2.4.3 Quiz – Planning and Scoping a Penetration Testing Assessment Answers
1. A contractor is hired to review and perform cybersecurity vulnerability assessments for a local health clinic facility. Which U.S. government regulation must the contractor understand before the contractor can start?
- GDPR
- GLBA
- HIPAA
- FedRAMP
2. An Internal Revenue Service office in New York is considering moving some services to a cloud computing platform. Which U.S. government regulation must the office follow in the process?
- GDPR
- FFIEC
- HIPAA
- FedRAMP
3. An US university in California plans to offer online courses to students in partner universities in France and Germany. Which regulation should the university follow when those courses are offered?
- GDPR
- HIPAA
- FERPA
- FedRAMP
4. Which U.S. government agency is responsible for enforcing the Privacy of Consumer Financial Information Rule of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLB Act)?
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC)
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
- Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)
5. In the healthcare sector, which term defines an entity that processes nonstandard health information it receives from another entity into a standard format?
- health plan
- healthcare provider
- business associates
- healthcare clearinghouse
6. In the healthcare sector, which term is used to define an entity that provides payment for medical services?
- health plan
- healthcare provider
- business associates
- healthcare clearinghouse
7. In e-commerce, what determines the application of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) requirements?
- merchant
- payment brand
- primary account number
- approved scanning vendor
8. What are two examples of sensitive authentication data associated with a payment card that requires compliance with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)? (Choose two.)
- expiration date
- cardholder name
- CAV2/CVC2/CVV2/CID
- primary account number
- full magnetic strip data or equivalent data on a chip
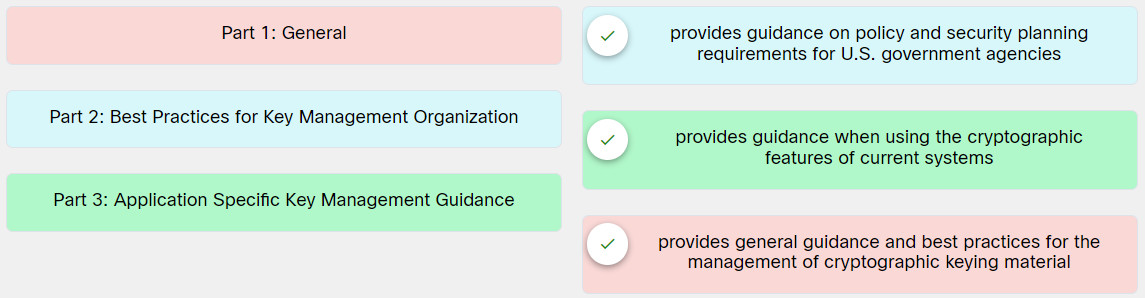
9. Match the parts of Recommendation for Key Management in the NIST SP 800-57 to the description.
10. An employee of a cybersecurity consulting firm in the U.S. is assigned to help assess the system and operation vulnerabilities of several financial institutions in Europe. The task includes penetration tests for compliance. What is a key element the employee must have before starting the assignment?
- state-of-the-art penetration testing tools
- valid user credentials to perform tests at each client institution
- detailed network diagrams and asset inventories from each client institution
- documentation of permission for performing the tests from the client institutions
11. A company hires a cybersecurity professional to perform penetration tests to assess government regulation compliance. Which legal document should be provided to the cybersecurity professional that specifies the expectations and constraints, including quality of work, timelines, and cost?
- statement of work (SOW)
- service-level agreement (SLA)
- non-disclosure agreement (NDA)
- master service agreement (MSA)
12. A company hires a cybersecurity professional to perform penetration testing to assess government regulation compliance. Which document will be provided to the cybersecurity professional that specifies a detailed and descriptive list of all the deliverables, including the scope of the project, the timeline and report delivery schedule, the location of the work, and the payment schedule?
- statement of work (SOW)
- service-level agreement (SLA)
- master service agreement (MSA)
- non-disclosure agreement (NDA)
13. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration testing to assess government regulation compliance. The company wants the consultant to disclose information to them and no one else. Which type of NDA agreement should be presented to the consultant?
- mutual NDA
- bilateral NDA
- unilateral NDA
- multilateral DNA
14. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration testing to assess government regulation compliance. Which document must the consultant receive that specifies the agreement between the consultant and the company for the penetration testing engagement?
- contract
- disclaimers
- statement of work
- non-disclosure agreement
15. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration testing to assess government regulation compliance. The consultant is preparing the final report after the penetration testing is completed. In which section of the report should the consultant cover the limitation of the work performed, such as the only dates when the testing is performed and that the findings mentioned in the report do not guarantee that all vulnerabilities are covered?
- disclaimers
- scope of work
- findings and analysis
- non-disclosure statement
16. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration tests and review the rules of engagement documents. What are three examples of typical elements in the rules of engagement document? (Choose three.)
- testing timeline
- payment schedule
- location of testing
- non-disclosure agreement
- preferred method of communication
- unknown-environment testing condition
17. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration tests and review the rules of engagement documents. The consultant notices that one element specifies that the tests should be performed toward only web applications on websites www1.company.com and www2.company.com, with no social engineering attacks and no cross-site scripting attacks. Which element in the document is used for the specification?
- location of testing
- types of allowed or disallowed tests
- IP addresses or networks from which testing will originate
- the security controls that could potentially detect or prevent testing
18. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to assess applications using different APIs. Which document should the company provide to the consultant about an XML-based language used to document a web service’s functionality?
- GraphQL documentation
- Swagger (OpenAPI) documentation
- Web Services Description Language (WSDL) document
- Web Application Description Language (WADL) document
19. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to assess applications using different APIs. Which document should the company provide to the consultant about a query language for APIs and a language for executing queries at runtime?
- GraphQL documentation
- Swagger (OpenAPI) documentation
- Web Services Description Language (WSDL) document
- Web Application Description Language (WADL) document
20. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to assess vulnerability on crucial web application devices such as web and database servers. Which document should the company provide to help the consultant document and define what systems are in the testing?
- examples of application requests
- source codes of the applications
- system and network architectural diagram
- software development kit (SDK) for specific applications
21. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration tests. What can cause scope creep of the engagement?
- lack of up-to-date testing tools
- lack of system and network architectural diagrams
- poor formatted request for proposal (RFP) by the company
- ineffective identification of what technical and nontechnical elements will be required for the penetration test
22. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration tests. What should be the consultant’s first step in validating the engagement scope?
- Confirm the contents of the request for proposal (RFP).
- Request user credentials in accessing targeted systems.
- Question the company contact person and review contracts.
- Ensure that systems and network architectural diagrams are accurate.
23. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration tests. The consultant is working with the company to set up communication procedures. Which two protocols should be considered for exchanging emails securely? (Choose two.)
- SCP
- PGP
- SFTP
- HTTPS
- S/MIME
24. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration tests. The consultant is discussing with the company about the penetration testing strategy. Which statement describes the term unknown-environment testing?
- This is a type of testing where the scope of the work could be extended later.
- This is a type of testing where the time frame of the work can be flexible and extension is possible.
- This type is a type of testing where the budget can be further negotiated throughout the testing.
- This type of testing is where the consultant will be provided with very limited information about the targeted systems and network.
25. A company hires a cybersecurity consultant to perform penetration tests. What is the key difference between unknown-environment testing and known-environment testing?
- the types of systems and network to be tested
- the amount of information provided to the consultant
- the tools and types of tests allowed during testing
- credentials and certificates required of the consultant
