7.3.3 The Access Layer Quiz Answers. Networking Basics Module 7 quiz exam answers
1. What will a Layer 2 switch do when the destination MAC address of a received frame is not in the MAC table?
- It initiates an ARP request.
- It broadcasts the frame out of all ports on the switch.
- It notifies the sending host that the frame cannot be delivered.
- It forwards the frame out of all ports except for the port at which the frame was received.
2. Which network device has the primary function to send data to a specific destination based on the information found in the MAC address table?
- hub
- router
- switch
- modem
3. What addressing information is recorded by a switch to build its MAC address table?
- the destination Layer 3 address of incoming packets
- the destination Layer 2 address of outgoing frames
- the source Layer 3 address of outgoing packets
- the source Layer 2 address of incoming frames
4. What is the purpose of the FCS field in a frame?
- to obtain the MAC address of the sending node
- to verify the logical address of the sending node
- to compute the CRC header for the data field
- to determine if errors occurred in the transmission and reception
5. What is one function of a Layer 2 switch?
- forwards data based on logical addressing
- duplicates the electrical signal of each frame to every port
- learns the port assigned to a host by examining the destination MAC address
- determines which interface is used to forward a frame based on the destination MAC address
6. Which information does a switch use to keep the MAC address table information current?
- the destination MAC address and the incoming port
- the destination MAC address and the outgoing port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the incoming port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the outgoing port
- the source MAC address and the incoming port
7. What process is used to place one message inside another message for transfer from the source to the destination?
- access control
- decoding
- encapsulation
- flow control
- the source MAC address and the incoming port
8. Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit shows a small switched network and the contents of the MAC address table of the switch. PC1 has sent a frame addressed to PC3. What will the switch do with the frame?
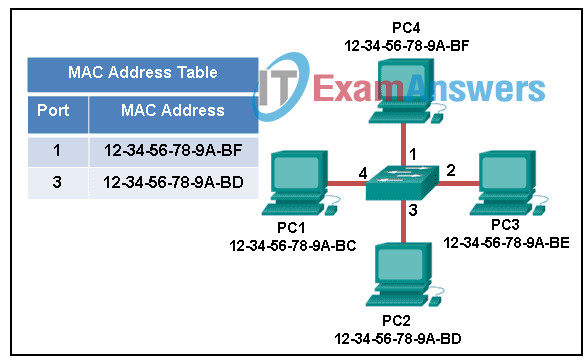
7.3.3 The Access Layer Quiz Answers
- The switch will discard the frame.
- The switch will forward the frame only to port 2.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports except port 4.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports.
- The switch will forward the frame only to ports 1 and 3.
9. Which three fields are found in an 802.3 Ethernet frame? (Choose three.)
- source physical address
- source logical address
- media type identifier
- frame check sequence
- destination physical address
- destination logical address
10. What will a host on an Ethernet network do if it receives a frame with a unicast destination MAC address that does not match its own MAC address?
- It will discard the frame.
- It will forward the frame to the next host.
- It will remove the frame from the media.
- It will strip off the data-link frame to check the destination IP address.
11. Which statement is correct about Ethernet switch frame forwarding decisions?
- Frame forwarding decisions are based on MAC address and port mappings in the MAC Address table.
- Frames addressed to unknown MAC addresses are dropped.
- Switches build up their MAC Address tables based on the destination MAC address of incoming frames.
- Unicast frames are always forwarded regardless of the destination MAC address.
