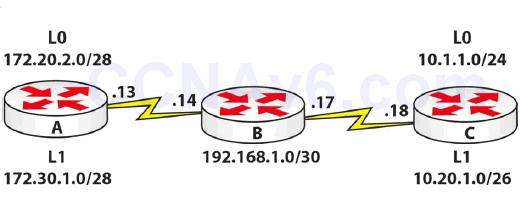
Instructions
Connect three routers together with a serial or crossover cable:
- Add IP addresses to the routers and Loopback interfaces on Routers A, B, and C, according to the diagram
- Ping between Routers A and B and between Routers B and C to test the serial lines (remember clock rates)
- Now set the serial lines to use PPP with CHAP (also set usernames and passwords)
- Configure OSPF on all routers; put one Loopback on either end in a non-zero area, but do not add 172.30.1.0 to OSPF
- Check the routing tables and make sure that you include both of the 192.168.1.x networks
- Create a NAT pool of 192.168.2.1 to 10/24, inclusive, on Router A; set an ACL to match the 172.30.1.0/28 subnet
- Set a static route on Router B for traffic destined to 192.168.2.0/24 to next-hop 192.168.1.13
- Turn on NAT debugging on Router A, and do an extended ping from 172.30.1.1 to Router B
Solution Hints and Commands
- Use the ip address on interface command to set an IP address
- CHAP: username and password for remote peer, ppp authentication chap on interfaces
- Use the router ospf x command to enter Router Configuration mode
- Define networks under the router ospf command with a network statement
- Use the ip access-list command for named ACLs
- Use the ip route command for static route configuration
- debug ip nat
NOTE: The two networks on Router B are 192.168.1.12/30 and 192.168.1.16/30
