14.4.3 Routing Between Networks Quiz Answers. Networking Basics Module 14 quiz exam answers
1. Which information is used by routers to forward a data packet toward its destination?
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source data-link address
- destination data-link address
2. If the default gateway is configured incorrectly on the host, what is the impact on communications?
- The host is unable to communicate on the local network.
- The host can communicate with other hosts on the local network, but is unable to communicate with hosts on remote networks.
- The host can communicate with other hosts on remote networks, but is unable to communicate with hosts on the local network.
- There is no impact on communications.
3. What role does a router play on a network?
- forwarding Layer 2 broadcasts
- forwarding frames based on a MAC address
- selecting the path to destination networks
- connecting smaller networks into a single broadcast domain
4. Which address should be configured as the default gateway address of a client device?
- the Layer 2 address of the switch management interface
- the Layer 2 address of the switch port that is connected to the workstation
- the IPv4 address of the router interface that is connected to the same LAN
- the IPv4 address of the router interface that is connected to the internet
5. Which device is used to transfer data from one IP local network to a remote network?
- NIC card
- switch
- router
- server
6. Refer to the exhibit. To allow IP communication between the two separate networks, what type of device is required?
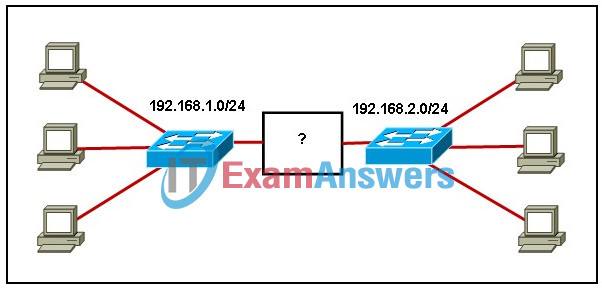
- server
- router
- switch
- access point
7. What is a benefit of adding a router within an IP network?
- increases the size of the local network
- keeps broadcasts contained within a local network
- reduces the number of hosts that can connect to the network
- controls host-to-host traffic within a single local network
8. Refer to the exhibit. Host H7 sends a packet with the destination IP address of 255.255.255.255. What does router R1 do when it receives the packet from host H7?
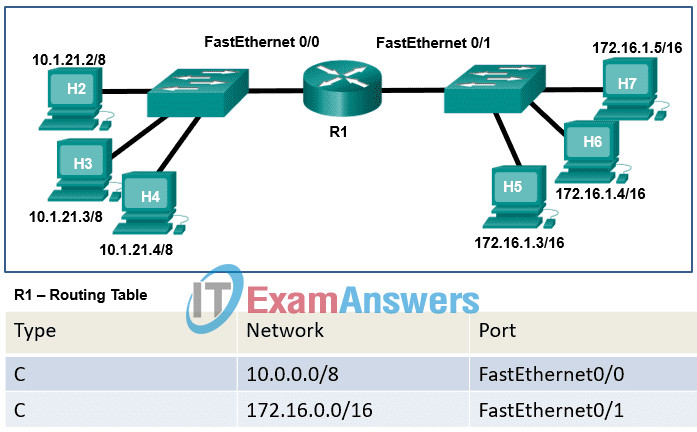
- examines the packet received on interface FastEthernet0/1 and does not forward the packet
- changes the Layer 2 header information and forwards the packet out all connected interfaces
- checks the routing table and forwards the packet out interface FastEthernet0/0
- changes the destination IP address and forwards the packet out interface FastEthernet0/0
9. What action will a router take when it receives a frame with a broadcast MAC address?
- It will not forward the frame to another network.
- It forwards the frame back to the sending host.
- It forwards the frame out of all connected interfaces.
- It forwards the frame back out the receiving interface.
10. What are two reasons to install routers to segment a network? (Choose two.)
- to limit the number of devices that can connect to the network
- to expand the network to a different geographic location
- to create smaller broadcast domains within the network
- to reduce the number of switches needed to connect devices
11. Which table does a router use to determine which interface to use to send packets to the destination network?
- ARP table
- routing table
- network table
- forwarding table
12. What action does the router take when it does not find a route to the destination network in its routing table?
- It drops the packet.
- It sends the packet as a broadcast.
- It returns the packet to the sender.
- It sends the packet out all connected interfaces.
